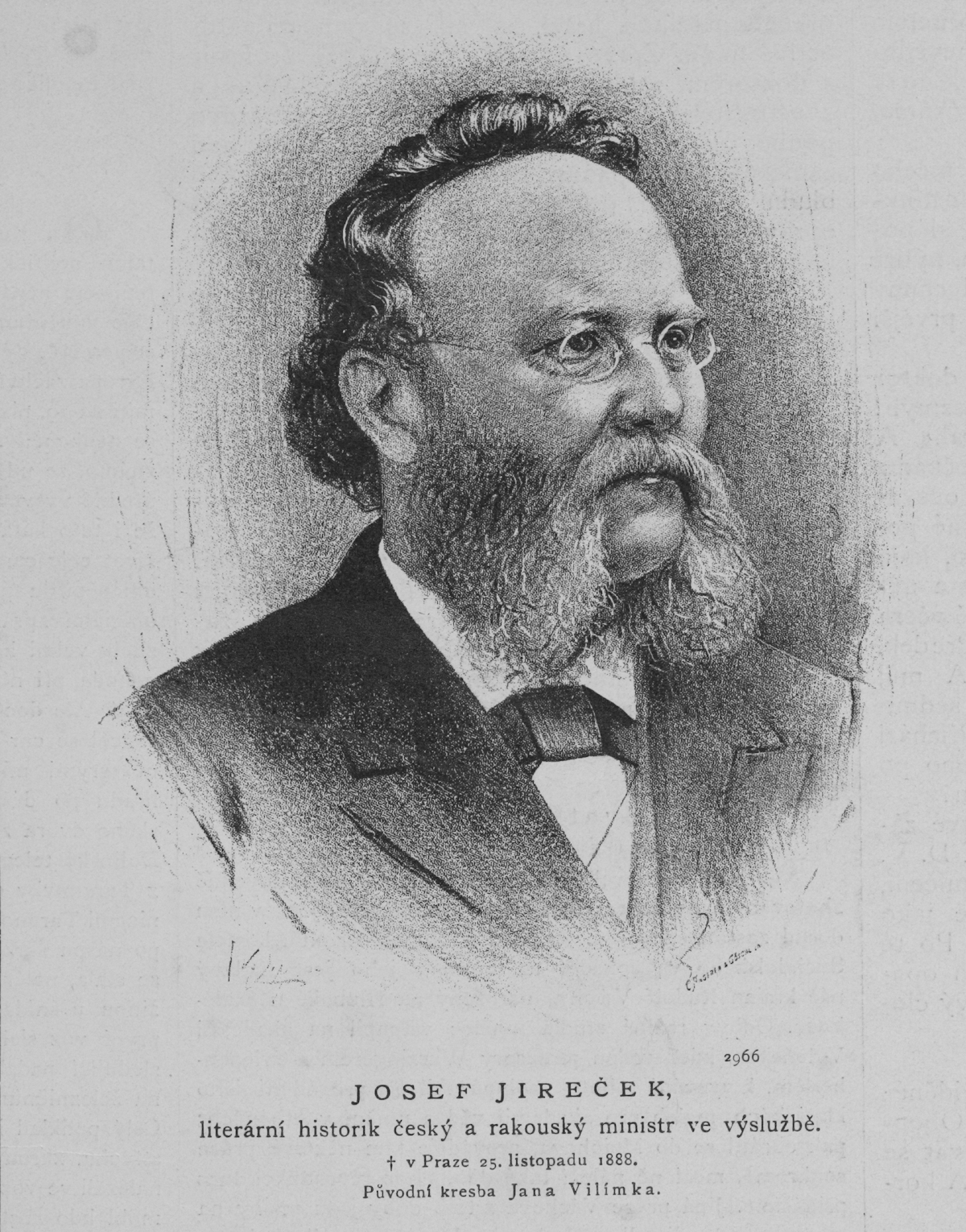|
Jožef Krajnc
Jožef Krajnc, also spelled Josef Krainc, Josef Krainz (17 February 1821 – 22 February 1875) was an Austro-Hungarian lawyer, philosopher and politician of Slovenian ancestry. Life Krajnc was born in Škale (today part of Velenje) in the Duchy of Styria to a farmer of the same name. From 1832 until 1841 he attended the high school in Celje, graduating with the ''matura''. From 1841 to 1845, he studied philosophy and law in Graz, obtaining a doctorate in both disciplines. From 1842 onward, he financed his studies as a private tutor to a wealthy landowner's family in Graz and Bad Radkersburg. From 1845 onward, Krajnc worked as judicial advisor first to the city council of Radkersburg, then to the council of Graz. For a short time in 1847, he worked as a judge in Graz. During the March Revolution, Krajnc served as a member of the Austrian Reichstag from 1848 to 1849, filling in for Vinzenz Gurnigg who did not accept his term. Among other duties, Krajnc was a member of the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of around 9 million. The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Roman Empire, Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Western Roman Empire, Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Jireček
Josef Jireček (9 October 1825, in Vysoké Mýto – 25 November 1888, in Prague) was a Czech scholar. He was born in Vysoké Mýto (then part of the Austrian Empire). He entered the Prague Bureau of Education in 1850 and became department minister in the Hohenwart cabinet in 1871. His efforts to secure equal educational privileges for the Slav nationalities in the Austrian dominions brought him into disfavour with the German element. He became a member of the Bohemian Landtag in 1878 and of the Austrian Reichsrat in 1879. His merits as a scholar were recognized in 1875 by his election as president of the Royal Czech Society of Sciences. He died in Prague on 25 November 1888. In 1862, he and his brother Hermenegild Jireček strove to defend the genuineness of the Königinhof Manuscript discovered by Václav Hanka. He published in Czech an anthology of Czech literature (3 volumes, 1858–1861), a biographical dictionary of Czech writers (2 volumes, 1875–1876), a Cz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Graz
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and Skills, skill, north of Ancient Athens, Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive Grove (nature), grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Slovenian Philosophers
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems and confirm cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |