|
Kaissa
Kaissa (russian: Каисса) was a chess program developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s. It was named so after Caissa, the goddess of chess. Kaissa became the first world computer chess champion in 1974 in Stockholm. History By 1967, a computer program by Georgy Adelson-Velsky, Vladimir Arlazarov, Alexander Bitman and Anatoly Uskov on the M-2 computer in Alexander Kronrod’s laboratory at the Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics had defeated Kotok-McCarthy running on the IBM 7090 at Stanford University. By 1971, Mikhail Donskoy joined with Arlazarov and Uskov to program its successor on an ICL System 4/70 at the Institute of Control Sciences. In 1972 the program played a correspondence match against readers of popular Russian newspaper, ''Komsomolskaya Pravda''. The readers won, 1½-½. It was the journalists of ''Komsomolskaya Pravda'' who gave the program its name, ''Kaissa''. Kaissa became the first world computer chess champion in 1974 in Stockh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgy Adelson-Velsky
Georgy Maximovich Adelson-Velsky (russian: Гео́ргий Макси́мович Адельсо́н-Ве́льский; name is sometimes transliterated as Georgii Adelson-Velskii) (8 January 1922 – 26 April 2014) was a Soviet and Israeli mathematician and computer scientist. Born in Samara, Adelson-Velsky was originally educated as a pure mathematician. His first paper, with his fellow student and eventual long-term collaborator Alexander Kronrod in 1945, won a prize from the Moscow Mathematical Society.Autobiography (in Russian) – from municipal web page. He and Kronrod were the last students of |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Donskoy
Mikhail Vladimirovich Donskoy (russian: Михаил Владимирович Донской), (9 September 1948 – 13 January 2009) was a Soviet and Russian computer scientist. In 1970 he graduated from Moscow State University and joined the Institute of Control Sciences of the USSR Academy of Sciences, where he became one of the lead developers of Kaissa, a computer chess program that won the first World Computer Chess Championship World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) is an event held periodically since 1974 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the International Computer Games Association. It is often held in conjunction with ... in 1974. After the dissolution of the Soviet computer chess initiative in the beginning of the 1980s he went into development of databases. In 1994 he established his own company, DISCo (Donskoy Interactive Software Company), which, among other projects, developed the Symbian interface for ABBYY ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caïssa
Caïssa ( a:isa is a fictional (anachronistic) Thracian dryad portrayed as the goddess of chess. She was first mentioned during the Renaissance by Italian poet Hieronymus Vida. Vida's poem Caïssa originated in a 658-line poem called ''Scacchia Ludus'' published in 1527 by Hieronymus Vida (Marco Girolamo Vida), which describes in Latin Virgilian hexameters a chess game between Apollo and Mercury in the presence of the other gods. In it, to avoid unclassical words such as ''rochus'' (chess rook) or ''alfinus'' (chess bishop), the rooks are described as towers (armored howdahs) on elephants' backs, and the bishops as archers: A leaked unauthorized 742-line draft version was published in 1525. Its text is very different, and in it Caïssa is called Scacchia, the chess rook is a cyclops, and the chess bishop is a centaur archer. The description of towers led to the modern name "castle" for the chess rook, and thus the term "castling", and the modern shape of the European roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Computer Chess Championship
World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) is an event held periodically since 1974 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the International Computer Games Association. It is often held in conjunction with the World Computer Speed Chess Championship and the Computer Olympiad, a collection of computer tournaments for other board games. Instead of using engine protocols, the games are played on physical boards by human operators. The WCCC is open to all types of computers including microprocessors, supercomputers, clusters, and dedicated chess hardware. Championship results In 2007, the reigning champion Junior declined to defend its title. For the 2009 edition, the rules were changed to limit platforms to commodity hardware supporting at most eight cores, thereby excluding supercomputers and large clusters. However, this was reversed in the following year and a parallel Software Championship was held instead; unlimited hardware i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess (Northwestern University)
Chess was a pioneering chess program from the 1970s, written by Larry Atkin, David Slate and Keith Gorlen at Northwestern University. Chess ran on Control Data Corporation's line of supercomputers. Work on the program began in 1968 while the authors were graduate students at the university. The first competitive version was Chess 2.0 which gradually evolved to Chess 3.6 and was rewritten as the 4.x series. It dominated the first computer chess tournaments, such as the World Computer Chess Championship and ACM's North American Computer Chess Championship. NWU Chess adopted several innovative or neglected techniques including bitboard data structures, iterative deepening, transposition tables, and an early form of forward pruning later called futility pruning. The 4.x versions were the first programs to abandon selective search in favor of full-width fixed-depth searching. In 1976, Chess 4.5 won the Class B section of the Paul Masson American Class Championships, the first time a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Arlazarov
Vladimir L’vovich Arlazarov ( Russian Арлазаров Владимир Львович) is a Russian computer scientist born in Moscow. Research work In 1965 at Alexander Kronrod’s laboratory at the Moscow Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Vladimir Arlazarov co-developed the ITEP Chess Program, together with Georgy Adelson-Velsky, Anatoly Uskov and Alexander Zhivotovsky, advised by Russian chess master Alexander Bitman and three-time world champion Mikhail Botvinnik. At the end of 1966 a four game match began between the Kotok-McCarthy-Program, running on an IBM 7090 computer, and the ITEP Chess Program on a Soviet M-20 computer. The match played over nine months was won 3-1 by the ITEP program, despite playing on slower hardware. By 1971, Mikhail Donskoy joined with Arlazarov and Uskov to program its successor on an ICL System 4/70 at the Institute of Control Sciences, called Kaissa, which became the first World Computer Chess Champ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitboard
A bitboard is a specialized bit array data structure commonly used in computer systems that play board games, where each bit corresponds to a game board space or piece. This allows parallel bitwise operations to set or query the game state, or determine moves or plays in the game. Bits in the same bitboard relate to each other by the rules of the game, often forming a game position when taken together. Other bitboards are commonly used as masks to transform or answer queries about positions. Bitboards are applicable to any game whose progress is represented by the state of, or presence of pieces on, discrete spaces of a gameboard, by mapping of the space states to bits in the data structure. Bitboards are a more efficient alternative board representation to the traditional ''mailbox'' representation, where each piece or space on the board is an array element. Bitboards are especially effective when the associated bits of various related states on the board fit into a single wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Computer Olympiad
The Computer Olympiad is a multi-games event in which computer programs compete against each other. For many games, the Computer Olympiads are an opportunity to claim the "world's best computer player" title. First contested in 1989, the majority of the games are board games but other games such as bridge take place as well. In 2010, several puzzles were included in the competition. History Developed in the 1980s by David Levy, the first Computer Olympiad took place in 1989 at the Park Lane Hotel in London. The games ran on a yearly basis until after the 1992 games, when the Olympiad's ruling committee was unable to find a new organiser. This resulted in the games being suspended until 2000 when the Mind Sports Olympiad resurrected them. Recently, the International Computer Games Association (ICGA) has adopted the Computer Olympiad and tries to organise the event on an annual basis. Games contested The games which have been contested at each olympiad are: 1st Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Chess
Computer chess includes both hardware (dedicated computers) and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysis, entertainment and training. Computer chess applications that play at the level of a chess master or higher are available on hardware from supercomputers to smart phones. Standalone chess-playing machines are also available. Stockfish, GNU Chess, Fruit, and other free open source applications are available for various platforms. Computer chess applications, whether implemented in hardware or software, utilize different strategies than humans to choose their moves: they use heuristic methods to build, search and evaluate trees representing sequences of moves from the current position and attempt to execute the best such sequence during play. Such trees are typically quite large, thousands to millions of nodes. The computational speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
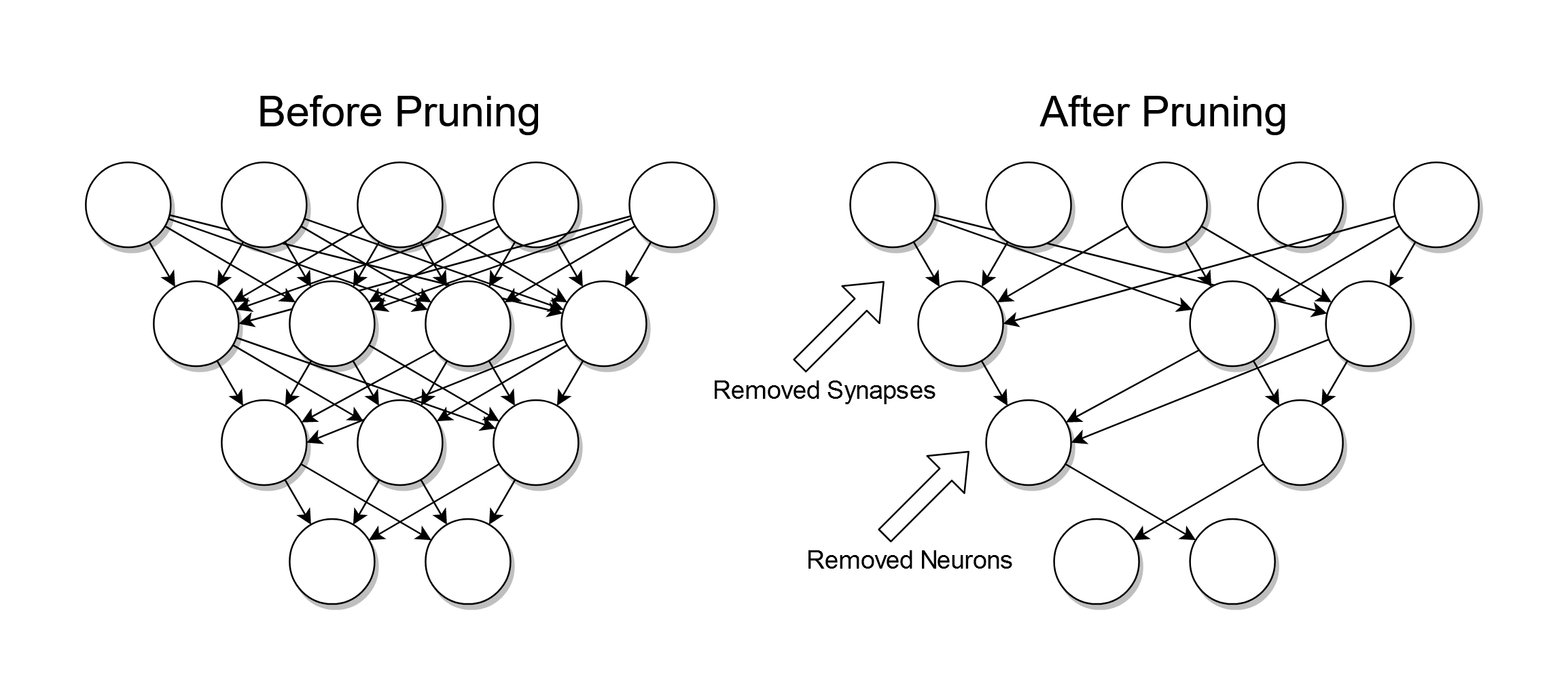
Pruning (algorithm)
Pruning is a data compression technique in machine learning and search algorithms that reduces the size of decision trees by removing sections of the tree that are non-critical and redundant to classify instances. Pruning reduces the complexity of the final classifier, and hence improves predictive accuracy by the reduction of overfitting. One of the questions that arises in a decision tree algorithm is the optimal size of the final tree. A tree that is too large risks overfitting the training data and poorly generalizing to new samples. A small tree might not capture important structural information about the sample space. However, it is hard to tell when a tree algorithm should stop because it is impossible to tell if the addition of a single extra node will dramatically decrease error. This problem is known as the horizon effect. A common strategy is to grow the tree until each node contains a small number of instances then use pruning to remove nodes that do not provide ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null-move Heuristic
In computer chess programs, the null-move heuristic is a heuristic technique used to enhance the speed of the alpha-beta pruning algorithm. Rationale Alpha-beta pruning speeds the minimax algorithm by identifying ''cutoffs'', points in the game tree where the current position is so good for the side to move that best play by the other side would have avoided it. Since such positions could not have resulted from best play, they and all branches of the game tree stemming from them can be ignored. The faster the program produces cutoffs, the faster the search runs. The null-move heuristic is designed to guess cutoffs with less effort than would otherwise be required, whilst retaining a reasonable level of accuracy. The null-move heuristic is based on the fact that most reasonable chess moves improve the position for the side that played them. So, if the player whose turn it is to move can forfeit the right to move (or make a null move - an illegal action in chess) and still have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |