|
Jungian Type Indicator
The Jungian Type Index (JTI) is an alternative to the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). Introduced by Optimas in 2001, the JTI was developed over a 10-year period in Norway by psychologists Thor Ødegård and Hallvard E: Ringstad. The JTI was designed to help capture individuals' preferred usage of the psychological functions identified by Carl Jung in his book ''Psychological Types'', such as thinking vs feeling and sensing vs intuition. The JTI's questions and methodology for identifying the preferred functions differs from the MBTI. For example, it eliminates word pairs, which can be troublesome to translate from English into other languages. In many languages, the sentence context frames the meaning of a word, while in English the words themselves may denote more meaning. Overview Similar to the MBTI, the JTI identifies four categories from which the 16 types are formed: Extraversion/Introversion, Intuiting/Sensing, Thinking/Feeling, Perceiving/Judging. A personality type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
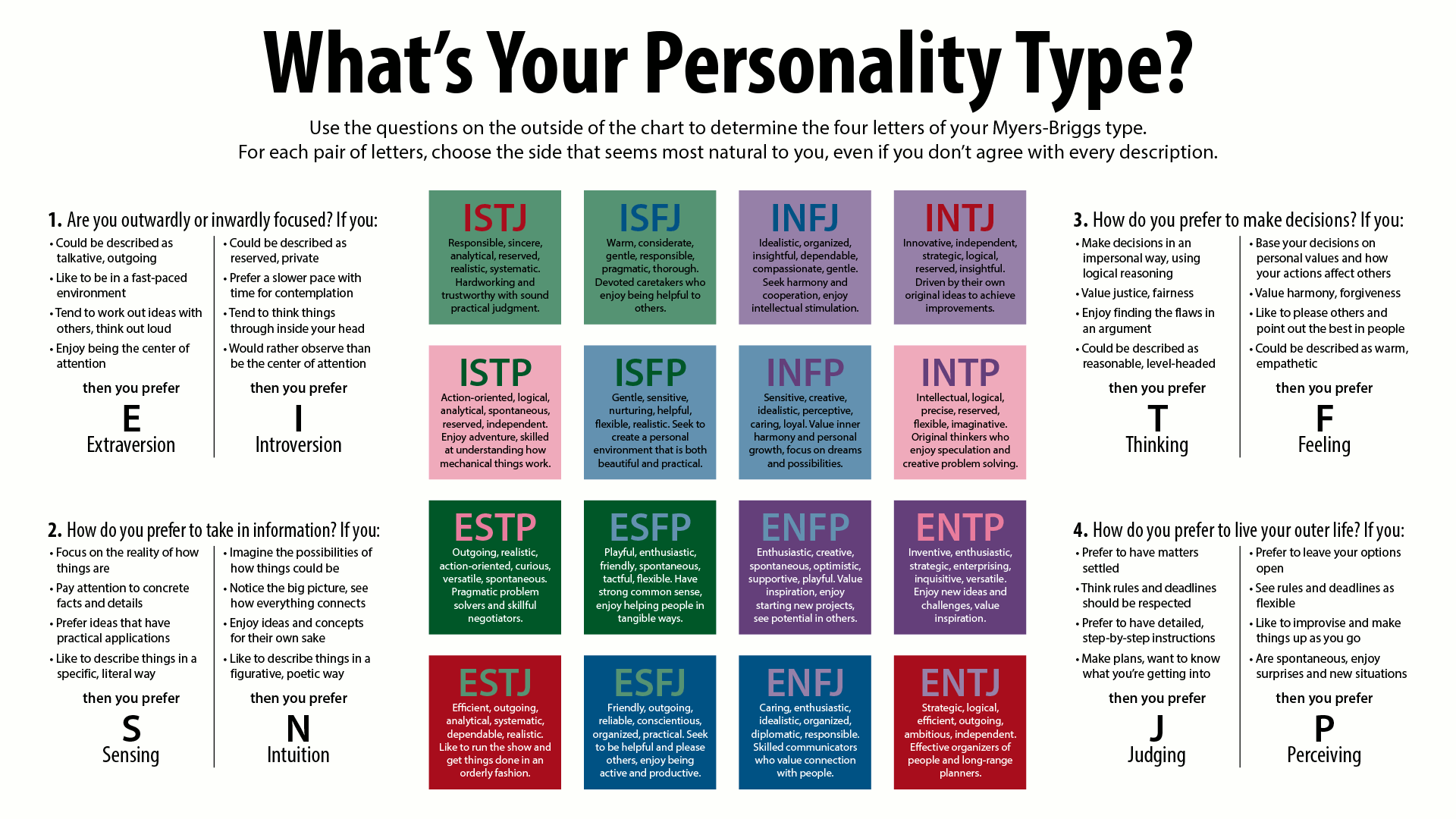
Myers–Briggs Type Indicator
The Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a self-report questionnaire that makes pseudoscientific claims to categorize individuals into 16 distinct "psychological types" or "personality types". The MBTI was constructed during World War II by Americans Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, inspired by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung's 1921 book ''Psychological Types''. The test assigns a binary value to each of four categories: introversion or extraversion, sensing or intuition, thinking or feeling, and judging or perceiving. One letter from each category is taken to produce a four-letter test result representing one of 16 possible types, such as "INFP" or "ESTJ". The perceived accuracy of test results relies on the Barnum effect, flattery, and confirmation bias, leading participants to personally identify with descriptions that are somewhat desirable, vague, and widely applicable. As a psychometric indicator, the test exhibits significant deficiencies, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist, psychotherapist, and psychologist who founded the school of analytical psychology. A prolific author of Carl Jung publications, over 20 books, illustrator, and correspondent, Jung was a complex and convoluted academic, best known for his concept of Jungian archetypes, archetypes. Alongside contemporaries Sigmund Freud, Freud and Alfred Adler, Adler, Jung became one of the most influential psychologists of the early 20th century and has fostered not only scholarship, but also popular interest. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. He worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. Jung established himself as an influential mind, developing a friendship with Sigmund Freud, founder of psychoanalysis, conducting a The Freud/Jung Letters, leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Types
''Psychological Types'' () is a book by Carl Jung that was originally published in German by Rascher Verlag in 1921, and translated into English in 1923, becoming volume 6 of '' The Collected Works of C. G. Jung''. In the book, Jung proposes four main functions of consciousness: two perceiving or non-rational functions ( Sensation and Intuition), and two judging or rational functions ( Thinking and Feeling). These functions are modified by two main attitude types: extraversion and introversion. Jung proposes that the dominant function, along with the dominant attitude, characterizes consciousness, while its opposite is repressed and characterizes the unconscious. Based on this, the eight outstanding psychological types are: Extraverted sensation / Introverted sensation; Extraverted intuition / Introverted intuition; Extraverted thinking / Introverted thinking; and Extraverted feeling / Introverted feeling. Jung, as such, describes in detail the effects of tensions between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungian Cognitive Functions
Psychological functions, as described by Carl Jung in his book ''Psychological Types'', are particular mental processes within a person's psyche that are present regardless of common circumstances. This is a concept that serves as one of the foundations for his theory on personality type. In his book, he noted four main psychological functions: ''thinking'', ''feeling'', ''sensation,'' and ''intuition''. He introduced them with having either an internally focused (''Extraversion and introversion#Introversion, introverted'') or externally focused (''Extraversion and introversion#Extraversion, extraverted'') tendency which he called "''attitude''". He also categorizes the functions as either ''rational'' (thinking and feeling) or ''irrational'' (intuition and sensation). Psychological functions and attitudes The four psychological functions may be subjugated to the control of consciousness, which can take two attitudes: * Extraversion: "a strong, if not exclusive, determination by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomy
A dichotomy () is a partition of a set, partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are Complement (set theory), complements. In logic, the partitions are dual (category theory), opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multicategorical variables as binary variables is called discretization, dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personality Tests
A personality test is a method of assessing human personality construct (psychology), constructs. Most personality assessment instruments (despite being loosely referred to as "personality tests") are in fact introspective (i.e., subjective) self-report questionnaire (Q-data, in terms of LOTS of data, LOTS data) measures or reports from life records (L-data) such as rating scales. Attempts to construct actual performance tests of personality have been very limited even though Raymond Cattell with his colleague Frank Warburton compiled a list of over 2000 separate objective tests that could be used in constructing objective personality tests. One exception, however, was the Objective-Analytic Test Battery, a performance test designed to quantitatively measure 10 factor-analytically discerned personality trait dimensions. A major problem with both L-data and Q-data methods is that because of item transparency, rating scales, and self-report questionnaires are highly susceptible to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |