|
Julius I Kán
Julius (I) from the kindred Kán ( hu, Kán nembeli (I.) Gyula; died 1237) was a powerful Hungarian baron and landowner, who held several secular positions during the reign of kings Emeric, Ladislaus III and Andrew II. He was the ancestor of the ''gens'' Kán which originated from Baranya County.Markó 2006, p. 235. Family Julius I (often called as "the Elder" or "the Great" by contemporary documents in order to distuingish him from his namesake son) was the first known member of the ''gens'' (clan) Kán, which originated from Baranya County, but later acquired large-scale domains in Transylvania too. The later members of the clan were usually styled themselves as "''Progenies Magni Jule Bani''" ("descendants of Ban Julius the Great"). He married the unknown surname Helena (died before 1250). They had two sons, by name Ladislaus I, who served as palatine (1242–1244/5), and Julius II, master of the cupbearers (1222–1228). His great-grandson was Ladislaus III Kán, an infamou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Of Hungary
The Palatine of Hungary ( hu, nádor or , german: Landespalatin, la, palatinus regni Hungariae) was the highest-ranking office in the Kingdom of Hungary from the beginning of the 11th century to 1848. Initially, Palatines were representatives of the monarchs, later (from 1723) the vice-regent (viceroy). In the early centuries of the kingdom, they were appointed by the king, and later (from 1608) were elected by the Diet of the Kingdom of Hungary. A Palatine's jurisdiction included only Hungary proper, in the Kingdom of Croatia until 1918 the ban held similar function as the highest office in the Kingdom (after the king himself), monarch's representative, commander of the royal army and viceroy (after the union of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia with Hungary in 1102). Title The earliest recorded Medieval Latin form of the title was ''comes palatii'' ("count of the palace"); it was preserved in the deed of foundation of the Tihany Abbey, issued in 1055. A new varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ispán
The ispánRady 2000, p. 19.''Stephen Werbőczy: The Customary Law of the Renowned Kingdom of Hungary in Three Parts (1517)'', p. 450. or countEngel 2001, p. 40.Curta 2006, p. 355. ( hu, ispán, la, comes or comes parochialis, and sk, župan)Kirschbaum 2007, p. 315. was the leader of a castle district (a fortress and the royal lands attached to it) in the Kingdom of Hungary from the early 11th century. Most of them were also heads of the basic administrative units of the kingdom, called counties, and from the 13th century the latter function became dominant. The ''ispáns'' were appointed and dismissed by either the monarchs or a high-ranking royal official responsible for the administration of a larger territorial unit within the kingdom. They fulfilled administrative, judicial and military functions in one or more counties. Heads of counties were often represented locally by their deputies, the vice-ispánsRady 2000, p. 41. ( hu, alispán,Nemes 1989, p. 21. la, viceco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly temperate- continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Romania from the north to the southwest, include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Settlement in what is now Romania began in the Lower Pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Authentication
A place of authentication ( hu, hiteleshely; la, locus credibilis) was a characteristic institution of medieval Hungarian law. Places of authentication were cathedral chapters and monasteries authorized to provide notarial A notary is a person authorised to perform acts in legal affairs, in particular witnessing signatures on documents. The form that the notarial profession takes varies with local legal systems. A notary, while a legal professional, is disti ... services, including the issuing of authentic copies of documents. References Sources * * * * * * * Legal history of Hungary Medieval Kingdom of Hungary Catholic Church in Hungary KOSZTA, LÁSZLÓ: Conclusions Drawn from the Prosopographic Analysis of the Canons Belonging to the Cathedral Chapters of Medieval Hungary (1200—1350), in: Universidade, Catâolica Portuguesa Carreiras Eclesiásticas no Ocidente Cristão (séc. XII–XIV) – Ecclesiastical Careers in Western Christianity (12th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oradea
Oradea (, , ; german: Großwardein ; hu, Nagyvárad ) is a city in Romania, located in Crișana, a sub-region of Transylvania. The seat of Bihor County, Oradea is one of the most important economic, social and cultural centers in the western part of Romania. The city is located in the north-west of the country, nestled between hills on the Crișana plain, on the banks of the river Crișul Repede, that divides the city into almost equal halves. Located about from Borș, one of the most important crossing points on Romania's border with Hungary, Oradea ranks tenth in size among Romanian cities. It covers an area of , in an area of contact between the extensions of the Apuseni Mountains and the Crișana-Banat extended plain. Oradea enjoys a high standard of living and ranks among the most livable cities in the country. The city is also a strong industrial center in the region, hosting some of Romania's largest companies. Besides its status as an economic hub, Oradea boasts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szolnok County
Szolnok County was a county in the Kingdom of Hungary The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephe ... between the 11th century and 1426. {{coord, 47, 15, N, 20, 30, E, display=title, region:HU_type:adm1st_source:GNS-enwiki Kingdom of Hungary counties in Transylvania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
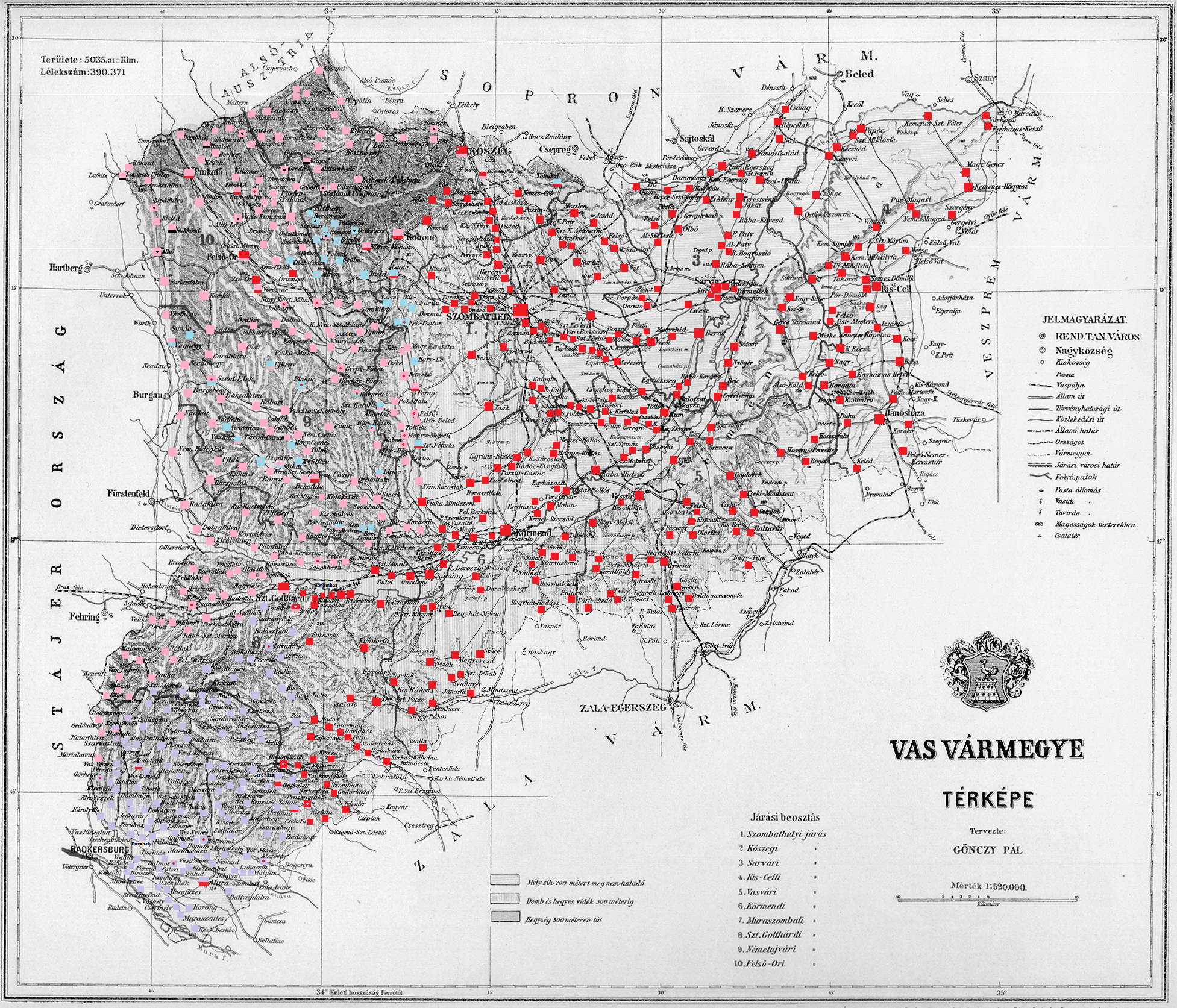
Vas County (former)
Vas (, , or ) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Hungary, Austria and Slovenia. Geography Vas County shared borders with the Austrian lands Lower Austria and Styria and the Hungarian counties Sopron, Veszprém and Zala. It stretched between the river Mura in the south, the foothills of the Alps in the west and the river Marcal in the east. The Rába River flowed through the county. Its area was 5474 km² around 1910. History Vas County arose as one of the first ''comitatuses'' of the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon, the western part of the county became part of Austria, and a small part in the southwest became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (from 1929 as Yugoslavia). The remainder stayed in Hungary. The former Yugoslavian part of the county was occupied and annexed by Hungary between 1941 and 1945 during World War II. In 1950, a small part of former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Of Slavonia
Ban of Slavonia ( hr, Slavonski ban; hu, szlavón bán; la, Sclavoniæ banus) or the Ban of "Whole Slavonia" ( hr, ban cijele Slavonije; hu, egész Szlavónia bánja; la, totius Sclavoniæ banus) was the title of the governor of a territory part of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary and Kingdom of Croatia. In the Kingdom of Croatia, Demetrius Zvonimir was the only notable person that ruled over the region of Slavonia with the title ban from around 1070 until 1075. From 1102, the title Ban of Croatia was appointed by the kings of Hungary, and there was at first a single ban for all of the Kingdom of Croatia, but later the Slavonian domain got a separate ban. It included parts of present-day Central Croatia, western Slavonia and parts of northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. From 1225, the title started being held by a separate dignitary from the title of the Ban of Croatia and Dalmatia, and existed until 1476, when it was joined with the latter title. According to the public la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bács County
BACS is the Bankers Automated Clearing Services, a scheme for the electronic processing of financial transactions. BACS or Bács may also refer to: Organisations * Bay Area Christian School, in League City, Texas, US * Boston Archdiocesan Choir School, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, US * British Association of Canadian Studies, a group for scholarly studies of Canadian culture Other uses * Bács (given name) * Bács-Bodrog County, a county in the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary from the 18th century to 1918 * Bács-Kiskun County, a county in Hungary, created from Bács-Bodrog and Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun counties after World War II * Bač, Serbia or Bács * Bacterial artificial chromosomes, a DNA construct See also * Bacsik, a surname (including a list of people with the name) * BAC (other) * BASC (other) BASC may refer to: * Berkeley APEC Study Center * Berlin Air Safety Center * British Association for Shooting and Conservation * Bulacan Agricultural State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodrog County
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary to the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–Hungarian border at the village of Felsőberecki (near Sátoraljaújhely) in Hungary, and Streda nad Bodrogom in Slovakia, where it is also the lowest point in Slovakia (94.3 m AMSL), and continues its flow through the Hungarian county Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén, until it meets the river Tisza, in Tokaj. A town along its course is Sárospatak, in Hungary. Its length is 67 km (15 in Slovakia, 52 in Hungary). Its watershed area is 13,579 km2 of which 972 km2 is in Hungary. The river is rich in fish Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopron County
Sopron (German: ''Ödenburg'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Austria and Hungary. The capital of the county was Sopron. Geography Sopron county shared borders with the Austrian land Lower Austria and the Hungarian counties Moson, Győr, Veszprém and Vas. The Lake Neusiedl (Hungarian: ''Fertő tó'', German: ''Neusiedler See'') lay in the county. Its area was about 3,256 km2 around 1910. History The Sopron comitatus arose as one of the first comitati of the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1920, by the Treaty of Trianon the western part of the county became part of Austria, while the eastern part became a part of Hungary. In 1921, it was decided by referendum that the city of Sopron and eight surrounding settlements would join Hungary instead of Austria. In 1950, Sopron county merged with Győr-Moson county to form Győr-Sopron county, while a small part of Sopron county went to Vas county. The county w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyitra County
Nyitra County ( hu, Nyitra vármegye; german: link=no, Neutraer Gespanschaft/Komitat Neutra; la, Comitatus Nitriensis; sk, Nitriansky komitát / Nitrianska stolica / Nitrianska župa) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory lay in what is now western Slovakia. Geography Nyitra County shared borders with the Austrian land Moravia and Trencsén County, Turóc County, Bars County, Komárom County and Pozsony County. In its final phase, it was a strip of land between the Morava river in the north and the town of Érsekújvár (present-day Nové Zámky) in the south, plus an outlier around the town of Privigye (present-day Prievidza). The river Vág (present-day Váh) flowed through the county. Its area was 5519 km2 around 1910. Capitals The capital of the county was the Nitra Castle ( hu, Nyitrai vár) and since the Late Middle Ages the town of Nyitra (present-day Nitra). History A predecessor to Nyitra county may have existed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |