|
Jumping Humpback Whale
Jumping or leaping is a form of locomotion or movement in which an organism or non-living (e.g., robotics, robotic) mechanical system propels itself through the air along a ballistic trajectory. Jumping can be distinguished from running, galloping and other gaits where the entire body is temporarily airborne by the relatively long duration of the aerial phase and high angle of initial launch. Some animals, such as the kangaroo, employ jumping (commonly called ''hopping'' in this instance) as their primary form of an Animal locomotion, locomotion, while others, such as frogs, use it only as a means to escape predators. Jumping is also a key feature of various activities and sports, including the long jump, high jump and show jumping. Physics All jumping involves the application of force against a substrate, which in turn generates a reactive force that propels the jumper away from the substrate. Any solid or liquid capable of producing an opposing force can serve as a substra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labanotation
Labanotation (grammatically correct form "Labannotation" or "Laban notation" is uncommon) is a system for analyzing and recording human movement (Notation, notation system), invented by Austro-Hungarian choreographer and dancer Rudolf von Laban (1879–1958, a central figure in European modern dance), who developed his notation on movements in the 1920s. History Laban's first book on the subject was published in German in 1928 called Schrifttanz (Written Dance); a similar version in French and English appeared in 1930. A few years later Laban's interest turned to other matters and he gave his notation system to the world. The German dancer, choreographer and pedagogue Albrecht Knust, who by 1930 had together with Laban's daughter Azra (Azraela) established the ''Tanz-Schreib-Stube'' (the first Dance Notation Bureau), was the first-ever full-time kinetographer-movement notator. Between 1946 and 1950 Knust wrote his major work Das Handbuch der Kinetographie Laban (The Manual of Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are amongst what are possibly the most ancient living groups of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago. Grasshoppers are typically ground-dwelling insects with powerful hind legs which allow them to escape from threats by leaping vigorously. Their front legs are shorter and used for grasping food. As hemimetabolous insects, they do not undergo complete metamorphosis; they hatch from an egg into a Nymph (biology), nymph or "hopper" which undergoes five moults, becoming more similar to the adult insect at each developmental stage. The grasshopper hears through the tympanal organ which can be found in the first segment of the abdomen attached to the thorax; while its sense of vision is in the compound eyes, a change in light intensity is perceived in the simple eyes (ocelli). At high population densities and under certain environmental conditions, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mud Skipper
Mudskippers are any of the 23 extant species of amphibious fish from the subfamily Oxudercinae of the goby family Oxudercidae. They are known for their unusual body shapes, preferences for semiaquatic habitats, limited terrestrial locomotion and jumping, and the ability to survive prolonged periods of time both in and out of water. Mudskippers can grow up to long, and most are a brownish green colour that ranges anywhere from dark to light. During mating seasons, the males will also develop brightly coloured spots in order to attract females, which can be red, green or blue. Unlike other fish, the mudskipper's eyes protrude from the top of its flat head. Their most noticeable feature however is their side pectoral fins that are located more forward and under their elongated body. These fins are jointed and function similarly to limbs, which allow the mudskipper to crawl from place to place. Although having the typical body form of any other gobiid fish, these front fins allow t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parachuting
Parachuting and skydiving are methods of descending from a high point in an atmosphere to the ground or ocean surface with the aid of gravity, involving the control of speed during the descent using a parachute or multiple parachutes. For human skydiving, there is often a phase of free fall (the skydiving segment), where the parachute has not yet been deployed and the body gradually accelerates to terminal velocity. In cargo parachuting, the parachute descent may begin immediately, such as a parachute- airdrop in the lower atmosphere of Earth, or it may be significantly delayed. For example, in a planetary atmosphere, where an object is descending "under parachute" following atmospheric entry from space, may occur only after the hypersonic entry phase and initial deceleration that occurs due to friction with the thin upper atmosphere. History The first parachute jump in history was made on 22 October 1797 by Frenchman André-Jacques Garnerin above Parc Monceau, Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliding
Gliding is a recreational activity and competitive air sports, air sport in which pilots fly glider aircraft, unpowered aircraft known as Glider (sailplane), gliders or sailplanes using naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to remain airborne. The word ''soaring'' is also used for the sport. Gliding as a sport began in the 1920s. Initially the objective was to increase the duration of flights but soon pilots attempted cross-country flights away from the place of launch. Improvements in aerodynamics and in the understanding of weather phenomena have allowed greater distances at higher average speeds. Long distances are now flown using any of the main sources of rising air: Ridge Lift, ridge lift, thermals and lee waves. When conditions are favourable, experienced pilots can now fly hundreds of kilometres before returning to their home airfields; occasionally flights of more than are achieved. Some competitive pilots fly in races around pre-defined course ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog Limbs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough skin texture due to wart-like parotoid glands tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal and purely cosmetic, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest and associated wetlands. They account for around 88% of extant amphibian species, and are one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar (250million years ago), but molecular clock dating suggests their divergence from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265million years ago. Adult frogs have a stou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apodeme
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. that of a human) which is enclosed underneath other soft tissues. Some large, hard and non-flexible protective exoskeletons are known as shell or armour. Examples of exoskeletons in animals include the cuticle skeletons shared by arthropods (insects, chelicerates, myriapods and crustaceans) and tardigrades, as well as the skeletal cups formed by hardened secretion of stony corals, the test/tunic of sea squirts and sea urchins, and the prominent mollusc shell shared by snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus. Some vertebrate animals, such as the turtle, have both an endoskeleton and a protective exoskeleton. Role Exoskeletons contain rigid and resistant components that fulfil a set of functional roles in addition to structural support in ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension (physics), tension. Tendons, like ligaments, are made of collagen. The difference is that ligaments connect bone to bone, while tendons connect muscle to bone. There are about 4,000 tendons in the adult human body. Structure A tendon is made of dense regular connective tissue, whose main cellular components are special fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tendon cells synthesize the tendon's extracellular matrix, which abounds with densely-packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers run parallel to each other and are grouped into fascicles. Each fascicle is bound by an endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibers. A set of fascicles is bound by an epitenon, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
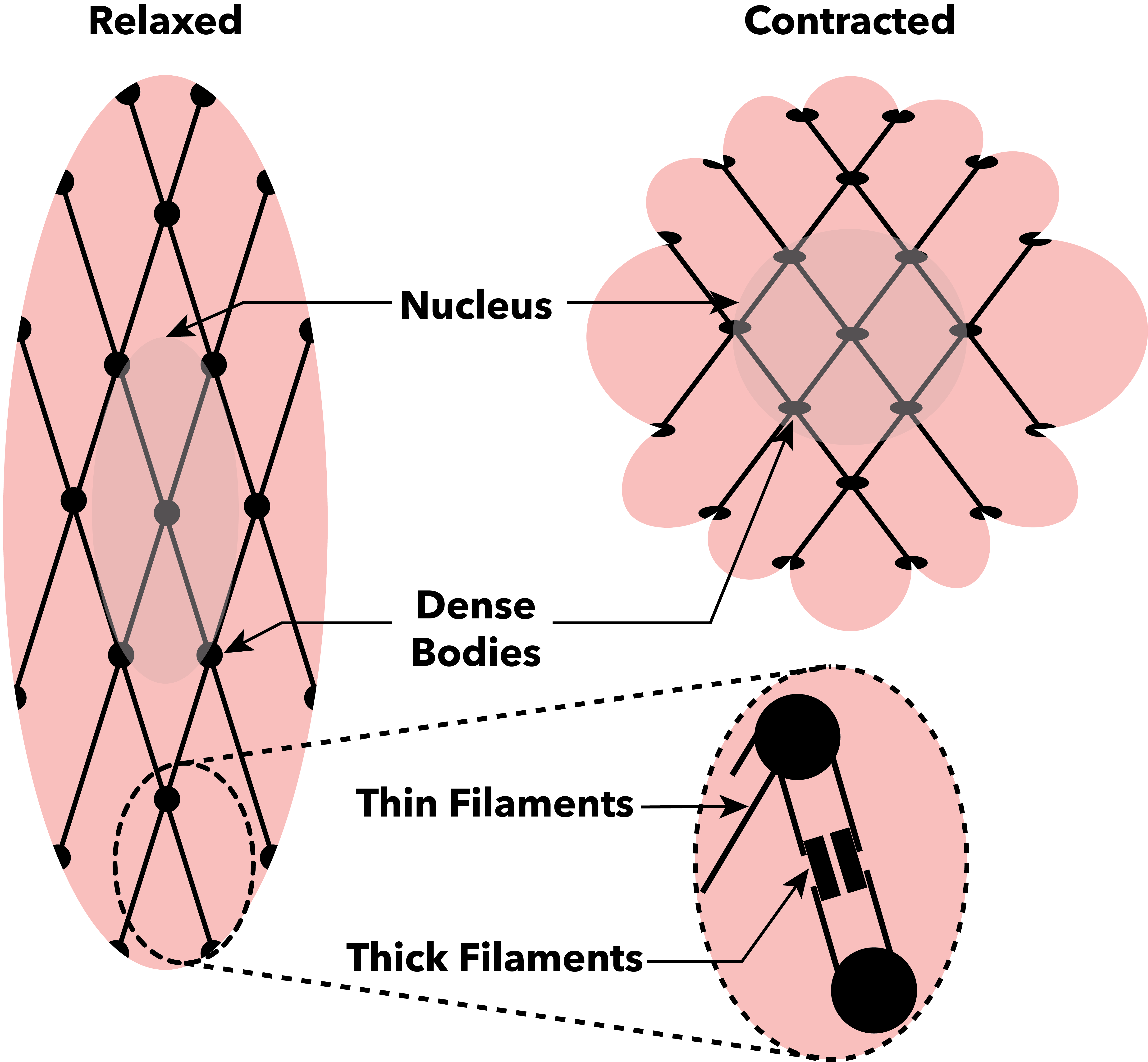
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |