|
KCNJ12
ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 12 is a lipid-gated ion channel that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNJ12'' gene. Function This gene encodes an inwardly rectifying K+ channel that may be blocked by divalent cations. This protein is thought to be one of multiple inwardly rectifying channels that contribute to the cardiac inward rectifier current (IK1). The gene is located within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Interactions KCNJ12 has been shown to interact with: * APBA1, * CASK, * DLG1, * DLG2, * DLG3, * DLG4, * LIN7A * LIN7B, and * LIN7C. See also * Inward-rectifier potassium channel Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific Lipid-gated_ion_channels, lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are acti ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inward-rectifier Potassium Channel
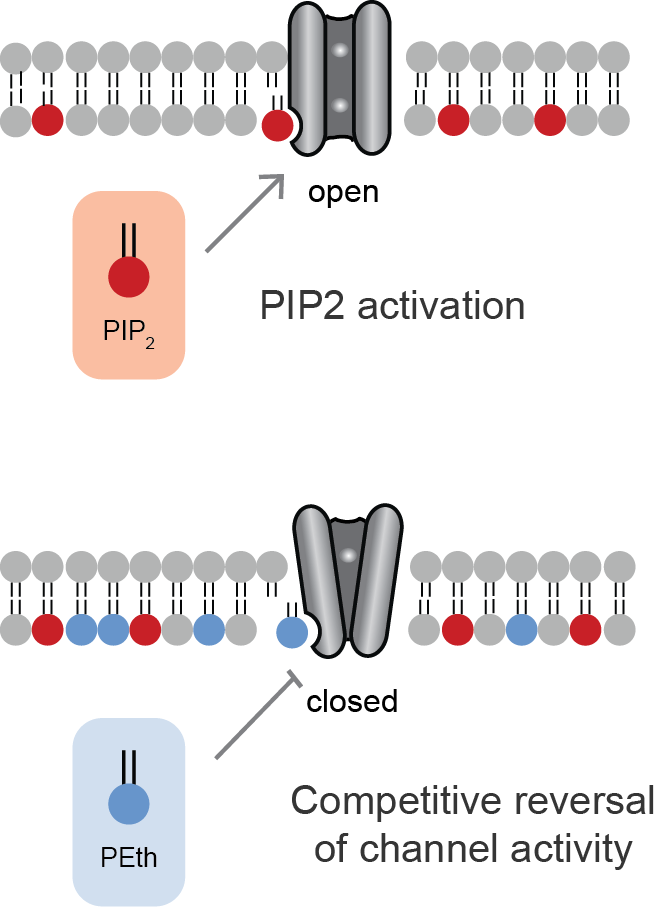
Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific Lipid-gated_ion_channels, lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are activated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PIP2). The malfunction of the channels has been implicated in several diseases. IRK channels possess a pore domain, homologous to that of voltage-gated ion channels, and flanking transmembrane domain, transmembrane segments (TMSs). They may exist in the membrane as homo- or heterooligomers and each monomer possesses between 2 and 4 TMSs. In terms of function, these proteins transport potassium, potassium (K+), with a greater tendency for K+ uptake than K+ export. The process of inward-rectification was discovered by Denis Noble in cardiac muscle cells in 1960s and by Richard Adrian, 2nd Baron Adrian, Richard Adrian and Alan Lloyd Hodgkin, Alan Hodgkin in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APBA1
Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APBA1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the X11 protein family. It is a neuronal adaptor protein that interacts with the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein (APP). It stabilises APP and inhibits production of proteolytic APP fragments including the A beta peptide that is deposited in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. This gene product is believed to be involved in signal transduction processes. It is also regarded as a putative vesicular trafficking protein in the brain that can form a complex with the potential to couple synaptic vesicle exocytosis to neuronal cell adhesion. Interactions APBA1 has been shown to interact with KCNJ12, CCS, CASK and Amyloid precursor protein Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many biological tissue, tissues and concentrated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLG2
Disks large homolog 2 (DLG2) also known as channel-associated protein of synapse-110 (chapsyn-110) or postsynaptic density protein 93 (PSD-93) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLG2'' gene. Function Chapsyn-110/PSD-93 a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family. The protein forms a heterodimer with a related family member that may interact at postsynaptic sites to form a multimeric scaffold for the clustering of receptors, ion channels, and associated signaling proteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described but their full-length nature has yet to be completely determined. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of DLG2 function. A knockout mouse line, called ''Dlg2tm1Dsb'' was generated. Male and female animals underwent a standardized phenotypic screen to determine the effects of deletion. Twenty four tests were carried out on homozygous mutant mice and five signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLG3
Disks large homolog 3 (DLG3) also known as neuroendocrine-DLG or synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP-102) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLG3'' gene. DLG3 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) superfamily of proteins. Interactions DLG3 has been shown to interact with: * APC, * CRIPT, * DLG4, * EXOC3, * EXOC4, * GRIN2A, * GRIN2B, * GRIN2C, * KCNJ12 * PTK2B, and * SYNGAP1. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of DLG3 function. A conditional knockout mouse line called ''Dlg3tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi'' was generated at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Male and female animals underwent a standardized phenotypic screen In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prop ... to determine the effects of deletion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLG4
PSD-95 (postsynaptic density protein 95) also known as SAP-90 (synapse-associated protein 90) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLG4'' (discs large homolog 4) gene. PSD-95 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family. With PSD-93 it is recruited into the same NMDA receptor and potassium channel clusters. These two MAGUK proteins may interact at postsynaptic sites to form a multimeric scaffold for the clustering of receptors, ion channels, and associated signaling proteins. PSD-95 is the best studied member of the MAGUK-family of PDZ domain-containing proteins. Like all MAGUK-family proteins, its basic structure includes three PDZ domains, an SH3 domain, and a guanylate kinase-like domain (GK) connected by disordered linker regions. It is almost exclusively located in the post synaptic density of neurons, and is involved in anchoring synaptic proteins. Its direct and indirect binding partners include neuroligin, NMDA receptors, AMPA re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIN7A
Lin-7 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LIN7A'' gene. Interactions LIN7A has been shown to interact with: * CASK, * DLG1, and * KCNJ12 ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 12 is a lipid-gated ion channel that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNJ12'' gene. Function This gene encodes an inwardly rectifying K+ channel that may be blocked by divalent cations. This prot .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIN7B
Lin-7 homolog B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LIN7B'' gene. Interactions LIN7B has been shown to interact with: * ACCN3, * GRIN2B, * KCNJ12 and * KCNJ4 Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 4, also known as KCNJ4 or Kir2.3, is a human gene. Function Several different potassium channels are known to be involved with electrical signaling in the nervous system. One class is a .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIN7C
Lin-7 homolog C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LIN7C'' gene. Interactions LIN7C has been shown to interact with: * DLG1, * KCNJ12, and * KCNJ4 Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 4, also known as KCNJ4 or Kir2.3, is a human gene. Function Several different potassium channels are known to be involved with electrical signaling in the nervous system. One class is a .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid-gated Ion Channels
Lipid-gated ion channels are a class of ion channels whose conductance of ions through the membrane depends directly on lipids. Classically the lipids are membrane resident anionic signaling lipids that bind to the transmembrane domain on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane with properties of a classic ligand. Other classes of lipid-gated channels include the mechanosensitive ion channels that respond to lipid tension, thickness, and hydrophobic mismatch. A lipid ligand differs from a lipid cofactor in that a ligand derives its function by dissociating from the channel while a cofactor typically derives its function by remaining bound. PIP2-gated channels Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) was the first and remains the best studied lipid to gate ion channels. PIP2 is a cell membrane lipid, and its role in gating ion channels represents a novel role for the molecule. Kir channels: PIP2 binds to and directly activates inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith–Magenis Syndrome
Smith–Magenis Syndrome (SMS), also known as 17p- syndrome, is a microdeletion syndrome characterized by an abnormality in the short (p) arm of chromosome 17. It has features including intellectual disability, facial abnormalities, difficulty sleeping, and numerous behavioral problems such as self-harm. Smith–Magenis syndrome affects an estimated between 1 in 15,000 to 1 in 25,000 individuals. Signs and symptoms Facial features of children with Smith–Magenis syndrome include a broad and square face, deep-set eyes, large cheeks, and a prominent jaw, as well as a flat nose bridge (in the young child; as the child ages it becomes more ski-jump shaped). Eyes tend to be deep-set, close together and upwards-slanted. Eyebrows are heavy with lateral extension. The mouth is the most noticeable feature; both upper and lower lips are full, and the mouth is wide. The mouth curves downwards and the upper lip curves outwards, due to a fleshy philtrum. These facial features become more no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |