|
Josip Vidmar
Josip Vidmar (; October 14, 1895 – April 11, 1992) was a notable Slovenian literary critic, essayist, and politician. From 1944 to 1946 he was speaker of the Slovenian People's Liberation Council (Slovenian Parliament). From 1952 to 1976 was president of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts, and from 1950 to 1964 he was the head of the academy's Institute of Literatures. Life Vidmar was born in Ljubljana, in a progressive middle-class family. Josip had an older brother, Milan Vidmar, a notable engineer, chess player and writer. Their sister Meta Vidmar studied with the famous Mary Wigman in Dresden and upon returning to Ljubljana in 1930 established the first school of modern dance in Slovenia. He completed gymnasium school in Ljubljana and studied at the Czech Technical University in Prague. During the World War I he fought in Austria-Hungarian units on the eastern front but deserted to Russian side. Anti-Yugoslavization writings At the time when in the ex-Austrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Slovenia
The president of Slovenia, officially the president of the Republic of Slovenia (), is the head of state of Slovenia. The office was established on 23 December 1991 when the National Assembly (Slovenia), National Assembly passed a new Constitution of Slovenia, constitution after the separation of Slovenia from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Five individuals have occupied the post of president of the Republic since Slovenia achieved its independence. The incumbent is Nataša Pirc Musar, Slovenia's first female president. The president's official workplace is the Government Building and President's Office, Presidential Palace in Ljubljana. Election and term of office The president is directly elected by universal adult suffrage for a term of five years. Any Slovenian citizen of legal age (18 or more) may run for President, but may only hold office for two terms. The president has no legally guaranteed legal immunity, immunity and may be impeached during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Republic Of Serbia
The Socialist Republic of Serbia ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, separator=" / ", Социјалистичка Република Србија, Socijalistička Republika Srbija), previously known as the People's Republic of Serbia ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, separator=" / ", Народна Република Србија, Narodna Republika Srbija, National Republic of Serbia), commonly abbreviated as Republic of Serbia, SR Serbia or simply Serbia, was one of the six Constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in what is now the modern day states of Serbia and the disputed territory of Kosovo. Its formation was initiated in 1941, and achieved in 1944–1946, when it was established as a federated republic within Yugoslavia. In that form, it lasted until the constitutional reforms from 1990 to 1992, when it was reconstituted, as the Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Republic of Serbia within the Federal Republic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
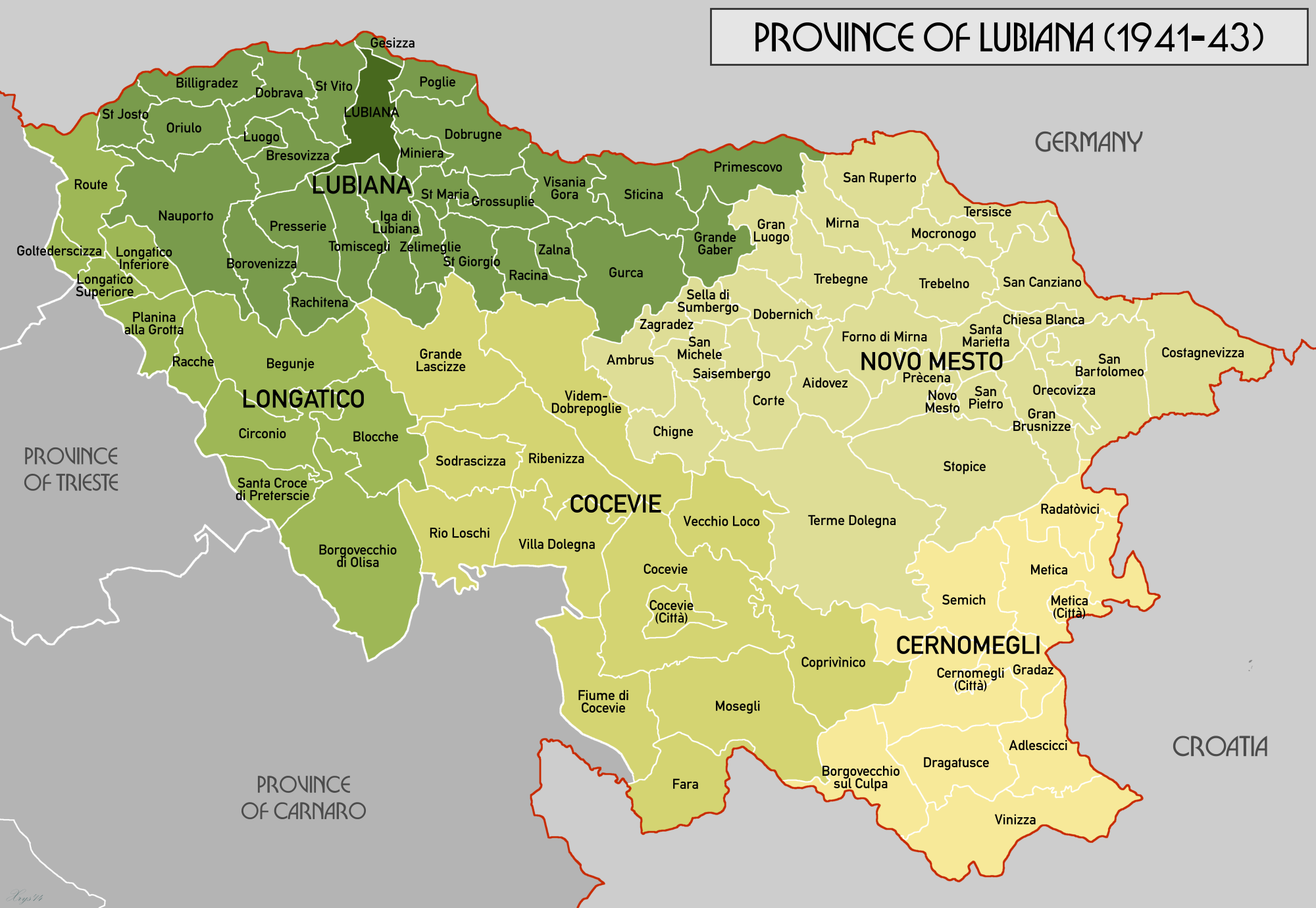
Province Of Ljubljana
The Province of Ljubljana (, , ) was the central-southern area of Slovenia. In 1941, it was annexed by the Kingdom of Italy, and after 1943 occupied by Nazi Germany. Created on May 3, 1941, it was abolished on May 9, 1945, when the Slovene Partisans and partisans from other parts of Yugoslavia liberated it from the Nazi Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral. Its administrative centre was Ljubljana. Background During World War II, the Drava Banovina was in a unique situation. Whereas Greece was trisected, this territory (roughly present-day Slovenia) experienced a further step—absorption and annexation into neighboring Nazi Germany, the Kingdom of Italy, Hungary, and the Independent State of Croatia.Gregor Joseph Kranjc (2013To Walk with the Devil, University of Toronto Press, Scholarly Publishing Division, p. 5 After Yugoslavia was invaded by Axis Powers on 6 April 1941, Germany and Hungary occupied and annexed the northern part of the region. The ethnic German Gottscheer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloquial name as early as 1922 due to its origins. "Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovene language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.) The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I of Yugosla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian language, language. They primarily live in Serbia, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro as well as in North Macedonia, Slovenia, Germany and Austria. They also constitute a significant diaspora with several communities across Europe, the Americas and Oceania. The Serbs share many cultural traits with the rest of the peoples of Southeast Europe. They are predominantly Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox Christians by religion. The Serbian language, Serbian language (a standardized version of Serbo-Croatian) is official in Serbia, co-official in Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is spoken by the plurality in Montenegro. Ethnology The identity of Serbs is rooted in Eastern Orthodoxy and traditions. In the 19th century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascist Italianization
Italianization ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or assimilation. It is also known for a process organized by the Kingdom of Italy to force cultural and ethnic assimilation of the native populations living, primarily, in the former Austro-Hungarian territories that were transferred to Italy after World War I in exchange for Italy having joined the Triple Entente in 1915; this process was mainly conducted during the period of Fascist rule between 1922 and 1943. Regions and populations affected Between 1922 and the beginning of World War II, the affected people were the German-speaking and Ladin-speaking populations of Trentino-Alto Adige, Friulians, and Slovenes and Croats in the Julian March. The program was later extended to areas annexed during World War II, affecting Slovenes in the Province of Ljubljana, and Croats in Gorski Kotar and coastal Dalmatia, Greeks in the Ionian islands and, to a lesser extent, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City of Trieste in the middle. The region has been contested frequently, with parts of it controlled at various times by the Republic of Venice, Austria-Hungary, Italy, and Yugoslavia among others. The Kingdom of Italy annexed most of the area after World War I according to the Treaty of London and later the Treaty of Rapallo. After World War II it was split, with Italy in the west and Yugoslavia in the east. Trieste had strategic importance as Austria-Hungary's primary seaport, and the coast of the Littoral was a resort destination known as the Austrian Riviera. The region was a multi-ethnic one, with Italians, Slovenes, Croats, Germans and Friulians being the main groups. In 1910, it had an area of and a population of 894,287. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Technical University In Prague
Czech Technical University in Prague (CTU) () is one of the largest universities in the Czech Republic with 8 faculties, and is one of the oldest institutes of technology in Central Europe. It is also the oldest non-military technical university in Europe. In the academic year 2020/21, Czech Technical University offered 130 degree programs in Czech and 84 in English. It was considered one of the top 10 universities in emerging Europe and Central Asia in the same year. History It was established as the Institute of Engineering Education in 1707, but as a secondary education (high school) instead of a tertiary university, by Emperor Joseph I as a response to Christian Josef Willenberg's petition addressed to preceding emperor Leopold I. In 1806, the institute of Engineering Education was transformed into Prague Polytechnical Institute (or Prague Polytechnic), i.e. a school independent of the University of Prague. This was a Europe-wide trend in the early 19th century, as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (school)
''Gymnasium'' (and Gymnasium (school)#By country, variations of the word) is a term in various European languages for a secondary school that prepares students for higher education at a university. It is comparable to the US English term ''University-preparatory school, preparatory high school'' or the British term ''grammar school''. Before the 20th century, the gymnasium system was a widespread feature of educational systems throughout many European countries. The word (), from Greek () 'naked' or 'nude', was first used in Ancient Greece, in the sense of a place for both physical and intellectual education of young men. The latter meaning of a place of intellectual education persisted in many European languages (including Albanian language, Albanian, Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Czech language, Czech, Dutch language, Dutch, Estonian language, Estonian, Greek language, Greek, German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, Montene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Dance
Modern dance is a broad genre of western concert dance, concert or theatrical dance which includes dance styles such as ballet, folk, ethnic, religious, and social dancing; and primarily arose out of Europe and the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was considered to have been developed as a rejection of, or rebellion against, classical ballet, and also a way to express social concerns like socioeconomic and cultural factors. In the late 19th century, modern dance artists such as Isadora Duncan, Maud Allan, and Loie Fuller were pioneering new forms and practices in what is now called improvisational or free dance. These dancers disregarded ballet's strict movement vocabulary (the particular, limited set of movements that were considered proper to ballet) and stopped wearing corsets and pointe shoes in the search for greater freedom of movement. Throughout the 20th century, sociopolitical concerns, major historical events, and the development of other art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Wigman
Mary Wigman (born Karoline Sophie Marie Wiegmann; 13 November 1886 – 18 September 1973) was a German dancer and choreographer who pioneered expressionist dance, dance therapy, and movement training without pointe shoes. She is considered one of the most important figures in the history of modern dance. She became one of the most iconic figures of Weimar German culture and her work was hailed for bringing the deepest of existential experiences to the stage. Early life Karoline Sophie Marie Wiegmann was born in Hanover, Province of Hanover in the Kingdom of Prussia. Wiegmann was the daughter of a bicycle dealer. Already as a child, she was called Mary, "because the Hanoverians were once kings of England and the House of Welf pride never quite got over the decline of the Kingdom of Hanover to a Prussian province. Development of expressionist dance, early career Wigman spent her youth in Hanover, England, the Netherlands and Lausanne. Wigman came to dance comparatively late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |