|
Kacha (king)
Kacha (Gupta script: ''Kā-cha'', IAST: Kāca, c. 4th century) was a king of India, possibly a member of the Gupta dynasty. He is known only from his gold coins, which are similar to those of the Gupta king Samudragupta. Kacha's identity is a matter of debate among modern historians: two popular theories are that he was either same as Samudragupta, or that he was a brother of Samudragupta. According to the first theory, Kacha may have assumed the regnal name "Samudra-gupta" after extending his empire's borders up to the ocean ("''samudra''"). According to the second theory, Kacha probably contested Samudragupta's claim to the throne, and ruled for a brief period. Alternative theories identify him with other Gupta rulers, or as a non-Gupta usurper. Coinage Kacha is known from some gold coins dated to the early Gupta period: these coins bear the legend "Kacha" under the king's image. However, he is not mentioned in the Gupta genealogies or any other source. The obverse of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharajadhiraja
Maharaja (also spelled Maharajah or Maharaj; ; feminine: Maharani) is a royal title in Indian subcontinent of Sanskrit origin. In modern India and medieval northern India, the title was equivalent to a prince. However, in late ancient India and medieval south India, the title denoted a king. The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious offices, although since in Marathi the suffix ''-a'' is silent, the two titles are near homophones. Historically, the title "Maharaja" has been used by kings since Vedic times and also in the second century by the Indo-Greek rulers (such as the kings Apollodotus I and Menander I) and then later by the Indo-Scythians (such as the king Maues), and also the Kushans as a higher ranking variant of "Raja". Eventually, during the medieval era, the title "Maharaja" came to be used by sovereign princes and vassal princes, and the title " Maharajadhiraja" was used by sovereign kings. Eventually, during the Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Prosody
Sanskrit prosody or Chandas refers to one of the six Vedangas, or limbs of Vedic studies.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Chandas" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A-M, Rosen Publishing, , page 140 It is the study of poetic metres and verse in Sanskrit. This field of study was central to the composition of the Vedas, the scriptural canons of Hinduism; in fact, so central that some later Hindu and Buddhist texts refer to the Vedas as ''Chandas''. The Chandas, as developed by the Vedic schools, were organized around seven major metres, each with its own rhythm, movements and aesthetics. Sanskrit metres include those based on a fixed number of syllables per verse, and those based on fixed number of morae per verse. Extant ancient manuals on Chandas include Pingala's ''Chandah Sutra'', while an example of a medieval Sanskrit prosody manual is Kedara Bhatta's ''Vrittaratnakara''. The most exhaustive compilations of Sanskrit prosody describe over 600 metres. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also synonymous with the former state of Madhya Bharat which was later merged with Madhya Pradesh. At present the historical Malwa region includes districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. Sometimes the definition of Malwa is extended to include the Nimar region south of the Vindhya Range, Vindhyas. The Malwa region had been a separate political unit from the time of the ancient Malava Kingdom. It has been ruled by several kingdoms and dynasties, including the Avanti (India), Avanti Kingdom, The Maurya Empire, Mauryans, the Malavas, the Gupta Empire, Guptas, the Paramara dynasty, Paramaras, The Rajput, Rajputs, the Delhi Sultanate, the Malwa Sultanate, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramagupta
Ramagupta (IAST: Rāma-gupta; r. c. late 4th century CE), according to the Sanskrit play '' Devichandraguptam'', was an emperor of the Gupta dynasty of northern India. The surviving fragments of the play, combined with other literary evidence, suggest that he agreed to surrender his wife Dhruvadevi to a Shaka enemy: However, his brother Chandragupta II killed the Shaka enemy, and later dethroned him, marrying Dhruvadevi. The official Gupta genealogy does not mention Ramagupta, and therefore, the historicity of the ''Devichandraguptam'' narrative is debated. Several other sources refer to the events mentioned in the play, but these sources do not mention Ramagupta by name, and may be based on the play itself. Three undated inscriptions, written in a variety of the Gupta script and discovered in central India, mention a king called Ramagupta: this seems to attest the existence of a Gupta emperor named Ramagupta, although it does not conclusively prove the historicity of the ''De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadha (Mahajanapada)
Magadha was a region and kingdom in ancient India, based in the eastern Ganges Plain. It was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas during the Second Urbanization period. The region was ruled by several dynasties, which overshadowed, conquered, and incorporated the other Mahajanapadas. Magadha played an important role in the development of Jainism and Buddhism and formed the core of the Maurya Empire (ca. 320–185 BCE). Geography The territory of the Magadha kingdom proper before its expansion was bounded to the north, west, and east respectively by the Gaṅgā, Son, and Campā rivers, and the eastern spurs of the Vindhya mountains formed its southern border. The territory of the initial Magadha kingdom thus corresponded to the modern-day Patna and Gaya districts of the Indian state of Bihar. The region of Greater Magadha also included neighbouring regions in the eastern Gangetic plains and had a distinct culture and belief. History Vedic period (semi-legendary) (ca. 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allahabad Pillar
The Allahabad Pillar is a ''stambha'', containing one of the pillar edicts of Ashoka, erected by Ashoka, emperor of the Maurya dynasty, who reigned in the 3rd century BCE. While it is one of the few extant pillars that carry Ashokan edicts, it is particularly notable for containing later inscriptions attributed to the Gupta emperor Samudragupta (4th century CE). Also engraved on the stone are inscriptions by the Mughal emperor Jahangir, from the 17th century. According to some scholars, the pillar was moved from its original location and installed within Akbar's Allahabad Fort in Prayagraj (formerly Allahabad), Uttar Pradesh by Emperor Akbar himself, but this theory is disputed by other scholars who point out the absence of any confirmatory evidence that the pillar was moved, and pre-Mughal inscriptions that indicate that it was already present in its current location. As the fort is now occupied by the Indian Army, the public are only allowed limited access to the premises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skandagupta
Skandagupta (Gupta script: ''Ska-nda-gu-pta'', r. –467) was a Gupta Empire, Gupta Emperor of India. His Bhitari pillar inscription of Skandagupta, Bhitari pillar inscription suggests that he restored the Gupta power by defeating his enemies, who may have been rebels or foreign invaders. He repulsed an invasion by the Indo-Hephthalites (known as Huna people, Hunas in India), probably the Kidarites. He seems to have maintained control of his inherited territory, and is generally considered the last of the great Gupta Emperors. The Gupta genealogy after him is unclear, but he was most probably succeeded by Purugupta, who appears to have been his younger half-brother. Early life Skandagupta was a son of the Gupta emperor Kumaragupta I. His mother may have been a junior queen or a concubine of Kumaragupta. This theory is based on the fact that Skandagputa's inscriptions mention the name of his father, but not of his mother. For example, Skandagupta's Bhitari pillar inscription o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaragupta I
Kumaragupta I was Gupta Empire, Gupta emperor from 415 until his death in 455. A son of the Gupta king Chandragupta II and Queen Dhruvadevi, he seems to have maintained control of his inherited territory, which extended from Gujarat in the west to Bengal region in the east. Kumaragupta performed an Ashvamedha sacrifice, which was usually performed to prove imperial sovereignty, although no concrete information is available about his military achievements. Based on the epigraphic and numismatic evidence, some modern historians have theorized that he may have subdued the Aulikaras of central India and the Traikutaka dynasty, Traikutakas of western India. The Nalanda mahavihara was possibly built during his reign. The Bhitari pillar inscription of Skandagupta, Bhitari pillar inscription states that his successor Skandagupta restored the fallen fortunes of the Gupta family, which has led to suggestions that during his last years, Kumaragupta suffered reverses, possibly against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II (r.c. 375–415), also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was an emperor of the Gupta Empire. Modern scholars generally identify him with King Chandra of the Iron pillar of Delhi, Delhi iron pillar inscription. Special:Diff/1281091362 He continued the Samudragupta#Military campaigns & territorial expansion, expansionist policy of his father Samudragupta through military conquests and marital alliances. Historical evidence attests to his remarkable victories, which include the defeat of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanids, the Gupta–Saka Wars, conquest of the Western Kshatrapas and the vassalization of the Hephthalites, Hunas. Under the reign of Chandragupta II, the Gupta Empire reached its zenith, directly controlling a vast territory which stretched from the Oxus River in the west to the Bengal region in the east, and from the foothills of the Himalayas in the north to the Narmada River in the south. Chandragupta II expanded hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain (unit)
A grain is a unit of measurement of mass, and in the troy weight, avoirdupois, and apothecaries' systems, equal to exactly . It is nominally based upon the mass of a single ideal seed of a cereal. From the Bronze Age into the Renaissance, the average masses of wheat and barley grains were part of the legal definitions of units of mass. Expressions such as "thirty-two grains of wheat, taken from the middle of the ear" appear to have been ritualistic formulas. Another source states that it was defined such that 252.458 units would balance of distilled water at an ambient air-water pressure and temperature of and respectively. Another book states that Captain Henry Kater, of the British Standards Commission, arrived at this value experimentally. The grain was the legal foundation of traditional English weight systems, and is the only unit that is equal throughout the troy, avoirdupois, and apothecaries' systems of mass. The unit was based on the weight of a single grain of ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
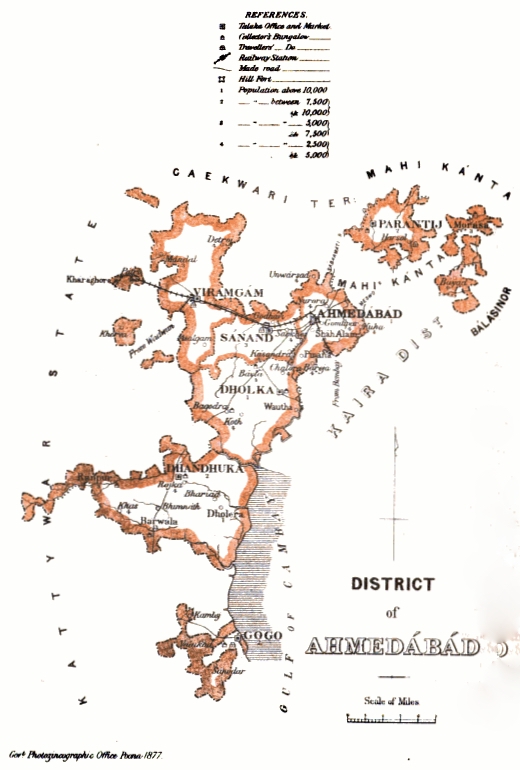
Ahmedabad District
Ahmedabad (Amdavad) district is a district comprises the city of Ahmedabad, in the central part of the state of Gujarat in western India. It is the seventh most populous district in India (out of 739). Ahmedabad District Surrounded By Kheda district in the east, Mehsana district in the north, Anand district in the south and Surendranagar district in the west. Etymology The area around Ahmedabad has been inhabited since the 11th century, when it was known as '' Ashaval''. At that time, Karna, the Chaulukya (Solanki) ruler of Anhilwara (modern Patan), waged a successful war against the Bhil king of Ashaval, and established a city called ''Karnavati'' on the banks of the Sabarmati. In 1411, this area came under the control of Muzaffar Shah I's grandson, Sultan Ahmed Shah, who selected the forested area along the banks of the Sabarmati river for a new capital city. He laid the foundation of a new walled city near Karnavati and named it Ahmedabad after himself. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |