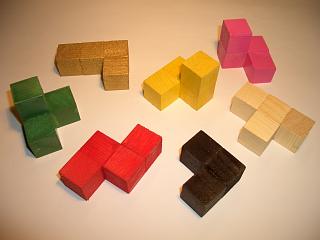|
Jotun Hein
Jotun John Piet Hein (born 19 July 1956) is Professor of Bioinformatics at the Department of Statistics of the University of Oxford and a professorial fellow of University College, Oxford. Hein was previously Director of the Bioinformatics Research Centre at Aarhus University, Denmark. Hein is the fourth son of Piet Hein, the Danish scientist, mathematician, inventor, designer, author, and poet who wrote the famed Grooks poetry collections and invented the Superegg and the Soma cube. When he was 12 years old, Jotun proved the Soma cube's "Basalt Rock" construction impossible, which was published in the puzzle's instruction manual as "Jotun's Proof." Hein's research interests are in molecular evolution, molecular population genetics and bioinformatics. Selected books * Hein, J; Schierup, M. H., and Wiuf, C. ''Gene Genealogies, Variation and Evolution – A Primer in Coalescent Theory''. Oxford University Press Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms ( SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Evolution
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cell (biology), cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, Neutral theory of molecular evolution, neutral evolution vs. natural selection, origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of speciation, evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genome, genomic and phenotype, phenotypic changes. History The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with comparative biochemistry, and the use of "fingerprinting" methods such as immune assays, gel electrophoresis and paper chromatography in the 1950s to explore homologous proteins. The field of molecular evolution came into i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of University College, Oxford
{{disambiguation ...
Fellows may refer to Fellow, in plural form. Fellows or Fellowes may also refer to: Places *Fellows, California, USA *Fellows, Wisconsin, ghost town, USA Other uses *Fellows Auctioneers, established in 1876. *Fellowes, Inc., manufacturer of workspace products *Fellows, a partner in the firm of English canal carriers, Fellows Morton & Clayton *Fellows (surname) See also *North Fellows Historic District, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Wapello County, Iowa *Justice Fellows (other) Justice Fellows may refer to: * Grant Fellows (1865–1929), associate justice of the Michigan Supreme Court * Raymond Fellows (1885–1957), associate justice of the Maine Supreme Judicial Court {{disambiguation, tndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Statisticians
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *'' Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 Births
Events January * January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan. * January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are killed for trespassing by the Huaorani people of Ecuador, shortly after making contact with them. * January 16 – Egyptian leader Gamal Abdel Nasser vows to reconquer Palestine. * January 25– 26 – Finnish troops reoccupy Porkkala, after Soviet troops vacate its military base. Civilians can return February 4. * January 26 – The 1956 Winter Olympics open in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy. February * February 11 – British spies Guy Burgess and Donald Maclean resurface in the Soviet Union, after being missing for 5 years. * February 14– 25 – The 20th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union is held in Moscow. * February 16 – The 1956 World Figure Skating Championships open in Garmisch, West Germany. * February 22 – Elvis P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and population structure. Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics. Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, laboratory, and field work. Population genetic models are used both for statistical inference from DNA sequence data and for proof/disproof of concept. What sets population genetics apart from newer, more phenotypic approaches to modelling evolution, such as evolutionary game theory and adaptive dynamics, is its emphasis on such genetic phenomena as dominance, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soma Cube
The Soma cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on quantum mechanics conducted by Werner Heisenberg. Seven pieces made out of unit cubes must be assembled into a 3×3×3 cube. The pieces can also be used to make a variety of other 3D shapes. The pieces of the Soma cube consist of all possible combinations of three or four unit cubes, joined at their faces, such that at least one inside corner is formed. There is one combination of three cubes that satisfies this condition, and six combinations of four cubes that satisfy this condition, of which two are mirror images of each other (see Chirality). Thus, 3 + (6 × 4) is 27, which is exactly the number of cells in a 3×3×3 cube. The Soma cube was popularized by Martin Gardner in the September 1958 Mathematical Games column in ''Scientific American.'' The book '' Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays'' also contains a detailed analysis of the Soma cube problem. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aarhus University
Aarhus University ( da, Aarhus Universitet, abbreviated AU) is a public research university with its main campus located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Group, the Guild, and Utrecht Network of European universities and is a member of the European University Association. The university was founded in Aarhus, Denmark, in 1928 and comprises five faculties in Arts, Natural Sciences, Technical Sciences, Health, and Business and Social Sciences and has a total of twenty-seven departments. It is home to over thirty internationally recognised research centres, including fifteen centres of excellence funded by the Danish National Research Foundation. The university has been ranked among the top 100 world's best universities. ''Times Higher Education'' ranks Aarhus University in the top 10 of the most beautiful universities in Europe (2018). The university's alumni include Bjarne Stroustrup, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superegg
In geometry, a superegg is a solid of revolution obtained by rotating an elongated superellipse with exponent greater than 2 around its longest axis. It is a special case of superellipsoid. Unlike an elongated ellipsoid, an elongated superegg can stand upright on a flat surface, or on top of another superegg. This is due to its curvature being zero at the tips. The shape was popularized by Danish poet and scientist Piet Hein (1905–1996). Supereggs of various materials, including brass, were sold as novelties or " executive toys" in the 1960s. Mathematical description The superegg is a superellipsoid whose horizontal cross-sections are circles. It is defined by the inequality :\left, \frac\^p + \left, \frac\^p \leq 1 where ''R'' is the horizontal radius at the "equator" (the widest part), and ''h'' is one half of the height. The exponent ''p'' determines the degree of flattening at the tips and equator. Hein's choice was ''p'' = 2.5 (the same one he used for the Sergel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grooks
A grook ( da, gruk) is a form of short aphoristic poem or rhyming aphorism, created by the Danish poet, designer, inventor and scientist Piet Hein, who wrote over 10,000 of them, mostly in Danish. They have been published in Danish in 20 volumes. Each grook has a unique line drawing accompanying the words of the poem and providing additional meaning. Some say that the name "''gruk''" is short for "''grin & suk''" (), but Piet Hein said he felt that the word had come out of thin air. The contemporary "''Hunden Grog''" ("Grog the Dog") stories by fellow cartoonist Storm P. has, in public opinion, been regarded as an inspiration. Piet Hein's ''gruks'' first started to appear in the daily newspaper "''Politiken''" shortly after the Nazi Occupation in April 1940 under the signature Kumbel Kumbell. The poems were meant as a spirit-building, yet slightly coded form of passive resistance. The grooks are multi-faceted and characterized by irony, paradox, brevity, precise use of languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)