|
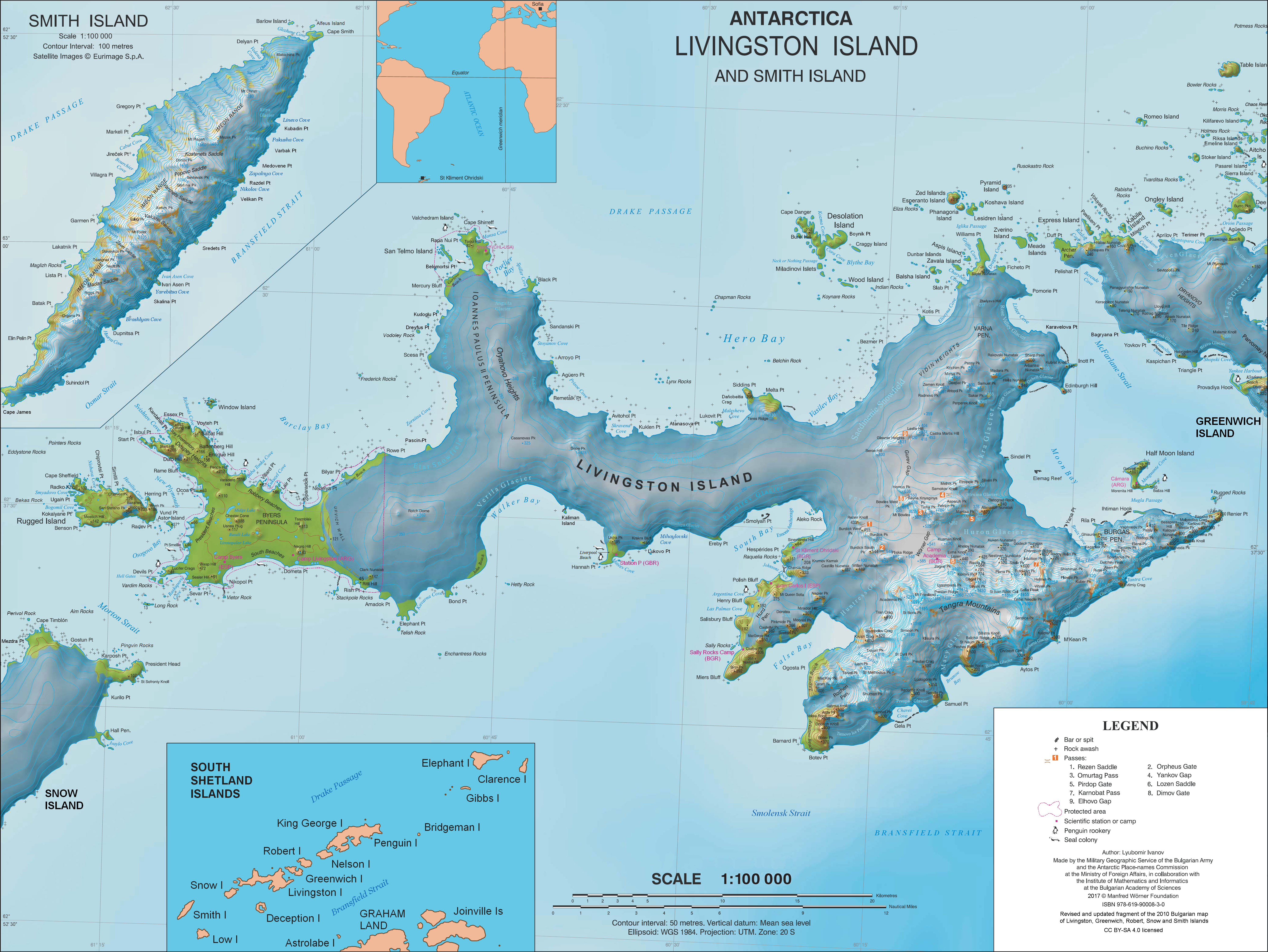
Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base
Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base, named after the former king of Spain, Juan Carlos I (), is a seasonal (November to March) scientific station operated by Spain, opened in January 1988. Situated on Hurd Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The base is controlled by the Marine Technology Unit of the Spanish National Research Council and is 20 miles away from the Spanish Antarctic base Gabriel de Castilla Base, Gabriel de Castilla. The base has undergone several renovations, the closest remodeling was completed in 2018 and it was inaugurated by the Ministry of Science (Spain), Science Minister, Pedro Duque, on February 2, 2019. This latest renovation involved the construction of "new facilities [that] have allowed it to double its capacity, up to 51 people, and increase the space available for scientific and technical personnel in laboratories." Location The base is on the coast of Española Cove, South Bay, Livingston Island, South Bay, in the northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the current research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rocks or on ice that are (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of these stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. Of the 56 signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, a total of 55 countries (as of 2023) operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The number of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,800 during the summer to around 1,200 during the winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnsons Glacier
Johnsons Glacier is the 1.8 km long and 2.3 km wide glacier on Hurd Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica bounded by Charrúa Ridge and Charrúa Gap to the north, Napier Peak to the east, Mirador Hill to the southeast, Hurd Ice Cap (from which it receives ice influx) to the southwest and Mount Reina Sofía to the west. It is draining northwestwards into Johnsons Dock. The glacier provides overland access from the Spanish base Juan Carlos Primero to the interior of the eastern Livingston Island. The feature receives its name from the adjacent Johnsons Dock. Location The midpoint of the glacier is located at (Detailed Spanish mapping in 1991, and Bulgarian mapping in 1996, 2005 and 2009). See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or, more generally, ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 Establishments In Antarctica
1989 was a turning point in political history with the "Revolutions of 1989" which ended communism in Eastern Bloc of Europe, starting in Poland and Hungary, with experiments in power-sharing coming to a head with the opening of the Berlin Wall in November, the Velvet Revolution in Czechoslovakia and the overthrow of the communist dictatorship in Romania in December; the movement ended in December 1991 with the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Revolutions against communist governments in Eastern Europe mainly succeeded, but the year also saw the suppression by the Chinese government of the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests in Beijing. It was the year of the first Brazilian direct presidential election in 29 years, since the end of the military government in 1985 that ruled the country for more than twenty years, and marked the redemocratization process's final point. F. W. de Klerk was elected as State President of South Africa, and his regime gradually dismantled the aparthei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Spain
Science and technology in Spain relates to the set of policies, plans and programs carried out by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and other organizations aimed at research, development and innovation (R&D&I), as well as the reinforcement Spanish scientific and technological infrastructures and facilities such as universities and commercial laboratories. Spain has become the ninth scientific power in the world with 2.5% of the total number of scientific publications, thus surpassing Russia in the world ranking of scientific production and surpassing Switzerland and Australia in scientific quality. Regulations Science Law of 1986 Law 13/1986 on the "Promotion and General Coordination of Scientific and Technical Research" placed science for the first time on the Spanish political agenda, laying the foundations for research and its financing, organization and coordination between the State and the autonomous regions. That regulation also led to the birth of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Antarctica
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outposts Of The South Shetland Islands
Outpost or outposts may refer to: Places * Outpost (military), a detachment of troops stationed at a distance from the main force or formation, usually at a station in a remote or sparsely populated location * Border outpost, an outpost maintained by a sovereign state on its border, usually one of a series placed at regular intervals, to watch over and safeguard its border with a neighboring state * Human outpost, an artificially-created, controlled human habitat located in an environment inhospitable for humans, such as the ocean floor, the Antarctic, in space, or on another planet * Outpost Estates, Los Angeles, California, a canyon neighborhood * Outpost Islands, Nunavut, Canada * Israeli outpost, a settlement built on land that was not legally purchased and was not given a building permit by the State of Israel Entertainment * ''The Outpost'', a 1909 play written by James Francis Jewell Archibald * ''Outpost'' (board game), from TimJim games * Outpost (chess), a str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Livingston Island
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ereby Point
Ereby Point () is a point lying east-northeast of Hannah Point along the north side of South Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The name "Erebys Bay" was applied to South Bay on an 1825 chart by James Weddell, "Ereby Point" was applied by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) an ... in 1961 in order to preserve Weddell's name in the area. Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Antarctic D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Byers
Camp Byers () is a Spanish seasonal base camp on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The locality is also designated for use as an International Field Camp. When necessary for scientific research purposes, temporary camping is allowed elsewhere on the protected peninsula under certain conditions. Measure 4 (2016), ATCM XXXIX Final Report. Santiago, 2016 The area was visited by early 19th century . Location The encampment is 1.2 km north-northwest of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Field Camps
Many research stations in Antarctica support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than tents used to support short term activities. Field camps are used for many things, from logistics (Sky Blu (Antarctica), Sky Blu) to dedicated scientific research (WAIS Divide Field Camp). List of field camps See also *Research stations in Antarctica *Demographics of Antarctica *List of Antarctic expeditions *Transport in Antarctica References * * {{cite web , url=https://www.comnap.aq/publications/maps/comnap_map_edition5_a0_2009-07-24.pdf , title=COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090915110710/https://www.comnap.aq/publications/maps/comnap_map_edition5_a0_2009-07-24.pdf , archive-date=September 15, 2009 Outposts of Antarctica, Antarctica-related lists, Field camps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |