|
KKR 25
{{galaxy-stub ...
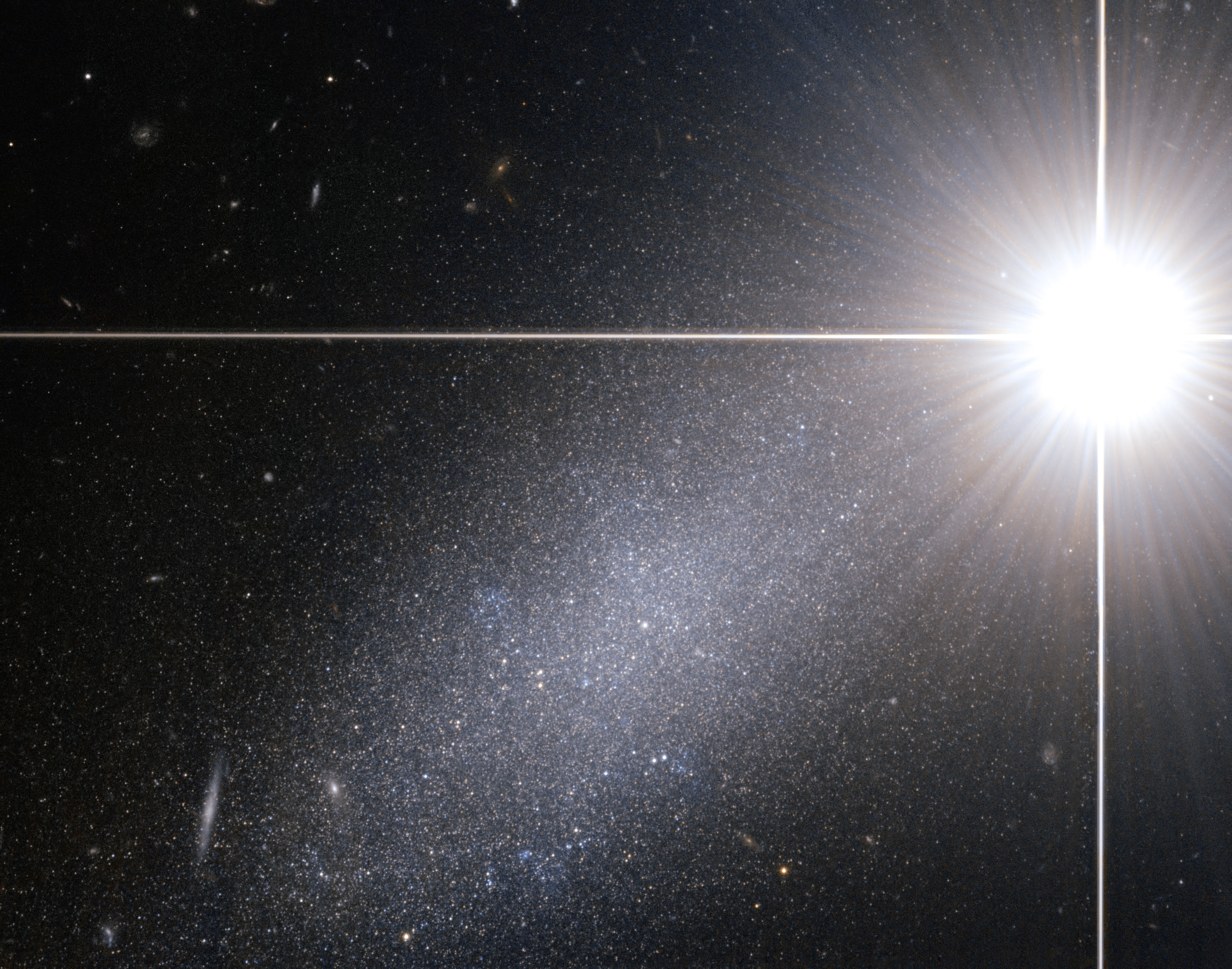
KKR 25 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation of Draco. It is about 6.4 million light years (1.95 megaparsecs) away from the Earth. KKR 25 is located outside the Local Group but the Local group is the nearest galaxy group with the M81 Group being the second nearest. See also *Galaxy *List of nearest galaxies References Irregular galaxies Draco Draco is the Latin word for serpent or dragon. Draco or Drako may also refer to: People * Draco (lawgiver) (from Greek: Δράκων; 7th century BC), the first lawgiver of ancient Athens, Greece, from whom the term ''draconian'' is derived * D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the positions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco (constellation)
Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The north pole of the ecliptic is in Draco. Draco is circumpolar from northern latitudes. There it is never setting and therefore can be seen all year. Features Stars Thuban (α Draconis) was the northern pole star from 3942 BC, when it moved farther north than Theta Boötis, until 1793 BC. The Egyptian Pyramids were designed to have one side facing north, with an entrance passage geometrically aligned so that Thuban would be visible at night. Due to the effects of precession, it would again be the pole star around the year AD 21000. It is a blue-white giant star of magnitude 3.7, 309 light-years from Earth. The traditional name of Alpha Draconis, Thuban, means "head of the serpent". There are three stars under magnitude 3 in Draco. The brighter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Galaxy
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure. Collectively they are thought to make up about a quarter of all galaxies. Some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force. Irregular galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust. This is not necessarily true for dwarf irregulars. Irregular galaxies are commonly small, about one tenth the mass of the Milky Way galaxy. Due to their small sizes, they are prone to environmental effects like crashing with large galaxies and intergalactic clouds. Types There are three major types of irregular galaxies: * An Irr-I galaxy (Irr I) is an irregular galaxy that features some structure but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Years
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaparsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 au subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree). This corresponds to astronomical units, i.e. 1\, \mathrm = 1/\tan \left( \ \mathrm \right)\, \mathrm. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. The word ''parsec'' is a portmanteau of "parallax of one second" and was coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913 to make calculations of astronomical distances from only raw observational data easy for astronomers. Partly for this reason, it is the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light-year remains prominent in popular s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Group
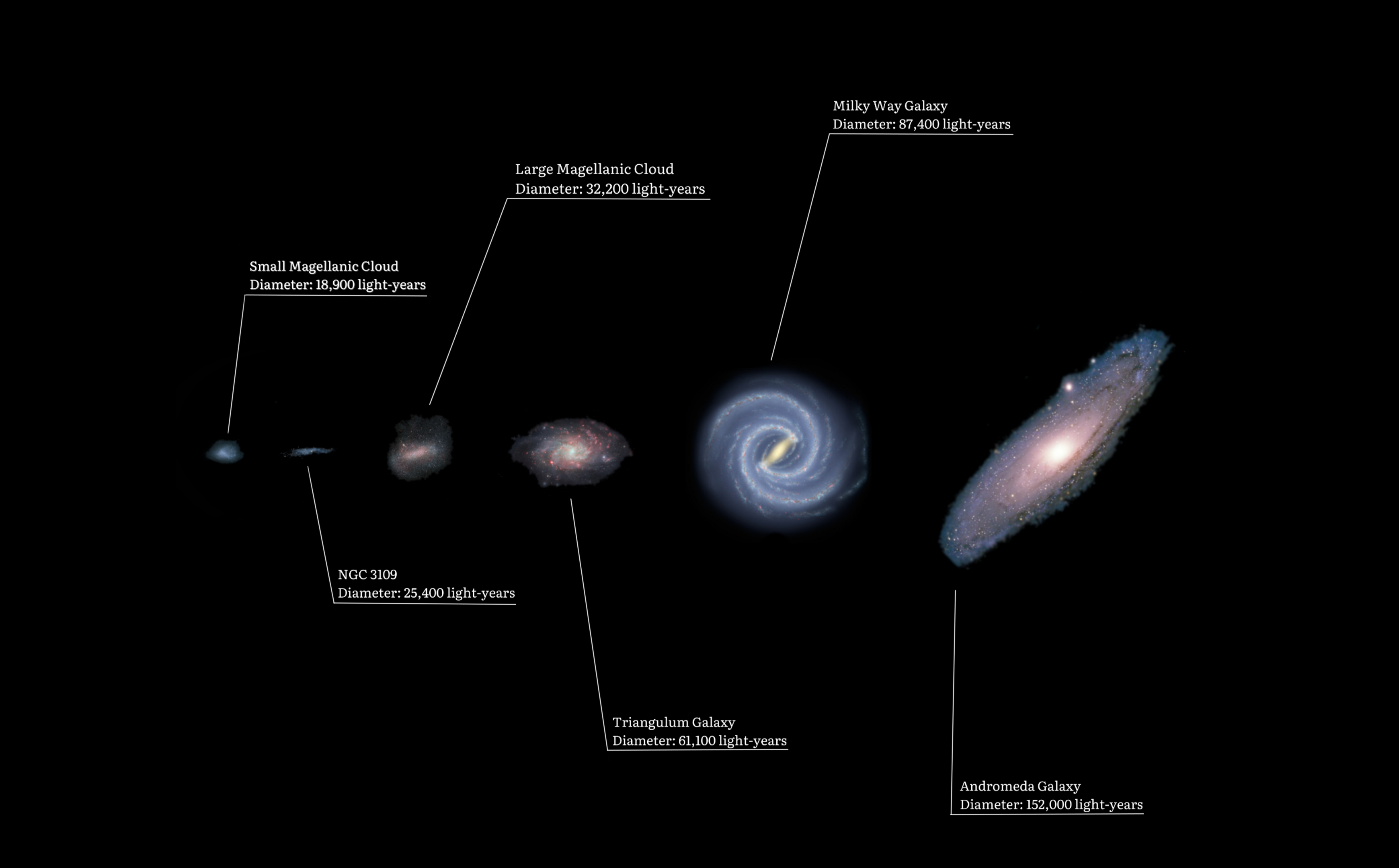
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Group
A galaxy group or group of galaxies (GrG) is an aggregation of galaxies comprising about 50 or fewer gravitationally bound members, each at least as luminous as the Milky Way (about 1010 times the luminosity of the Sun); collections of galaxies larger than groups that are first-order clustering are called galaxy clusters. The groups and clusters of galaxies can themselves be clustered, into superclusters of galaxies. The Milky Way galaxy is part of a group of galaxies called the Local Group. Characteristics Groups of galaxies are the smallest aggregates of galaxies. They typically contain no more than 50 galaxies in a diameter of 1 to 2 megaparsecs (Mpc).see 1022 m for distance comparisons Their mass is approximately 1013 solar masses. The spread of velocities for the individual galaxies is about 150 km/s. However, this definition should be used as a guide only, as larger and more massive galaxy systems are sometimes classified as galaxy groups. Groups are the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M81 Group
The M81 Group is a galaxy group in the constellations Ursa Major and Camelopardalis that includes the galaxies Messier 81 and Messier 82, as well as several other galaxies with high apparent brightnesses. The approximate center of the group is located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc, making it one of the nearest groups to the Local Group. The group is estimated to have a total mass of (1.03 ± 0.17). The M81 Group, the Local Group, and other nearby groups all lie within the Virgo Supercluster (i.e. the Local Supercluster). Members The table below lists galaxies that have been identified as associated with the M81 Group by I. D. Karachentsev. Note that the object names used in the above table differ from the names used by Karachentsev. NGC, IC, UGC, and PGC numbers have been used in many cases to allow for easier referencing. Interactions within the group Messier 81, Messier 82, and NGC 3077 are all strongly interacting with each other. Observations of the 21-centime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nearest Galaxies
This is a list of known galaxies within 3.8 megaparsecs (12.4 million light-years) of the Solar System, in ascending order of heliocentric distance, or the distance to the Sun. This encompasses about 50 major Local Group galaxies, and some that are members of neighboring galaxy groups, the M81 Group and the Centaurus A/M83 Group, and some that are currently not in any defined galaxy group. The list aims to reflect current knowledge: not all galaxies within the 3.8 Mpc radius have been discovered. Nearby dwarf galaxies are still being discovered, and galaxies located behind the central plane of the Milky Way are extremely difficult to discern. It is possible for any galaxy to mask another located beyond it. Intergalactic distance measurements are subject to large uncertainties. Figures listed are composites of many measurements, some of which may have had their individual error bars tightened to the point of no longer overlapping with each other. List See also * Lists of astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Galaxies
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure. Collectively they are thought to make up about a quarter of all galaxies. Some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force. Irregular galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust. This is not necessarily true for dwarf irregulars. Irregular galaxies are commonly small, about one tenth the mass of the Milky Way galaxy. Due to their small sizes, they are prone to environmental effects like crashing with large galaxies and intergalactic clouds. Types There are three major types of irregular galaxies: * An Irr-I galaxy (Irr I) is an irregular galaxy that features some structure but not e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |