|
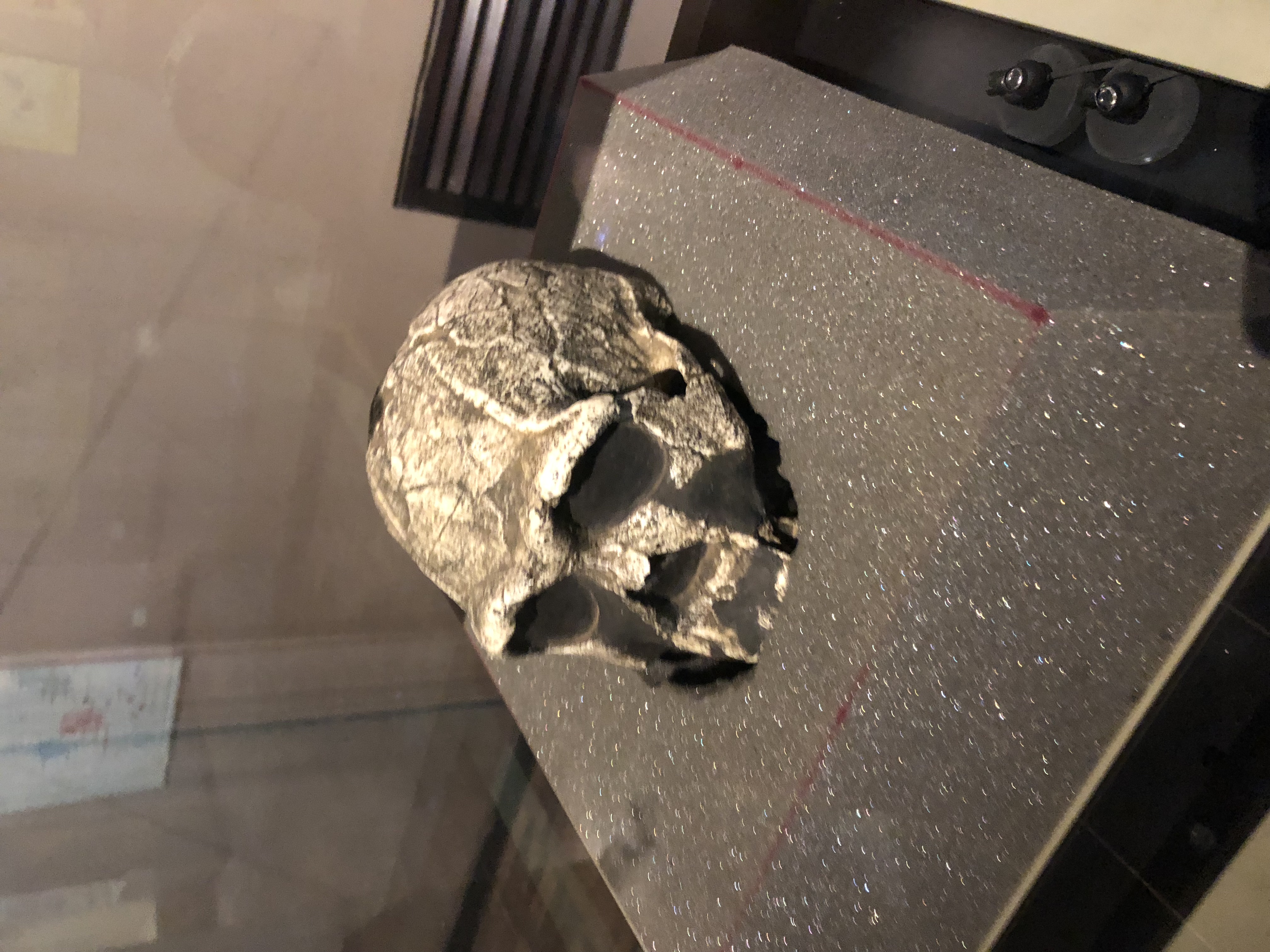
KNM-ER 3733
KNM ER 3733 is a fossilized hominid cranium of the extinct hominid ''Homo ergaster'', alternatively referred to as African ''Homo erectus''. It was discovered in 1975 in Koobi Fora, Kenya, right next to Lake Turkana, in a survey led by Richard Leakey, by a field worker called Bernard Ngeneo. KNM ER 3733 is one of the oldest ''Homo ergaster'' skulls in the world. Recent research using magnetostratigraphy has determined the age of KNM-ER 3733 to be million years old. KNM ER 3733 is a find of a near-complete cranium. Its brain size is about 850ccm. KNM ER 3733 was compared to male fossils KNM ER 3883 and KNM WT 15000 (Turkana Boy), who were also found at the Koobi Fora site, and conjectured to be female. The features of KNM ER 3733 are less robust compared to the two male crania. It is considered an adult because of the extensive wear of its teeth, the fact that its third molars were present before the individual died, and because its cranial sutures were fully fused, which is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into '' H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate ''H. ergaster'' as "African ''Homo erectus''" or "''Homo erectus ergaster''". The name ''Homo ergaster'' roughly translates to " working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of ''H. ergaster'' mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most ''H. ergaster'' fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, that indicate long-term anatomical continuity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
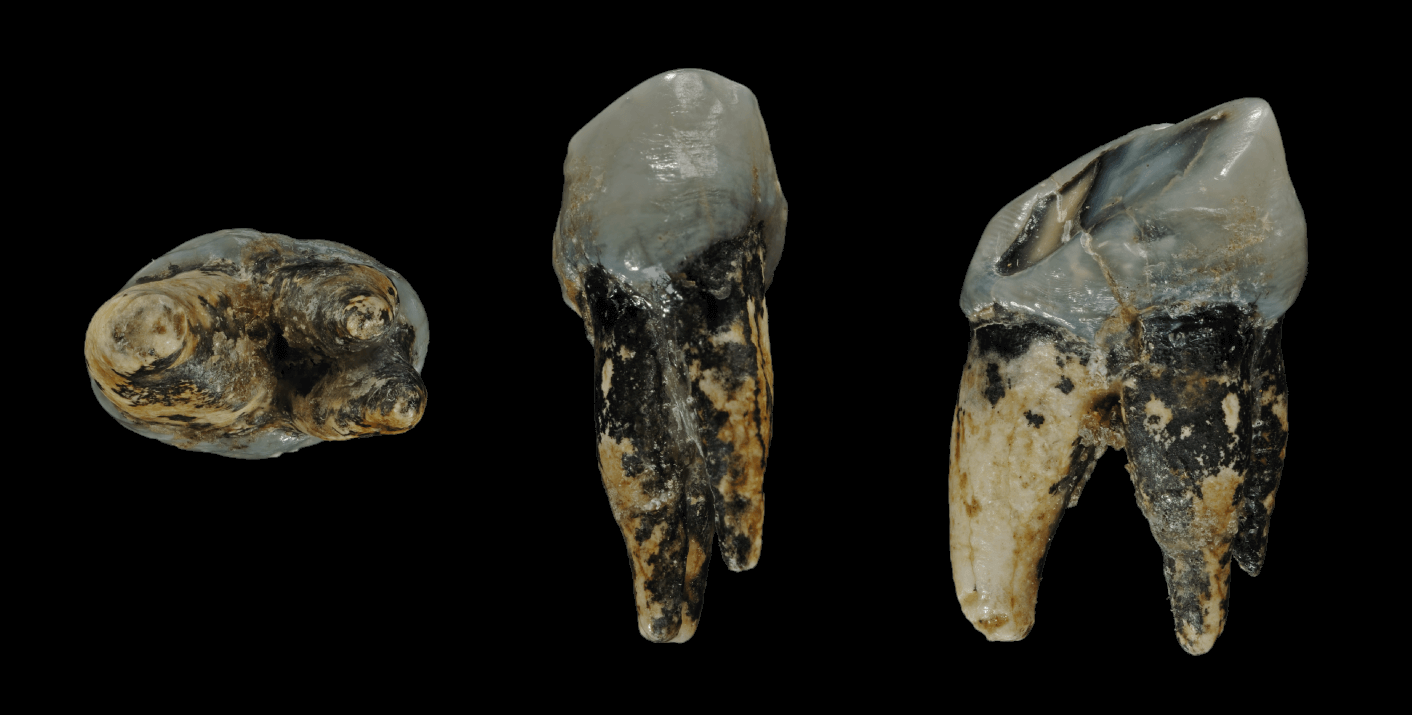
Homo Erectus KNM ER 3733
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called archaic humans) classified as either ancestral or closely related to modern humans; these include ''Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The oldest member of the genus is ''Homo habilis'', with records of just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus ''Paranthropus'', is probably most closely related to the species ''Australopithecus africanus'' within ''Australopithecus''.'''' The closest living relatives of ''Homo'' are of the genus ''Pan (genus), Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos), with the ancestors of ''Pan'' and ''Homo'' estimated to have diverged around 5.7–11 million years ago during the Late Miocene. ''H. erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and spread throughout Africa (deba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Kenya
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Ergaster Fossils
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called archaic humans) classified as either ancestral or closely related to modern humans; these include ''Homo erectus'' and '' Homo neanderthalensis''. The oldest member of the genus is '' Homo habilis'', with records of just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus ''Paranthropus'', is probably most closely related to the species ''Australopithecus africanus'' within ''Australopithecus''.'''' The closest living relatives of ''Homo'' are of the genus '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos), with the ancestors of ''Pan'' and ''Homo'' estimated to have diverged around 5.7–11 million years ago during the Late Miocene. ''H. erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and spread throughout Africa (debatably as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KNM WT 15000
Turkana Boy, also called Nariokotome Boy, is the name given to fossil KNM-WT 15000, a nearly complete skeleton of a ''Homo erectus'' youth who lived 1.5 to 1.6 million years ago. This specimen is the most complete early hominin skeleton ever found. It was discovered in 1984 by Kamoya Kimeu on the bank of the Nariokotome River near Lake Turkana in Kenya. Estimates of the individual's age at death range from 7 to 11 years old. Adolescence and maturity Although the specimen is largely considered male due to the shape of the pelvis, the sex is ultimately undetermined due to its prepubescent age. Estimates of the age at death depend on whether the maturity stage of the teeth or skeleton is used, and whether that maturity is compared to that of Homo sapiens or to chimpanzees. A key factor is that modern humans have a marked adolescent growth spurt, whereas chimpanzees do not. Initial research assumed a modern human type of growth, but recent evidence from other fossils suggests thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but shows some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossil Sites
This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of the entries in this list are considered Lagerstätten (sedimentary deposits that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues). Lagerstätten are indicated by a note () in the noteworthiness column. Fossils may be found either associated with a geological formation or at a single geographic site. Geological formations consist of rock that was deposited during a specific period of time. They usually extend for large areas, and sometimes there are different important sites in which the same formation is exposed. Such sites may have separate entries if they are considered to be more notable than the formation as a whole. In contrast, extensive formations associated with large areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostratigraphy
Magnetostratigraphy is a geophysical correlation technique used to date sedimentary and volcanic sequences. The method works by collecting oriented samples at measured intervals throughout the section. The samples are analyzed to determine their ''characteristic remanent magnetization'' (ChRM), that is, the polarity of Earth's magnetic field at the time a stratum was deposited. This is possible because volcanic flows acquire a thermoremanent magnetization and sediments acquire a depositional remanent magnetization, both of which reflect the direction of the Earth's field at the time of formation. This technique is typically used to date sequences that generally lack fossils or interbedded igneous rock. It is particularly useful in high-resolution correlation of deep marine stratigraphy where it allowed the validation of the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis related to the theory of plate tectonics. Technique When measurable magnetic properties of rocks vary stratigraphically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KNM-ER 1470
''Homo rudolfensis'' is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because ''H. rudolfensis'' coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confidently assigned to this species beyond the lectotype skull KNM-ER 1470 and other partial skull aspects. No bodily remains are definitively assigned to ''H. rudolfensis''. Consequently, both its generic classification and validity are debated without any wide consensus, with some recommending the species to actually belong to the genus ''Australopithecus'' as ''A. rudolfensis'' or ''Kenyanthropus'' as ''K. rudolfensis'', or that it is synonymous with the contemporaneous and anatomically similar '' H. habilis''. ''H. rudolfensis'' is distinguished from ''H. habilis'' by larger size, but it is also argued that this species actually consists of male ''H. habilis'' specimens, assuming that ''H. habilis'' was sexually dimorphic and males were much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
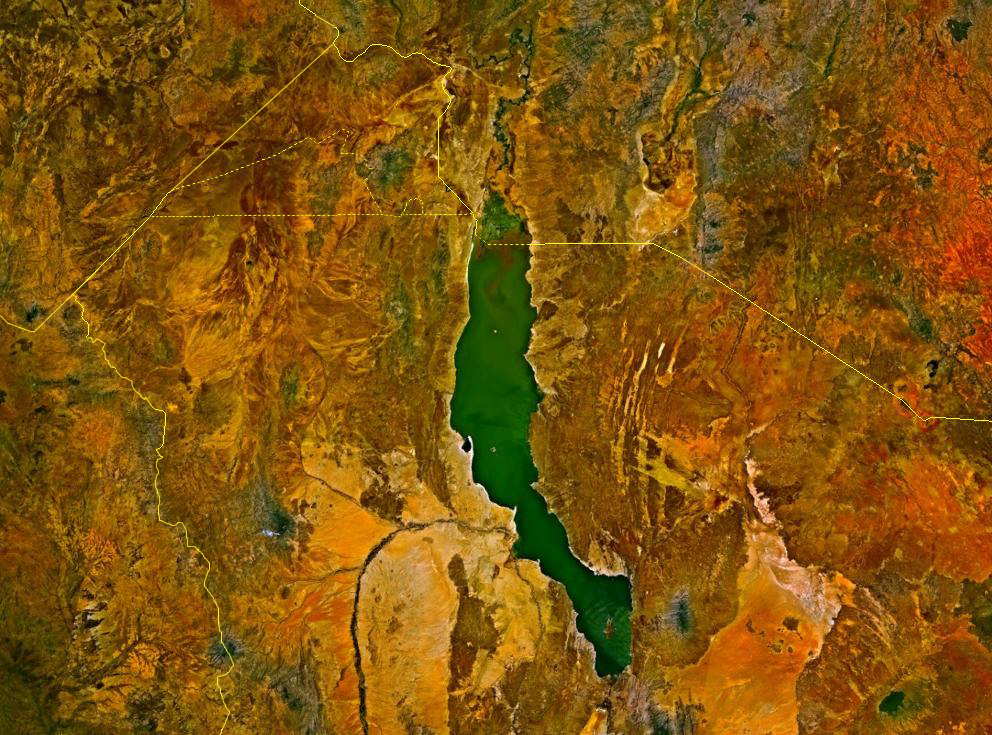
Koobi Fora
Koobi Fora refers primarily to a region around Koobi Fora Ridge, located on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana in the territory of the nomadic Gabbra people. According to the National Museums of Kenya, the name comes from the Gabbra language: The ridge itself is an outcrop of mainly Pliocene/Pleistocene sediments. It is composed of claystones, siltstones, and sandstones that preserve numerous fossils of terrestrial mammals, including early hominin species. Presently, the ridge is being eroded into a badlands terrain by a series of ephemeral rivers that drain into the northeast portion of modern Lake Turkana. In 1968 Richard Leakey established the Koobi Fora Base Camp on a large sandspit projecting into the lake near the ridge, which he called the Koobi Fora Spit. Consequently, the government of Kenya in 1973 reserved the region as Sibiloi National Park, establishing a headquarters for the National Museums of Kenya on Koobi Fora Spit. The reserve is well-maintained and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Leakey
Richard Erskine Frere Leakey (19 December 1944 – 2 January 2022) was a Kenyan paleoanthropologist, conservationist and politician. Leakey held a number of official positions in Kenya, mostly in institutions of archaeology and wildlife conservation. He was director of the National Museum of Kenya, founded the NGO WildlifeDirect, and was the chairman of the Kenya Wildlife Service. Leakey served in the powerful office of cabinet secretary and head of public service during the tail end of President Daniel Toroitich Arap Moi's government. Leakey co-founded the "Turkana Basin Institute" in an academic partnership with Stony Brook University, where he was an anthropology professor. He served as the chair of the Turkana Basin Institute until his death. Early life Earliest years Richard Erskine Frere Leakey was born on 19 December 1944 in Nairobi. As a small boy, Leakey lived in Nairobi with his parents: Louis Leakey, curator of the Coryndon Museum, and Mary Leakey, director o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Turkana
Lake Turkana () is a saline lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya, with its far northern end crossing into Ethiopia. It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. By volume it is the world's fourth-largest salt lake after the Caspian Sea, Issyk-Kul, and Lake Van (passing the shrinking South Aral Sea), and among all lakes it ranks 24th. Lake Turkana is now threatened by the construction of the Gilgel Gibe III Dam in Ethiopia due to the damming of the Omo river which supplies most of the lake's water. Although the lake commonly has been—and to some degree still is—used for drinking water, its salinity (slightly brackish) and very high levels of fluoride (much higher than in fluoridated water) generally make it unsuitable for drinking directly, and it has also been a source of diseases spread by contaminated water. Increasingly, communities on the lake's shores rely on underground springs for drinking water. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |