|
Jung Ju-young
Chung Ju-yung or Jung Joo-young (; 25 November 1915 – 21 March 2001) was a South Korean entrepreneur and the founder of Hyundai Group, one of the largest chaebols in South Korea. Raised as the eldest son of a poor Korean farmer, Chung was an integral part of the rapid development of Korea's economy, growing Hyundai Heavy Industries into the largest shipbuilder in the world, as well as increasing Hyundai Motor Group into the largest automobile manufacturer in Korea and the third largest in the world. Chung was also a vital contributor to the development of South Korea's infrastructure after the Korean War; with President Park Chung Hee, Chung constructed the Gyeongbu Expressway to connect Seoul to Busan in 1970. Chung's business ventures steered through the tumultuous times of Japanese colonial rule in Korea and the post-Korean War stresses on the economy. Chung explained his success in his statement: "Our people succeeded because they devoted their enterprising spirits. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeong (Korean Name)
Jung () is a Latin alphabet rendition of the Korean family name "정", also often spelled Jeong, Chung, Joung or Jong. As of the South Korean census of 2015, there were 2,407,601 people by this name in South Korea or 4.84% of the population. The Korean family name is mainly derived from three homophonous hanja. (2,151,879), (243,803) and (11,683). The rest of the homophonous hanjas include: (139), (41), (29), (22) and (5). Latin-alphabet spelling In a study by the National Institute of the Korean Language based on a sample of year 2007 applications for South Korean passports, it was found that 48.6% of people with this surname chose to have it spelled in Latin letters as Jung in their passports. The Revised Romanization transcription Jeong was at second place with 37.0%, while Chung came in third at 9.2%. It was the only one out of the top five surnames (the others being Kim, Park, Lee, and Choi) for which the Revised Romanization spelling was used by more than a few pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyeongbu Expressway
The Gyeongbu Expressway (; Asian Highway Network ) is the second oldest and most heavily travelled expressway in South Korea, connecting Seoul to Suwon, Daejeon, Gumi, South Korea, Gumi, Daegu, Gyeongju, Ulsan and Busan. It has the route number 1, signifying its role as South Korea's most important expressway. The entire length from Seoul to Busan is and the posted speed limit is , enforced primarily by speed cameras. History Inspired by the Autobahn during a trip to Germany, President of South Korea, South Korean President Park Chung Hee proposed the construction of the Gyeongbu Expressway as an election pledge in 1967. * February 1968 - Construction begins at the behest of South Korean President Park Chung Hee, who named Park Myung-keun in charge of construction. * 21 December 1968 - Seoul-Suwon segment opens to traffic. * 30 December 1968 - Suwon-Osan segment opens to traffic. * 29 September 1969 - Anseong-Cheonan segment opens to traffic. * 10 December 1969 - Cheonan-Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korean Won
The South Korean won (symbol: ₩; code: KRW; ) is the official currency of South Korea. A single won is divided into 100 jeon, the monetary subunit. The jeon is no longer used for everyday transactions, and it appears only in foreign exchange rates. The currency is issued by the Bank of Korea, based in the capital city of Seoul. Etymology The old "won" was a cognate of the Chinese yuan, which was derived from the Spanish-American silver dollar. It is derived from the hanja (, ), meaning "round", which describes the shape of the silver dollar. The won was subdivided into 100 (), itself a cognate of the East Asian unit of weight mace and synonymous with money in general. The current won (1962 to present) is written in hangul only and does not officially have any hanja associated with it. First South Korean won History The Korean won, Chinese yuan and Japanese yen were all derived from the Spanish-American silver dollar, a coin widely used for international trade bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
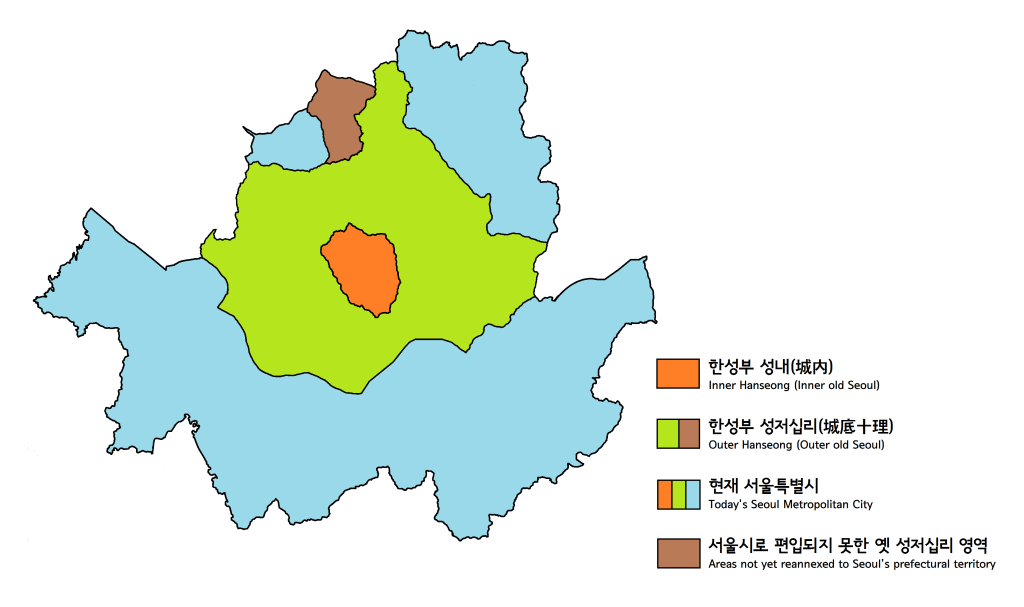
Hanseong
The region now corresponding to Seoul, South Korea has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of a number of kingdoms since it was established. Prehistoric It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the , located in Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas. Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong, which is believed to be inside modern-day Seoul. Baekje subsequently developed from a member state of the Mahan confederacy into one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. There are several city wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keijō
, or Gyeongseong (), was an administrative district of Korea under Japanese rule that corresponds to the present Seoul, the capital of South Korea. History When the Empire of Japan annexed the Korean Empire, it made Seoul the colonial capital. While under colonial rule (1910–1945), the city was called Keijō (; , literally meaning "capital city" in Hanja Hanja (; ), alternatively spelled Hancha, are Chinese characters used to write the Korean language. After characters were introduced to Korea to write Literary Chinese, they were adapted to write Korean as early as the Gojoseon period. () ....). Keijō was an urban city () that had 2 wards: Keijō itself and Ryusan-ku (龍山區, , ). Gyeongseong was part of Gyeonggi Province, instead of being an independent city or prefecture as in Joseon and present days. In 1914, several outer districts of the prefecture were annexed to neighboring Goyang County (now Goyang City, reducing the administrative size of the prefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewage systems, pipelines, structural element, structural components of buildings, and railways. Civil engineering is traditionally broken into a number of sub-disciplines. It is considered the second-oldest engineering discipline after military engineering, and it is defined to distinguish non-military engineering from military engineering. Civil engineering can take place in the public sector from municipal public works departments through to federal government agencies, and in the private sector from locally based firms to Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 companies. History Civil engineering as a discipline Civil engineering is the application of physical and scientific principles for solv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kowon
Kowŏn County is a county in South Hamgyŏng province, North Korea. It lies at the southern tip of the province. Physical features The highest point is Palbongsan. The western reaches of the county are high and mountainous, while the east is a low-lying plain. Major rivers and streams include the Chŏnt'an River (전탄강), Tŏkchi River (덕지강), Sabakch'ŏn (사박천), and the Kuryongch'ŏn (구룡천). 54% of the county's area is forested. The climate is generally continental, but is moderated by foehn winds blowing from the mountains. This makes it one of the warmer parts of the province. Administrative divisions Kowŏn county is divided into 1 ''ŭp'' (town), 1 ''rodongjagu'' (workers' district) and 18 '' ri'' (villages): Economy Agriculture Agriculture is the predominant local industry. Orcharding and livestock raising are also carried out, as is sericulture (silk farming). Mining and manufacturing There are deposits of limestone in the county, and mining and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chongjin
Chŏngjin (; ) is the capital of North Korea's North Hamgyong Province (함경북도) and the country's List of cities in North Korea, third-largest city. Sometimes called the City of Iron, it is located in the northeast of the country. History Prehistory According to archaeological findings near the lower areas of the Tumen River, Tumen river, evidence of human living traces back to the Paleolithic period. Ancient and medieval history According to the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', the region was where the tribe kingdoms of Buyeo, Mohe people, Mohe, Okjeo, Yilou, Yemaek and Sushen existed. The region later was the territory of Goguryeo. After the fall of Goguryeo in 668, the region was ruled by the Tang dynasty. During the reign of Balhae, the region was under the subdivision Donggyeongyongwonbu. The region was under the rule of the Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasty and Yuan dynasty after the fall of Balhae by the Liao dynasty, Khitans. Modern history Chongjin w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge ( ) is a British multinational corporation, multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, academic journals, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioral science, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 140,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and Imprint (trade name), imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Confucianism
Korean Confucianism, or Korean Ruism, is the form of Confucianism that emerged and developed in Korea. One of the most substantial influences in Korean intellectual history was the introduction of Confucian thought as part of the cultural influence from China. Today the legacy of Confucianism remains a fundamental part of Korean society, shaping the moral system, the way of life, social relations between old and young, high culture, and is the basis for much of the legal system. Confucianism in Korea is sometimes considered a pragmatic way of holding a nation together without the civil wars and internal dissent that were inherited from the Goryeo dynasty. Origins of Confucian thought Confucius ( , ) is generally thought to have been born in 551 BC and raised by his mother following the death of his father when Confucius was three years old. The Latinized name "Confucius" by which most Westerners recognize him is derived from "", probably first coined by 16th-century Jesuit missi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Korea Times
''The Korea Times'' () is a daily English-language newspaper in South Korea. It is a sister paper of the ''Hankook Ilbo'', a major Korean language, Korean-language daily. It is the oldest active daily English-language newspaper in South Korea. Since the late 1950s, it had been published by the Hankook Ilbo Media Group, but following an embezzlement scandal in 2013–2014 it was sold to Dongwha Group in 2015. The president-publisher of ''The Korea Times'' is Oh Young-jin. Description The newspaper's headquarters is located in the same building with ''Hankook Ilbo'' on Sejong-daero between Sungnyemun and Seoul Station in Seoul, South Korea. The paper is not to be confused with ''The Korea Daily News'', a 1904 to 1910 newspaper which briefly ran under the title ''Korea Times''. It is also unrelated to another paper by Lee Myo-muk, Ha Kyong-tok and Kim Yong-ui in September 1945. History ''The Korea Times'' was founded by Helen Kim five months into the 1950-53 Korean War. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |