|
KAB-1500L
KAB-1500L is a Russian precision guided weapon, part of KAB-1500 family, a laser guided bomb and also the current production standard for use on 4+ and 4++ generation fighter jets, like the Sukhoi Su-30MKI/Sukhoi Su-30MKK, Sukhoi Su-34 and Sukhoi Su-35. It is claimed to be the Russian equivalent to USA's Paveway II/ Paveway III Although it's a much larger device at 6x the size as the paveway is 500lbs so it's a closer match to the KAB-500L that uses similar guidance technology and is designed to hit railway, ammunition depots, railway terminals, highway bridges, military and industrial facilities, ships and transport vessels. The KAB-1500LG-F-E has an impact fuze which includes 3 different delay modes for target attack and it can also be mounted on older aircraft, like the Sukhoi Su-24 and the Mikoyan MiG-27 The Mikoyan MiG-27 (russian: Микоян МиГ-27; NATO reporting name: Flogger-D/J) is a variable-sweep ground-attack aircraft, originally built by the Mikoyan-G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAB-1500
KAB-1500 is a Russian precision guided weapon which comes in three versions: KAB-1500L, KAB-1500S-E The KAB-1500S-E (russian: КАБ-1500С-Э) is a precision guided bomb, part of KAB-1500 family, designed for the Russian Federation Air Force (RFAF) to carry out precision attacks, using 24-channel GLONASS and is equivalent to the United States ... and TV-guided KAB-1500KR. Variants * KAB-1500LG-F-E Guided bomb with a laser gyro-stabilized seeker and a HE (high-explosive) warhead * KAB-1500LG-Pr-E Guided bomb with a laser gyro-stabilized seeker and a penetrator warhead * KAB-1500LG-OD-E Guided bomb with a laser gyro-stabilized seeker and a FAE (fuel-air-explosive) warhead * KAB-1500Kr-Pr Guided bomb with an electro-optical correlation seeker and a penetrator warhead * KAB-1500Kr Guided bomb with an EO (electro-optical) correlation TV seeker and a HE warhead * KAB-1500Kr-OD Guided bomb with an electro-optical correlation TV seeker and a FAE warhead References {{weapon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAB-500L
The KAB-500L is a laser-guided bomb developed by the Soviet Air Force, entering service in 1975. It remains in service with the CIS and post-Soviet Russian Air Force. The KAB-500L is a standard FAB-500 general-purpose bomb, which has a nominal weight of , fitted with a semi-active laser seeker and guidance fins, turning it into an unpowered guided bomb. The KAB-500L is long and weighs . Its warhead makes up of the total weight, of which roughly 50% is blast-effect high explosive. Russian sources credit it with a CEP of . The technology of KAB-500L is also used for larger bombs, such as the KAB-1500L family. It is also deployed by the Indian Air Force. The primary launch platform is Su-30MKI. This bomb is also used by Royal Malaysian Air Force on its Sukhoi Su-30MKM. KAB-500S-E KAB-500S-E is a Precision-Guided Munition (PGM) whose guidance system is based on GLONASS. The weapon can be dropped from aircraft flying at an altitude from 500 meters to 5000 meters and with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAB-1500S-E
The KAB-1500S-E (russian: КАБ-1500С-Э) is a precision guided bomb, part of KAB-1500 family, designed for the Russian Federation Air Force (RFAF) to carry out precision attacks, using 24-channel GLONASS and is equivalent to the United States Air Force (USAF) Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) family of Global Positioning System (GPS) guided weapons. It is believed to be similar to the KAB-500S-E, and to use the same Kompas PSN-2001 (Pribor Sputnikovoy Navigatsii) satellite receiver. KTRV has fully completed testing of products of the K08B and K029B (UPAB-1500B) types, both products are in serial production and are delivered to combat units. Russia intends to fit it to the Su-24M, Su-34, Su-35 and Mig-35 aircraft. They hope to export to India and China. See also *KAB-1500L KAB-1500L is a Russian precision guided weapon, part of KAB-1500 family, a laser guided bomb and also the current production standard for use on 4+ and 4++ generation fighter jets, like the Sukhoi S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
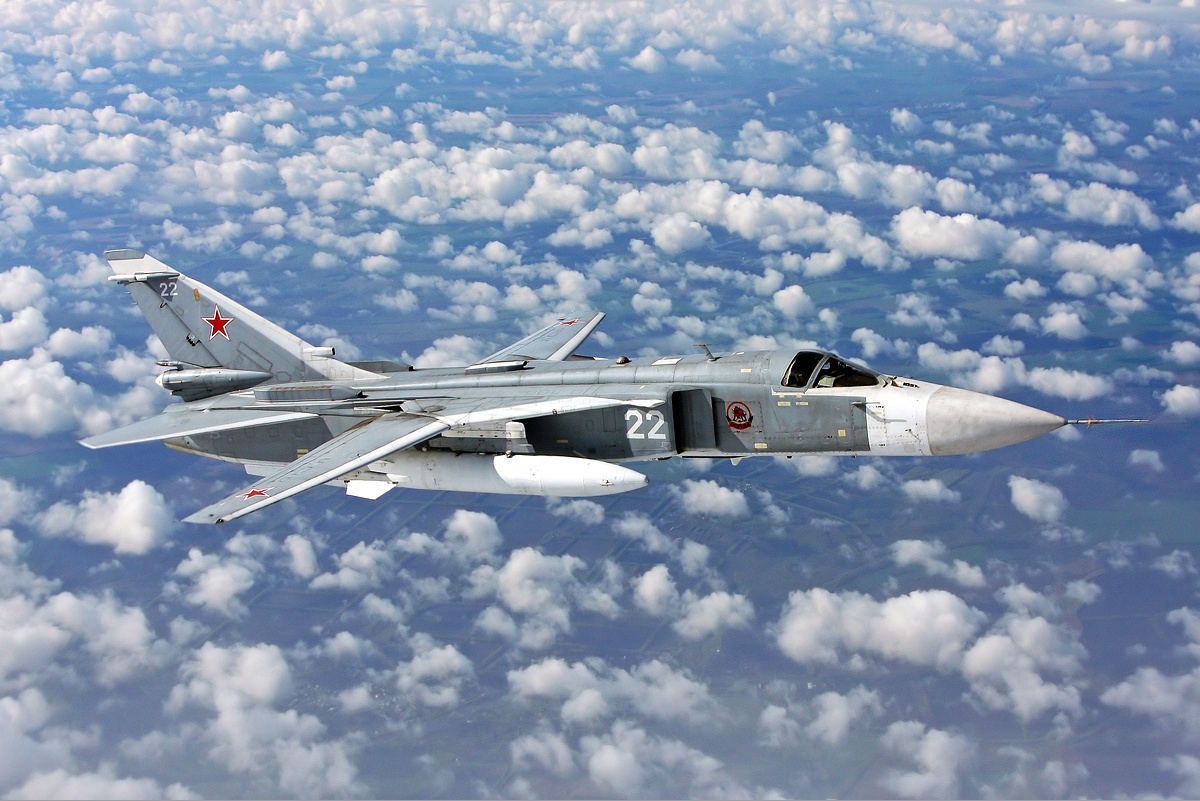
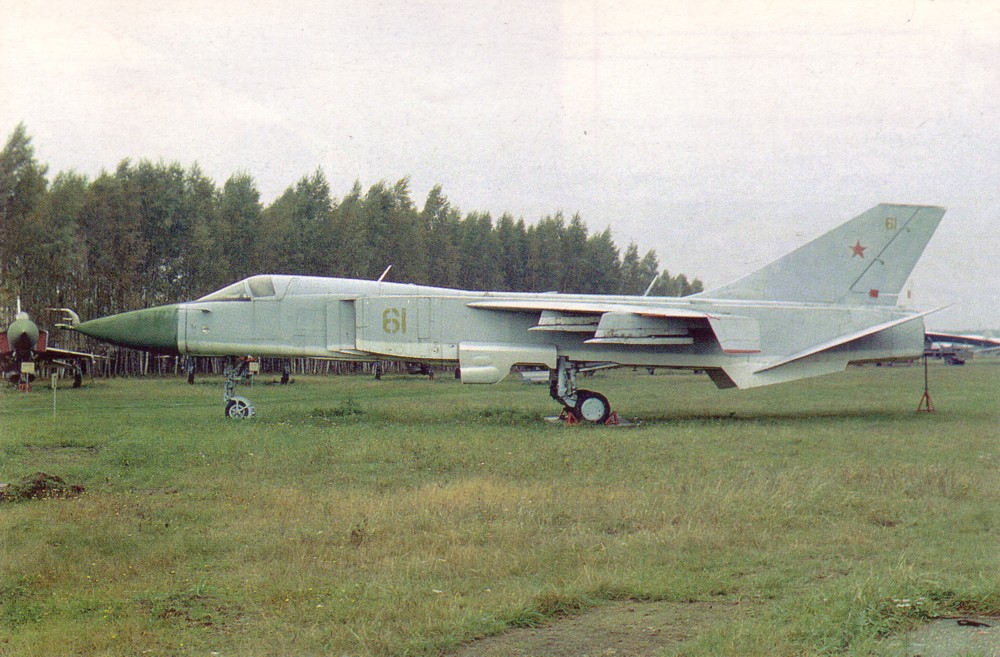
Sukhoi Su-24M
The Sukhoi Su-24 ( NATO reporting name: Fencer) is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was the first of the USSR's aircraft to carry an integrated digital navigation/attack system. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force, Syrian Air Force, Ukrainian Air Force, Algerian Air Force and various other air forces to which it was exported. Development Background One of the conditions for accepting the Sukhoi Su-7B into service in 1961 was the requirement for Sukhoi to develop an all-weather variant capable of precision air strikes. Preliminary investigations with ''S-28'' and ''S-32'' aircraft revealed that the basic Su-7 design was too small to contain all the avionics required for the mission. OKB-794 (later known as Leninets) was tasked with developing an advanced nav/attack system, codenamed ''Puma'', which would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-30MKI
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI (NATO reporting name: Flanker-H) is a twinjet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). A variant of the Sukhoi Su-30, it is a heavy, all-weather, long-range fighter. Development of the variant started after India signed a deal with Russia in 2000 to manufacture 140 Su-30 fighter jets. The first Russian-made Su-30MKI variant was accepted into the Indian Air Force in 2002, while the first Su-30MKI assembled in India entered service with the IAF in 2004. The IAF has nearly 260 Su-30MKIs in inventory as of January 2020. The Su-30MKI is expected to form the backbone of the Indian Air Force's fighter fleet to 2020 and beyond.Pandit, Rajat"Russia conducts first test of fifth generation Sukhoi." ''The Times of India'', 30 January 2010. The aircraft is tailor-made for Indian specifications and integrates Indian systems and avionics as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
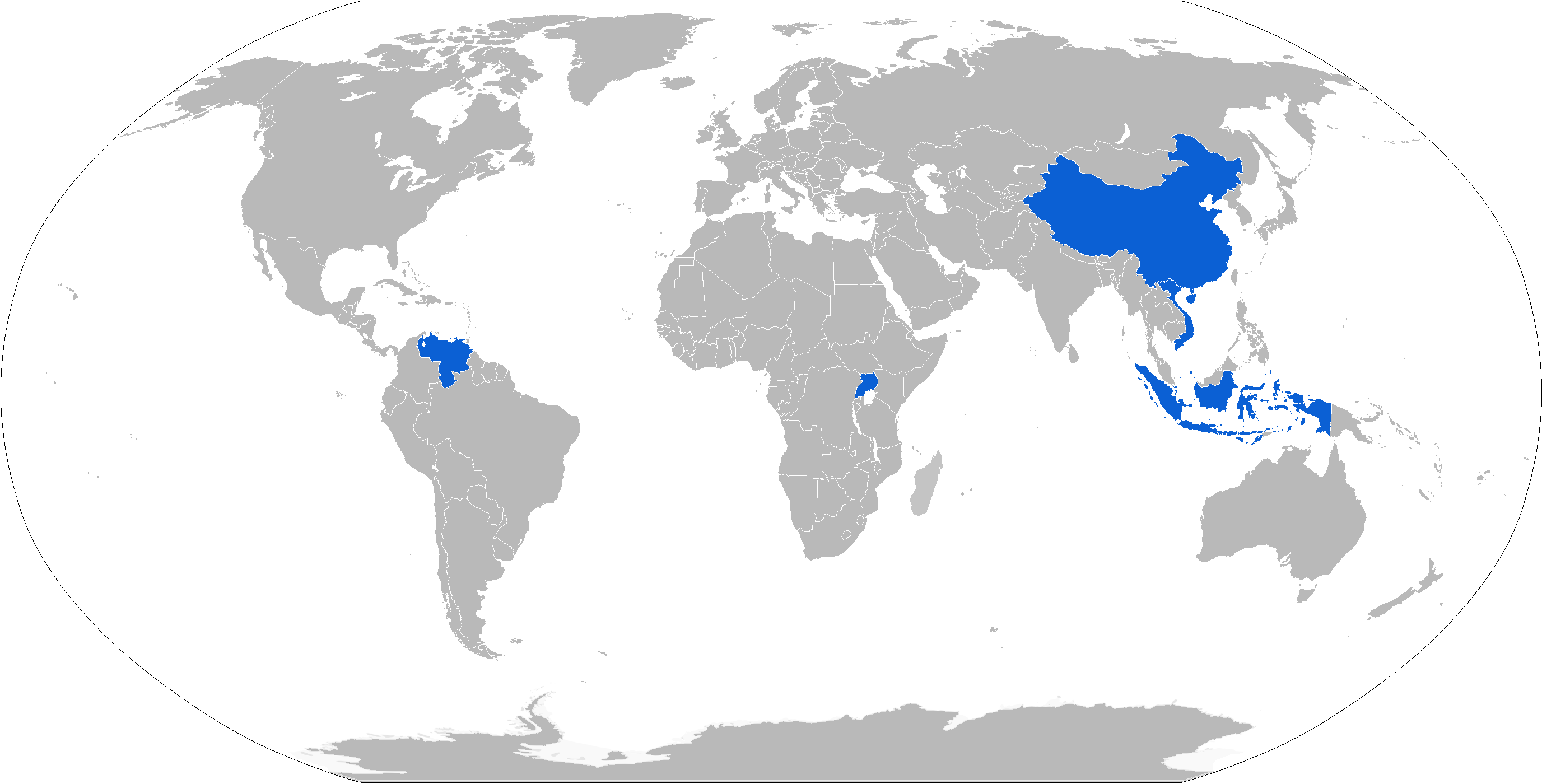
Sukhoi Su-30MKK
The Sukhoi Su-30MKK ( NATO reporting name: Flanker-G)MKK stands for Russian ''Mnogofunktzionniy Kommercheskiy Kitayski'' ( Cyrillic: Многофунктзионний Коммерческий Китайски), "Multifunctional Commercial for China". is a modification of the Sukhoi Su-30, incorporating advanced technology from the Sukhoi Su-35 variant. The Su-30MKK was developed by Sukhoi in 1997, as a result of a direct Request for tender between the Russian Federation and China. It is a heavy class, all-weather, long-range strike fighter, and like the Sukhoi Su-30, comparable to the American McDonnell Douglas F-15E Strike Eagle. Su-30MK2 is a further improvement to Su-30MKK with upgraded avionics and maritime strike capabilities. The MKK and MK2 are currently operated by the People's Liberation Army Air Force, Indonesian Air Force, Vietnam People's Air Force, Venezuelan Air Force and the Ugandan Air Force. Development The People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-34
The Sukhoi Su-34 (russian: Сухой Су-34; NATO reporting name: Fullback) is a Soviet-origin Russian twin-engine, twin-seat, all-weather supersonic medium-range fighter-bomber/ strike aircraft. It first flew in 1990, intended for the Soviet Air Forces, and it entered service in 2014 with the Russian Air Force. Based on the Sukhoi Su-27 Flanker air superiority fighter, the Su-34 has an armoured cockpit with side-by-side seating for its two pilots. The Su-34 is designed primarily for tactical deployment against ground and naval targets (tactical bombing/attack/ interdiction roles, including against small and mobile targets) on solo and group missions in daytime and at night, under favourable and adverse weather conditions and in a hostile environment with counter-fire and electronic warfare (EW) counter-measures deployed, as well as for aerial reconnaissance. The Su-34 is planned to eventually replace the Su-24 tactical strike fighter and the Tu-22M long-distance bomber. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-35S
The Sukhoi Su-35 (russian: link=no, Сухой Су-35; NATO reporting name: Flanker-E) is the designation for two improved derivatives of the Su-27 air-defence fighter. They are single-seat, twin-engine, supermaneuverable aircraft, designed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau and built by Sukhoi. The type was originally developed by the Soviet Union from the Su-27 and was known as the Su-27M. It incorporated canards and a multi-function radar giving it multi-role capabilities. The first prototype made its maiden flight in June 1988. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union Sukhoi re-designated it as the Su-35 to attract export orders. Fourteen aircraft were produced and used for tests and demonstrations; one example had thrust-vectoring engines and was in turn redesignated the Su-37. A sole Su-35UB two-seat trainer was also built in the late 1990s that resembled the Su-30MK family. In 2003, Sukhoi embarked on a second modernization of the Su-27 to serve as an interim aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Guided Weapon
A precision-guided munition (PGM, smart weapon, smart munition, smart bomb) is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gulf War guided munitions accounted for only 9% of weapons fired, but accounted for 75% of all successful hits. Despite guided weapons generally being used on more difficult targets, they were still 35 times more likely to destroy their targets per weapon dropped. Because the damage effects of explosive weapons decrease with distance due to an inverse cube law, even modest improvements in accuracy (hence reduction in miss distance) enable a target to be attacked with fewer or smaller bombs. Thus, even if some guided bombs miss, fewer air crews are put at risk and the harm to civilians and the amount of collateral damage may be reduced. The advent of precision-guided munitions resulted in the renaming of older, low-technology, bombs as "unguid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-35
The Sukhoi Su-35 (russian: link=no, Сухой Су-35; NATO reporting name: Flanker-E) is the designation for two improved derivatives of the Su-27 air-defence fighter. They are single-seat, twin-engine, supermaneuverable aircraft, designed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau and built by Sukhoi. The type was originally developed by the Soviet Union from the Su-27 and was known as the Su-27M. It incorporated canards and a multi-function radar giving it multi-role capabilities. The first prototype made its maiden flight in June 1988. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union Sukhoi re-designated it as the Su-35 to attract export orders. Fourteen aircraft were produced and used for tests and demonstrations; one example had thrust-vectoring engines and was in turn redesignated the Su-37. A sole Su-35UB two-seat trainer was also built in the late 1990s that resembled the Su-30MK family. In 2003, Sukhoi embarked on a second modernization of the Su-27 to serve as an interim a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-24
The Sukhoi Su-24 ( NATO reporting name: Fencer) is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was the first of the USSR's aircraft to carry an integrated digital navigation/attack system. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force, Syrian Air Force, Ukrainian Air Force, Algerian Air Force and various other air forces to which it was exported. Development Background One of the conditions for accepting the Sukhoi Su-7B into service in 1961 was the requirement for Sukhoi to develop an all-weather variant capable of precision air strikes. Preliminary investigations with ''S-28'' and ''S-32'' aircraft revealed that the basic Su-7 design was too small to contain all the avionics required for the mission. OKB-794 (later known as Leninets) was tasked with developing an advanced nav/attack system, codenamed ''Puma'', which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Air Force
"Air March" , mascot = , anniversaries = 12 August , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = , decorations = , battle_honours = , battle_honours_label = , flying_hours = , website = , commander1 = President Vladimir Putin , commander1_label = Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Defence Forces , commander2 = Army General Sergei Surovikin , commander2_label = Commander-in-Chief of the Aerospace Forces , commander3 = Lieutenant general , commander3_label = Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Air Force , notable_commanders = , identification_symbol = , identification_symbol_label = Flag , identification_symbol_2 = , identification_symbol_4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

