|
June Tenth Movement
The June Tenth Movement () was a 1926 student protest primarily held in Keijō (Seoul), Korea against Japanese colonial rule. Background From 1910 to 1945, Korea was a colony of the Empire of Japan. In 1919, the March First Movement peaceful protests caused a spike in the Korean independence movement, particularly amongst the Korean diaspora. However, by 1926, the independence movement had encountered a lull. Japan quelled international pressure to reform (in part via its policies), the Korean Provisional Government in Shanghai was encountering difficulties, and Korean militant resistance in Manchuria had peaked in 1921. Furthermore, the divisions between the political left and right in Korea intensified. On April 26, 1926, the former Emperor of Korea Sunjong died. As the March First Movement had occurred in the wake of the death of Sunjong's father Gojong, the Japanese military braced for a similar wave of protests. It gathered 7,000 soldiers in Keijō (Seoul), and anchore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Independence Movement
The Korean independence movement was a series of diplomatic and militant efforts to liberate Korea from Japanese rule. The movement began around the late 19th or early 20th century, and ended with the surrender of Japan in 1945. As independence activism on the peninsula was largely suppressed by Japan, many significant efforts were conducted abroad by the Korean diaspora, as well as by a number of sympathetic non-Koreans. In the mid-19th century, Japan and China were forced out of their policies of isolationism by the West. Japan then proceeded to rapidly modernize, forcefully open Korea, and establish its own hegemony over the peninsula. Eventually, it formally annexed Korea in 1910. The 1919 March First Movement protests are widely seen as a significant catalyst for the international independence movement, although domestically the protests were violently suppressed. In the aftermath of the protests, thousands of Korean independence activists fled abroad, mostly to China. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Busan
Busan (), officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second list of cities in South Korea by population, most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.3 million as of 2024. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea, with its port being South Korea's busiest and the sixth-busiest in the world. The surrounding "Southeastern Maritime Industrial Region" (including Ulsan, South Gyeongsang Province, South Gyeongsang, Daegu, and part of North Gyeongsang Province, North Gyeongsang and South Jeolla Province, South Jeolla) is South Korea's largest industrial area. The large volumes of port traffic and urban population in excess of 1 million make Busan a Large-Port metropolis using the Southampton System of Port-City classification. As of 2019, Busan Port is the primary port in Korea and the world's sixth-largest container port. Busan is divided into 15 major administrative districts and a single co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwangju Student Independence Movement
Gwangju (; ), formerly romanized as Kwangju, is South Korea's sixth-largest metropolis. It is a designated metropolitan city under the direct control of the central government's Home Minister. The city was also the capital of South Jeolla Province until the provincial office moved to the southern village of Namak in Muan County in 2005 because Gwangju was promoted to a metropolitan city and was independent of South Jeolla Province. Its name is composed of the words ''gwang'' () meaning "light" and ''ju'' () meaning "province". Gwangju was historically recorded as ''Muju'' (), in which "Silla merged all of the land to establish the provinces of Gwangju, Ungju, Jeonju, Muju and various counties, plus the southern boundary of Goguryeo and the ancient territories of Silla" in the ''Samguk sagi.'' In the heart of the agricultural Jeolla region, the city is also famous for its rich and diverse cuisine. History The city was established in 57 BC. It was one of the administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeonju
Jeonju (, , ) is the capital and List of cities in South Korea, largest city of North Jeolla Province, South Korea. It is both urban and rural due to the closeness of Wanju County which almost entirely surrounds Jeonju (Wanju County has many residents who work in Jeonju). It is an important tourist center famous for Korean food, historic buildings, sports activities, and innovative festivals. In May 2012, Jeonju was chosen as a Creative City for Gastronomy as part of UNESCO's Creative Cities Network. This honour recognizes the city's traditional home cooking handed down over thousands of years, its active public and private food research, a system of nurturing talented chefs, and its hosting of distinctive food festivals. Jeonju is a city with over 1,300 years of history and culture. The city has produced many scholars and has a developed publishing industry. Cityscape File:Sunset In Jeonju South Korea Travel Photography (253309367).jpeg, Jeonju Hanok Village File:Jeonju Gyeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongju
Gongju (; ) is a city in South Chungcheong Province, South Korea. History Gongju was formerly named Ungjin and was the capital of Baekje from AD 475 to 538. In this period, Baekje was under threat from Goguryeo. Goguryeo had overrun the previous capital of Seoul, Hanseong (modern-day Seoul), which forced Baekje to find a new center of strength. In 538, King Seong of Baekje, King Seong moved the capital to Sabi (Korea), Sabi (in modern-day Buyeo County). However, Gongju remained an important center until the kingdom's fall in 660. New capital On August 11, 2004, the South Korean Prime Minister Lee Hae-chan announced that the country's capital will be moved from Seoul to Gongju (approximately south of Seoul) and Yeongi County, Yeongi commencing in 2007. A site was chosen for the project, which was scheduled to be completed by 2030. It was envisaged that government and administrative functions will move to the new capital, along with (possibly) the National Assembly and supr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. According to the 2008 population census, it has a population of 3,255,288. Pyongyang is a Special cities of North Korea, directly administered city () with a status equal to that of the Provinces of North Korea, North Korean provinces. Pyongyang is one of the oldest cities in Korea. It was the capital of two ancient Korean kingdoms, Gojoseon and Goguryeo, and served as the secondary capital of Goryeo. Following the establishment of North Korea in 1948, Pyongyang became its ''de facto'' capital. The city was again devastated during the Korean War, but was quickly rebuilt after the war with Soviet Union, Soviet assistance. Pyongyang is the political, industrial and transport center of North Korea. It is estimated that 99% of those living in Pyongy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunsan
Gunsan (; ), also romanized as Kunsan, is a Administrative divisions of South Korea, city in North Jeolla Province, South Korea. It is on the south bank of the Geum River just upstream from its exit into the Yellow Sea. It has emerged as a high-tech manufacturing industrial city and an international trade seaport that is approximately southwest of Seoul on the midwest coast of the Korean Peninsula. Kunsan Air Base operated by the United States Air Force is in the city. To encourage investment, a free trade zone has been declared. History Gunsan was a small fishing village on the banks of the Geum River, near where the river spills into the Yellow Sea. It sits on the fertile western ''Honam'' plain where much rice is harvested. Gunsan became a port in the late 19th century largely due to pressure from the Japanese on the Koreans to ship rice to Japan. In 1899, Gunsan Port officially opened up to international trade. Gunsan was largely settled by Japanese during the period of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulsan
Ulsan (; ), officially the Ulsan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's seventh-largest metropolitan city and the eighth-largest city overall, with a population of over 1.1 million inhabitants. It is located in the south-east of the country, neighboring Busan to the south and facing Gyeongju to the north. Ulsan is the industrial powerhouse of South Korea, forming the heart of the Ulsan Industrial District. It has the world's largest automobile assembly plant, operated by the Hyundai Motor Company; the world's largest shipyard, operated by Hyundai Heavy Industries; and the world's third largest oil refinery, owned by SK Energy. In 2020, Ulsan had a GDP per capita of $65,352, the highest of any region in South Korea. Ulsan is the city that built the first automobile hydrogen charging station in the country in 2009. In addition, the first hydrogen ship charging station in the country was installed in Jangsaengpo Port in 2021. Currently, the Ulsan Green Hydrogen Town project, a hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chongju
Chŏngju (; also Jŏngju) is a '' si'', or city, in southern North P'yŏngan Province, North Korea. Prior to 1994, it was designated as a ''kun'' or county. The terrain is mostly level, but mountainous in the north. To the south lies the Chongju Plain, where the hills do not rise above . Chŏngju also includes approximately 10 islands in the Yellow Sea. History Artifacts from the Neolithic period and the Bronze Age were found in the Taesan-ri area (this was formerly a region of Seoksandong and Taesandong under the administrative division of Teokeon-myeon), showing evidence of human existence at the time in the area. When it was under the control of Goguryeo, it was under the subdivision of Mannyeon County, and it was under control of the Pyongyang Amnok subdivision during the Balhae period. After the fall of balhae and before Goryeo reacquired the area, the region was occupied by the jurchens. During the Goryeo period, it was known as ''guju'', meaning "turtle province". In 123 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dansungsa
Dansungsa () was one of Korea's earliest and most historic movie theaters. It was first established in 1907, during the Korean Empire period, in what is now Jongno 3-ga in Seoul. It was once widely believed to be the oldest movie theater in Korea, but in recent years, that title is now thought to belong to Ae Kwan Theater, which was founded in Incheon in 1895. The theater held a position of prominence in Korean society for many decades. However, by the 1980s, it saw declining popularity and increasing competition. After the rise of multiplex movie theaters in the 1990s, the theater made an attempt to convert into one itself. It reopened in 2008 as a multiplex, but failed to recoup on its investments and went bankrupt soon afterwards. In 2010, the building was converted into a regular office building that now sells jewelry. In 2019, a museum dedicated to the theater was opened in the building. History Dansungsa was first built as a single screen, two-story wooden building in 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
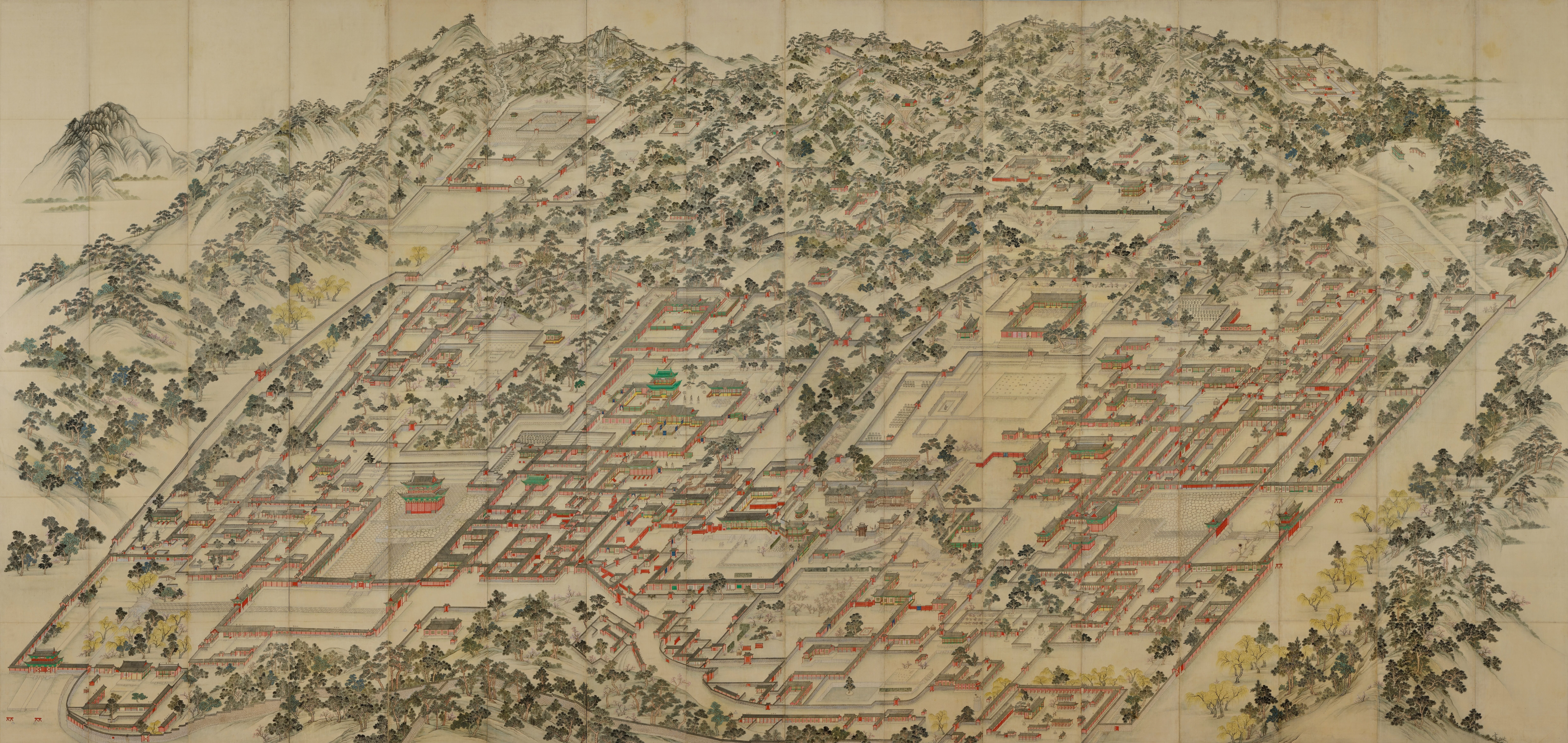
Changdeokgung
Changdeokgung () is a former royal palace in Seoul, South Korea. A UNESCO World Heritage Site and a Historic Sites (South Korea), Historic Site of South Korea, it is among the best preserved of all Korean palaces. It and its neighboring palace Changgyeonggung have together been called the "East Palace". Changdeokgung was established in 1405. It was the second palace to be established in Seoul, after Joseon's official main palace Gyeongbokgung. Despite Gyeongbokgung's legally superior status, a majority of kings preferred to reside in Changdeokgung instead. In 1592, amidst the Imjin War, Changdeokgung and all the other palaces in the city were completely destroyed. After the war, due to budgetary constraints, Gyeongbokgung was not repaired, while Changdeokgung and Changgyeonggung were. This effectively made Changdeokgung Joseon's main palace for several centuries. In the late 19th century, under the reign of the penultimate Korean monarch Gojong of Korea, Gojong, Gyeongbokgung was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |