|
Kairomone
A kairomone is a semiochemical released by an organism that mediates interspecific interactions in a way that benefits a different species at the expense of the emitter. Derived from the Greek καιρός, meaning "''opportune moment""kairomone, n.". OED Online. September 2012. Oxford University Press. http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/241005?redirectedFrom=kairomone (accessed 3 October 2012).'', it serves as a form of "eavesdropping", enabling the receiver to gain an advantage, such as locating food or evading predators, even if it poses a risk to the emitter. Unlike allomones, which benefit the producer at the receiver's cost, or synomones, which are mutually beneficial, kairomones favor only the recipient. Primarily studied in entomology, kairomones can play key roles in predator-prey dynamics, mate attraction, and even applications in pest control. Predator detection and prey localization An example of this can be found in the Ponderosa Pine tree (''Pinus ponderosa''), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
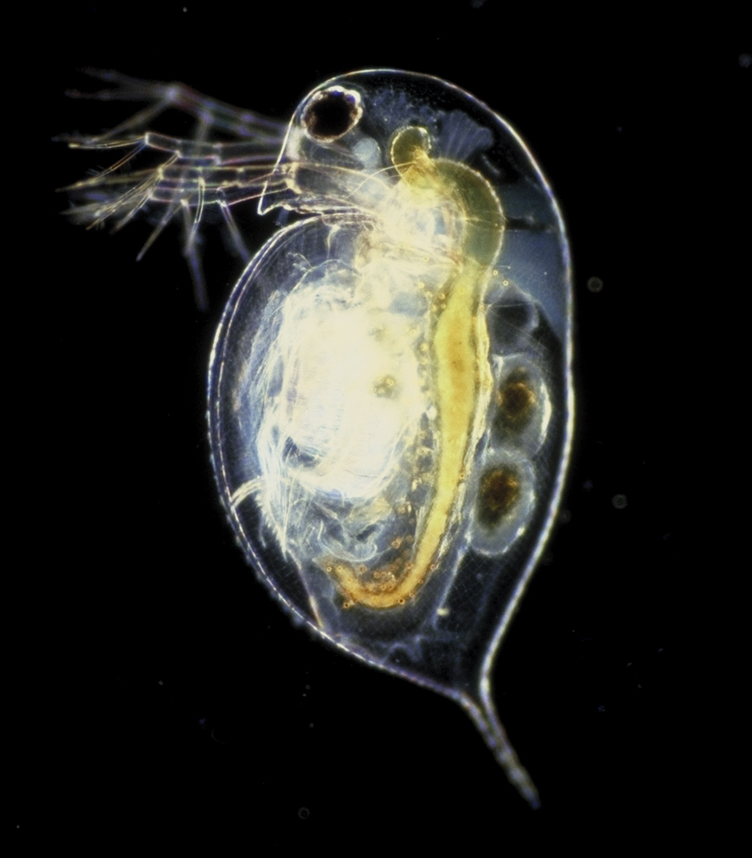
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the Order (biology), order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their Saltation (gait), saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to Fresh water, freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are ''Daphnia pulex, D. pulex'' (small and most common) and ''Daphnia magna, D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae group instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, although this division is not visible. The hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiochemical
A semiochemical, from the Greek wiktionary:σημεῖον, σημεῖον (''semeion''), meaning "signal", is a chemical substance or mixture released by an organism that affects the behaviors of other individuals. Semiochemical communication can be divided into two broad classes: communication between individuals of the same species (intraspecific) or communication between different species (Interspecies communication, interspecific). It is usually used in the field of chemical ecology to encompass pheromones, allomones, kairomones, attractants and Animal repellent, repellents. Many insects, including Parasitoid#Parasitoidal insects, parasitic insects, use semiochemicals. Pheromones are intraspecific signals that aid in finding mates, food and habitat resources, warning of enemies, and avoiding competition. Interspecific signals known as allomones and kairomones have similar functions. In nature Pheromone A pheromone (from Greek ''phero'' "to bear" + ''hormone'' from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator-induced Polyphenism
A polyphenic trait is a trait for which multiple, discrete phenotypes can arise from a single genotype as a result of differing environmental conditions. It is therefore a special case of phenotypic plasticity. There are several types of polyphenism in animals, from having sex determined by the environment to the castes of honey bees and other social insects. Some polyphenisms are seasonal, as in some butterflies which have different patterns during the year, and some Arctic animals like the snowshoe hare and Arctic fox, which are white in winter. Other animals have predator-induced or resource polyphenisms, allowing them to exploit variations in their environment. Some nematode worms can develop either into adults or into resting dauer larvae according to resource availability. Definition upright=1.2, Polyphenism in termites A : Primary king B : Primary queen C : Secondary queen D : Tertiary queen E : Soldiers F : Worker A polyphenism is the occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bark Beetle
A bark beetle is the common name for the subfamily of beetles Scolytinae. Previously, this was considered a distinct family (Scolytidae), but is now understood to be a specialized clade of the "true weevil" family (Curculionidae). Although the term "bark beetle" refers to the fact that many species feed in the inner bark (phloem) layer of trees, the subfamily also has many species with other lifestyles, including some that bore into wood, feed in fruit and seeds, or tunnel into herbaceous plants. Well-known species are members of the type genus '' Scolytus'', namely the European elm bark beetle ''S. multistriatus'' and the large elm bark beetle ''S. scolytus'', which like the American elm bark beetle '' Hylurgopinus rufipes'', transmit Dutch elm disease fungi (''Ophiostoma''). The mountain pine beetle ''Dendroctonus ponderosae'', southern pine beetle '' Dendroctonus frontalis'', and their near relatives are major pests of conifer forests in North America. A similarly aggres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allomone
An allomone (from Ancient Greek ' "other" and pheromone) is a type of semiochemical produced and released by an individual of one species that affects the behaviour of a member of another species to the benefit of the originator but not the receiver. Production of allomones is a common form of defense against predators, particularly by plant species against insect herbivores. In addition to defense, allomones are also used by organisms to obtain their prey or to hinder any surrounding competitors. Many insects have developed ways to defend against these plant defenses (in an evolutionary arms race). One method of adapting to allomones is to develop a positive reaction to them; the allomone then becomes a kairomone. Others alter the allomones to form pheromones or other hormones, and yet others adopt them into their own defensive strategies, for example by regurgitating them when attacked by an insectivorous insect. A third class of allelochemical (chemical used in interspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. Hyperuricemia, High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism. Uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most stable. Uric acid is a diprotic acid with pKa, p''K''a1 = 5.4 and p''K''a2 =&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the Host (biology), host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from Scavenger, scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with Herbivore, herbivory, as Seed predation, seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predation behavior varies significantly depending on the organism. Many predators, especially carnivores, have evolved distinct hunting strategy, hunting strategies. Pursuit predation involves the active search for and pursuit of prey, whilst ambush predation, ambush predators instead wait for prey to present an opportunity for capture, and often use stealth or aggressive mimicry. Other predators are opportunism, opportunistic or om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus''). Mice are also popular as pets. In some places, certain kinds of field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter. Mice are typically distinguished from rats by their size. Generally, when a muroid rodent is discovered, its common name includes the term ''mouse'' if it is smaller, or ''rat'' if it is larger. The common terms ''rat'' and ''mouse'' are not taxonomically specific. Typical mice are classified in the genus '' Mus'', but the term ''mouse'' is not confined to members of ''Mus'' and can also apply to species from other genera such as the deer mouse (''Peromyscus''). Domestic mice sold as pets often differ substantially in size from the common house mouse. This is attributable to breedin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midge
A midge is any small fly, including species in several family (biology), families of non-mosquito nematoceran Diptera. Midges are found (seasonally or otherwise) on practically every land area outside permanently arid deserts and the frigid zones. Some midges, such as many Phlebotominae (sand fly) and Simuliidae (black fly), are vectors of various diseases. Many others play useful roles as prey for insectivores, such as various Wallum Sedge Frog, frogs and Hirundinidae, swallows. Others are important as detritivores, and form part of various nutrient cycles. The habits of midges vary greatly from species to species, though within any particular family, midges commonly have similar ecological roles. Examples of families that include species of midges include: * Blephariceridae, net-winged midges * Cecidomyiidae, gall midges * Ceratopogonidae, biting midges (also known as no-see-ums or punkies in North America and sandflies in Australia) * Chaoboridae, phantom midges * Chiron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaoborus Flavicans
''Chaoborus flavicans'' is a species of fly in the family Chaoboridae. It is found in the Palearctic The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across Europe and Asia, north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. Th ....Bei-Bienko, G.Y. & Steyskal, G.C. (1988) ''Keys to the Insects of the European Part of the USSR'', Volume V: Diptera and Siphonaptera, Parts I,II. Amerind Publishing Co., New Delhi. References Chaoboridae Diptera of Asia Diptera of Europe Insects described in 1830 Taxa named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen {{Culicoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. A larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. In the case of smaller primitive arachnids, the larval stage differs by having three instead of four pairs of legs. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptodora
''Leptodora'' is a genus containing two species of large, nearly transparency and translucency, transparent Predation, predatory water fleas. They grow up to long, with two large antenna (biology), antennae used for swimming and a single compound eye. The legs are used to catch copepods that it comes into contact with by chance. ''Leptodora kindtii'' is found in temperate lakes across the Northern Hemisphere and is probably the only water flea species ever species description, described in a newspaper; ''L. richardi'' is only known from eastern Russia. For most of the year, ''Leptodora'' reproduces parthenogenesis, parthenogenetically, with males only appearing late in the season, to produce winter eggs which hatch the following spring. ''Leptodora'' is the only genus in its family, the Leptodoridae, and suborder, Haplopoda. Description Adults of ''Leptodora'' are the largest planktonic cladocerans native to North America; reports vary concerning the largest size, but adult femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |