|
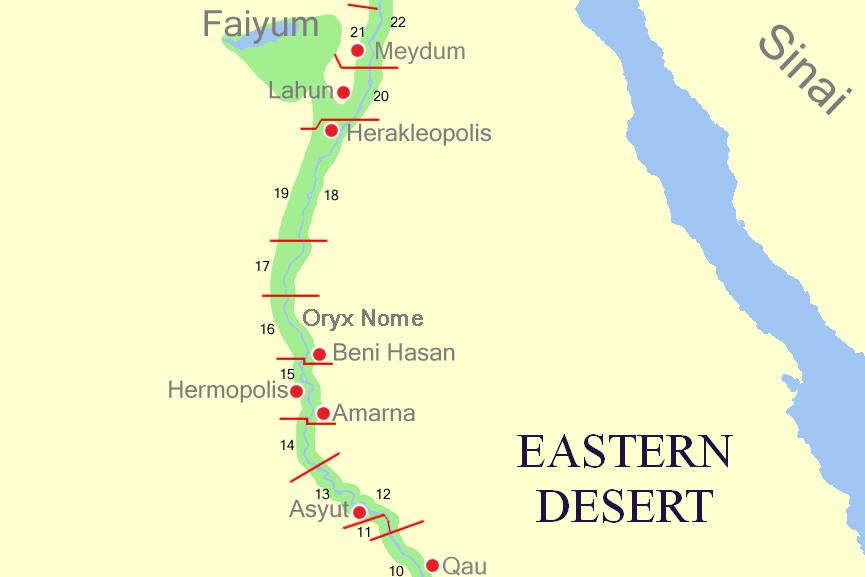
Kafr Ammar
Kafr Ammar () is a village in the Giza Governorate of Egypt. The modern village is located on the site of the ancient city of Acanthus (Greek: ; in Ptolemy, ), also known as Tenis (), on the western bank of the Nile, 120 stadia south of Memphis. The town was situated in the Memphite Nome, and therefore in the Heptanomis. It was renowned for a temple dedicated to Osiris and derived its name from a sacred enclosure composed of acanthus plants. Some scholars identify it with the ancient Egyptian city of ''Shena-chen'' () or ''Shenou-anchou'' (). See also * List of ancient Egyptian towns and cities * Tarkhan (Egypt) Tarkhan is an ancient Egyptian necropolis, located around 50 km south of Cairo on the west bank of the Nile. The cemetery was excavated in two seasons by Flinders Petrie. Tombs of almost all periods were found, but most importantly many bel ... References * {{coord, 29.80, N, 31.24, E, type:city, display=title Populated places in Giza Governorate Cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bent Pyramid
The Bent Pyramid is an ancient Egyptian pyramid located at the royal necropolis of Dahshur, approximately south of Cairo, built under the Old Kingdom King Sneferu. A unique example of early pyramid development in Ancient Egypt, Egypt, this was the second of four pyramids built by Sneferu. The Bent Pyramid rises from the desert at a 54-degree inclination, but the top section (above ) is built at the shallower angle of 43 degrees, lending the pyramid a visibly "bent" appearance. Overview Archaeologists now believe that the Bent Pyramid represents a change from the Step pyramid, step-sided pyramids of before to smooth-sided Pyramid, pyramids. It has been suggested that due to the steepness of the original angle of inclination the structure may have begun to show signs of instability during construction, forcing the builders to adopt a shallower angle to avert the structure's collapse. This theory appears to be born out by the fact that the adjacent Red Pyramid, built immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (, ; Bohairic ; ), or Men-nefer, was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt that was known as ''mḥw'' ("North"). Its ruins are located in the vicinity of the present-day village of Mit Rahina (), in markaz (county) Badrashin, Giza, Egypt. Along with the Memphite Necropolis, pyramid fields that stretch on a desert plateau for more than on its west, including the famous Giza pyramid complex, Pyramids of Giza, Memphis and its necropolis have been listed as a World Heritage Site. The site is open to the public as an open-air museum. According to legends related in the early third century BC by Manetho, a priest and historian who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the Hellenistic period of ancient Egypt, the city was founded by Pharaoh, King Menes. It was the List of Egyptian capitals, capital of ancient Egypt (''Kemet'' or ''Kumat'') during both the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom and remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Giza Governorate
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarkhan (Egypt)
Tarkhan is an ancient Egyptian necropolis, located around 50 km south of Cairo on the west bank of the Nile. The cemetery was excavated in two seasons by Flinders Petrie. Tombs of almost all periods were found, but most importantly many belonging to the time of Egyptian state formation, the Early Dynastic period around 3100 BC. Petrie found more than 2,000 tombs, most of them simple holes in the ground belonging to common people. However, there were also several mastabas of the First Dynasty, decorated with a palace facade. The most important finds include a tomb with many seal impressions belonging to king Narmer and the Tarkhan dress, the world's oldest piece of woven clothing. The cemeteries of the later periods are called Kafr Ammar, although lying side by side with the earlier tombs. From a Roman period tomb came a Fayum mummy portrait. Tomb 1060 Tomb 1060 is the oldest and largest mastaba at Tarkhan. It was divided into several rooms, most likely used for storin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Egyptian Towns And Cities
This is a list of known ancient Egyptian towns and cities. http://www.ucl.ac.uk/. Retrieved on 2016-03-05. The list is for sites intended for permanent settlement and does not include fortresses and other locations of intermittent habitation. Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Nubia Red Sea Coast See also * Nome (Egypt), NomeReferences {{Portal bar, Ancient Egypt Archaeological sites in Egypt, List Ancient Egypt-related lists, Towns and cities Cities in ancient Egypt, List Lists of cities by country, Egypt ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthus (genus)
''Acanthus'' is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae, native to tropical and warm temperate regions, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean Basin and Asia. This flowering plant is nectar-producing and depends on Butterfly, butterflies, such as ''Anartia fatima'', and other nectar-feeding organisms to distribute its pollen. Common names include Acanthus and bear's breeches. The generic name derives from the Greek term (''akanthos'') for ''Acanthus mollis'', a plant that was commonly imitated in Corinthian capitals. The genus comprises Herbaceous plant, herbaceous perennial plants, rarely subshrubs, with spiny leaves and flower raceme, spikes bearing white or purplish flowers. Size varies from in height. Species 29 species are accepted: #''Acanthus albus'' #''Acanthus arboreus'' Peter Forsskål, Forssk. (1775) #''Acanthus austromontanus'' Kaj Borge Vollesen, Vollesen — This species is native to southwestern Tanzania #''Acan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Enclosure
In the study of the history of religions and anthropology, a sacred enclosure refers to any structure intended to separate two spaces: a sacred space and a profane space. Generally, it is a separation wall erected to mark the difference between the two spaces, acquiring significant symbolic meaning. Many human cultures have made use of sacred enclosures, found in Mesopotamia, as well as in pre-Columbian America, sub-Saharan Africa, such as in Notsé, or in Mediterranean cultures, such as Greece and Rome. The use of sacred enclosures is also a crucial aspect of the Abrahamic religions, as seen in the construction of the Temple of Jerusalem or pilgrimages such as the Hajj. In some cases, this separation is placed within a single sacred space, dividing it, as with enclosures separating people according to their gender in certain churches, mosques, and synagogues. The term refers to the structure that establishes, reinforces, or accentuates separations, but it is sometimes used m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a Pharaoh, pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother Set (deity), Set cut him to pieces after killing him, with her sister Nephthys, Osiris' sister-wife, Isis, searched Egypt to find each part of Osiris. She collected all but one – Osiris’s genitalia. She then wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the Christianization of the Roman Empire, rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptanomis
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed " Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphite Nome
A nome (, from , ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch (, "Great Chief"). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός ''nomós'' meaning "pasture" extended to "dwelling" and "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ( /sɛpɑt/). Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the division into nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Solar System, and unlike most Greek mathematicians, Ptolemy's writings (foremost the ''Almagest'') never cease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |