|
Jowangsin
Jowangshin (in Hangul, ''조왕신'', in hanja, 竈王神) is the goddess of fire and the hearth in Korean shamanism. As the goddess of the hearth, the rituals dedicated to her were generally kept alive by housewives. She is no longer the subject of worship, but still remains one of the most famous Korean deities. History It is regarded that Jowangshin was worshipped by the Korean people for millennia, since the Proto Three Kingdoms era. For example, in the ''Sanguo Zhi'', a history book of China, there are records of a kitchen god. "There are many different rituals that they (the people of the Samhan, Samhan Confederacy, in modern South Korea) hold, but all worship a kitchen god in their western wings." Ritual Jowangshin was regarded to embody a bowl of water held on a clay altar above the hearth. The housewife awoke early every morning and poured fresh water from a nearby well into the bowl, then knelt before it, wishing for luck. The ritual of Jowangshin was especially well d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasa Bonpuli
The ''Chasa Bonpuri'', known in other versions as the ''Chesa Bonpuri'' (1933 version) or the ''Cheseo Bonpuri'' (2006 and 2008 versions), is a Korean myth of Jeju Island. It is a myth that tells how Gangnim, the death god, came to be. As one of the best-known myths in the Korean peninsula, the ''Chasa Bonpuri'' is a characteristic Heroic epic, hero epic. Etymology The term ''Chasa Bonpuri'' (차사 본풀이) means "Solving the origins of the death god"; modern academic circles synonymize "Bonpuli" with "myth". ''Chasa'' is the Standard Korean pronunciation of the Chinese language, Chinese word ''Chaishi'' (差使), meaning "messenger". In the Jeju language however, ''chaishi'' is pronounced ''Chesɒ'' or ''Cheshi'', leading to the different names per each version. Collections The Chasa Bonpuli has been directly collected from shamans nine times; below is a chart of these collections. Major plot Like all oral myths, there are multiple versions of the ''Chasa Bonpuli' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasa Bon-puri
The ''Chasa Bonpuri'', known in other versions as the ''Chesa Bonpuri'' (1933 version) or the ''Cheseo Bonpuri'' (2006 and 2008 versions), is a Korean myth of Jeju Island. It is a myth that tells how Gangnim, the death god, came to be. As one of the best-known myths in the Korean peninsula, the ''Chasa Bonpuri'' is a characteristic hero epic. Etymology The term ''Chasa Bonpuri'' (차사 본풀이) means "Solving the origins of the death god"; modern academic circles synonymize "Bonpuli" with "myth". ''Chasa'' is the Standard Korean pronunciation of the Chinese word ''Chaishi'' (差使), meaning "messenger". In the Jeju language however, ''chaishi'' is pronounced ''Chesɒ'' or ''Cheshi'', leading to the different names per each version. Collections The Chasa Bonpuli has been directly collected from shamans nine times; below is a chart of these collections. Major plot Like all oral myths, there are multiple versions of the ''Chasa Bonpuli''. The best-known version, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munjeon Bonpuli
The ''Munjeon Bonpuri'' (), meaning 'Annals of the Door', 'Book of the Door', 'Narration of the Door' or 'Explanation of the Door', is a myth of Jeju Island regarding Gasin, or deities that are believed to reside within the house. Plot In the village of Namseon in the kingdom of Junyeon lived Namseonbi and his wife, Yeosan Buin. Yeosan Buin was a very capable wife who raised the money for the family. However, her husband Namseonbi wasted all of the money whenever Yeosan Buin gathered enough. The family of Yeosan Buin had nine members: Namseonbi, Yeosan Buin, and their seven sons. The name of the seventh was Nokdisaengin. The family was frequently hungry, as a result of their poverty. Yeosan Buin was worried by their pitiful condition, and bought fine cotton clothes and hats and fifty silver coins by selling her treasures she had brought from her family. She suggested that with these accessories, they buy grain, which was cheap in their village, and sell it in other villages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ông Táo
Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶), Vua Bếp (𢂜灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and the emissary between heaven to earth. Mythology A long time ago, there was a couple, Trọng Cao and his wife Thị Nhi who were married for many years but had no children. One day, they quarreled over some trivial matter, and the husband, in a fit of anger, beat and threw his wife out of their home. Although Thị Nhi still loved her husband, she had no choice but to go away. Thị Nhi went far away and met a very kind man called Phạm Lang. He married her and he loved Thị Nhi very much. Their life was happy and peaceful but Thị Nhi could not forget her first love. As for Trọng Cao, he had been filled with remorse from the day he sent his wife away. He waited, and waited hopelessly for his wife’s return. Eventually, he decided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
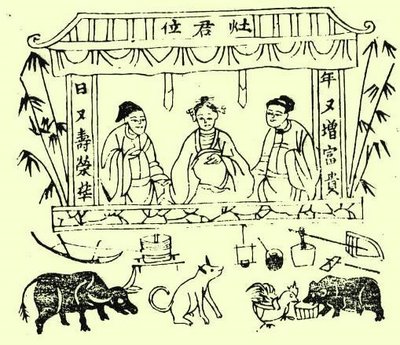
Zàojūn
Kitchen gods are mythical beings that represent abstract concepts such as luck or just propel the minor changes of everyday life. Little things that cannot be explained, such as losing small objects like socks in the laundry, are often attributed to these creatures because the explanation eludes the believer. See also *Di Penates *Hestia *Household deity * Jowangsin is a Korean kitchen god. * Kōjin is a Japanese kitchen god. *List of deities * Ông Táo Ông Táo (翁灶) also known as Táo Quân (灶君, Mandarin Táo), Táo Vương (灶王), Thần Bếp (神灶), Vua Bếp (𢂜灶) or the Kitchen god is regarded in Vietnamese culture as the advocate of the Vietnamese family with the gods and ... is a Vietnamese kitchen god. * Zàojūn is a Chinese kitchen god. References European mythology {{europe-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gashin Cult
Gasin faith () refers to belief and rituals surrounding gods of the household in Korean shamanism. These deities, called ''gasin'', are believed to protect the various objects (such as ''jangdok'') and rooms of the house. Joryeong faith The faith of Joryeong is the deification of one's ancestors. The earliest mention of the faith is in the ''Samguk Sagi'', a Medieval Korean history book, which mentions the 'golden chest' of Kim Alji, the first member of the Gyeongju Kim clan. This bears resemblance to modern ancestor worship. In the modern Honam region in southwest Korea, Koreans keep a large pot in the house, filled with rice. This is called the ''Jeseok Ogari'', and holds rice. The Jeseok Ogari is accompanied with ''Mom Ogari'', which are smaller potteries. The name of the ancestor or rice is put in the Mom Ogari. In the Yeongnam region, Jeseok Ogari and Mom Ogari is called Sejon Danji and Josang Dangsegi. In festivals and birthdays, the family holds a jesa to the Jeseok Oga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasin Faith
Gasin faith () refers to belief and rituals surrounding gods of the household in Korean shamanism. These deities, called ''gasin'', are believed to protect the various objects (such as '' jangdok'') and rooms of the house. Joryeong faith The faith of Joryeong is the deification of one's ancestors. The earliest mention of the faith is in the ''Samguk Sagi'', a Medieval Korean history book, which mentions the 'golden chest' of Kim Alji, the first member of the Gyeongju Kim clan. This bears resemblance to modern ancestor worship. In the modern Honam region in southwest Korea, Koreans keep a large pot in the house, filled with rice. This is called the ''Jeseok Ogari'', and holds rice. The Jeseok Ogari is accompanied with ''Mom Ogari'', which are smaller potteries. The name of the ancestor or rice is put in the Mom Ogari. In the Yeongnam region, Jeseok Ogari and Mom Ogari is called Sejon Danji and Josang Dangsegi. In festivals and birthdays, the family holds a jesa to the Jeseok O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hestia
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia (; ) is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians. In Greek mythology, newborn Hestia, along with four of her five siblings, was devoured by her father Cronus, who feared being overthrown by one of his offspring. Zeus, the youngest child, escaped with his mother's help, and made his father disgorge all his siblings. Cronus was supplanted by this new generation of deities; and Hestia thus became one of the Olympian gods, the new rulers of the cosmos, alongside her brothers and sisters. In spite of her status, she has little prominence in Greek mythology. Like Athena and Artemis, Hestia elected never to marry and remained an eternal virgin goddess instead, forever tending to the hearth of Olympus. As the goddess of sacrificial fire, Hestia received the first offering at every domestic sacrifice. In the public domain, the hearth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makgeolli
''Makgeolli'' (), sometimes anglicized to makkoli (, ), is a Korean alcoholic drinks, Korean alcoholic drink. It is a milky, off-white, and lightly sparkling rice wine that has a slight viscosity, and tastes slightly sweet, tangy, bitter, and astringent. Chalky sediment gives it a cloudy appearance. As a low proof drink of six to nine percent alcohol by volume, it is often considered a "communal beverage" rather than hard liquor. In Korea, ''makgeolli'' is often unpasteurized, and the wine continues to mature in the bottle. Because of the short shelf life of unpasteurized "draft" ''makgeolli'', many exported ''makgeolli'' undergo pasteurization, which deprives the beverage of complex enzymes and flavor compounds. Recently, various fruits such as strawberries and bananas have been added to makgeolli to create forms with new flavours. Names The name ''makgeolli'' () is a compound (linguistics), compound, consisting of ''mak'' (; in this context "just now") and a deverbal noun deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamuy-huci
Kamuy-huci (カムイフチ, ''Kamui Fuchi'') is the Ainu ''kamuy'' (''goddess'') of the hearth. Her full name is Apemerukoyan-mat Unamerukoyan-mat (''Rising Fire Sparks Woman/ Rising Cinder Sparks Woman''), and she is also known as Iresu Kamuy (''People Teacher''). She is among the most important ''kamuy'' of Ainu mythology, serving as keeper of the gateway between the world of humans and the world of ''kamuy''. Depiction Kamuy-huci is a woman who lives in the hearth. Her position is so important that she never leaves her home. Accordingly, the hearth fire must never be extinguished completely.Ashkenazy, Michael. ''Handbook of Japanese Mythology''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio, 2003. 191-192 She wears six layers of kimono tied with a sash, and another six layers of kimono on top that are left to flutter freely. Mythology There are a few myths of Kamuy-huci's origins. In the most common, she descends from the heavens, accompanied by Kanna Kamuy, the ''kamuy'' of thunder a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |