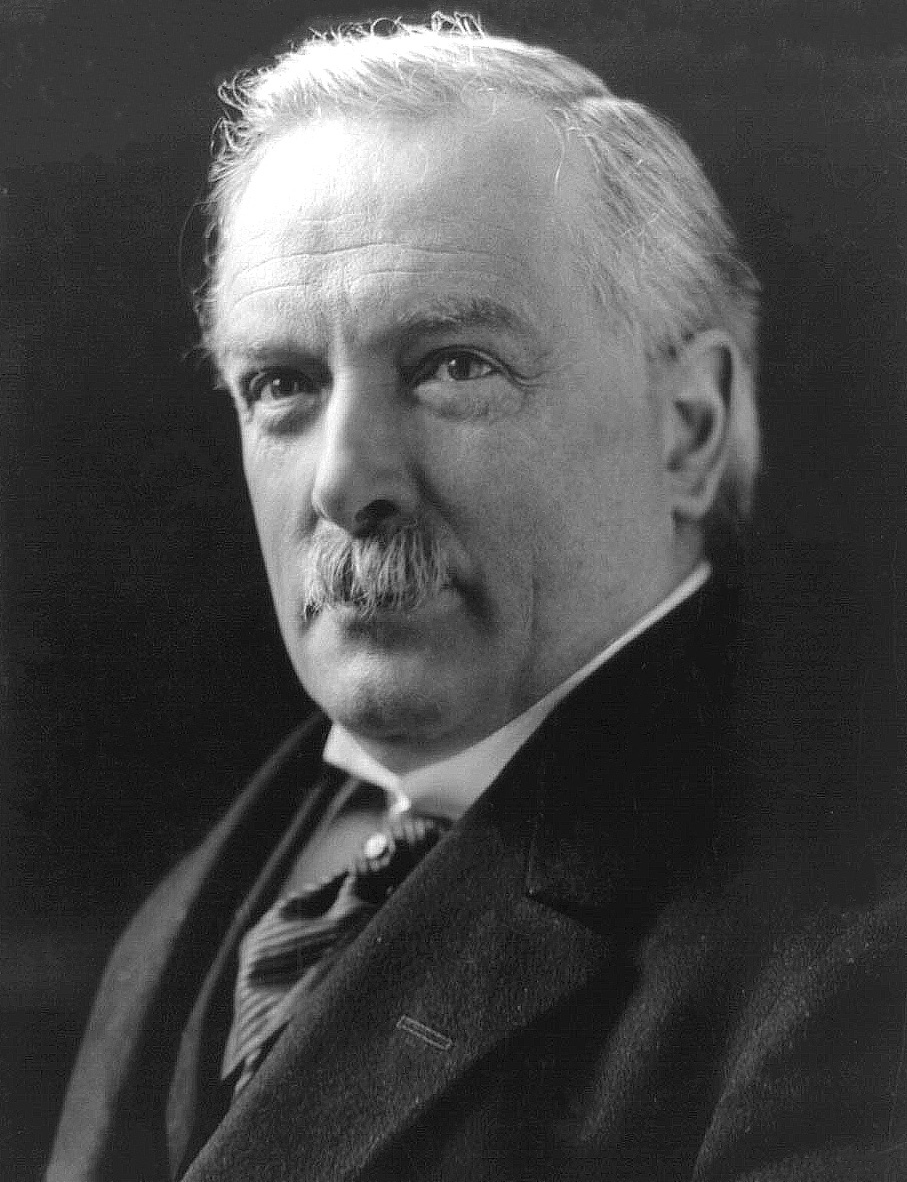|
Joseph McGarrity
Joseph McGarrity (28 March 1874 – 4 September 1940) was an Irish-American political activist best known for his leadership in Clan na Gael in America and his support of Irish Republicanism back in Ireland. Early years McGarrity was born in Carrickmore, County Tyrone, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1874. His family grew up in poverty, motivating his need to immigrate later in life. He grew hearing his father discussing Irish politics, including topics such as the Fenians, the Irish Parliamentary Party, and Irish Home Rule. By the time he was an adult, he had developed a keen interest in politics himself. He immigrated to the United States in 1892 at the age of 18. He is reputed to have walked to Dublin before boarding a cattle boat to Liverpool disguised as a drover, and then sailing to America using a ticket belonging to someone else. He settled in 4900 Wynfield Ave West Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and became successful in the liquor business; however, his bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrickmore
Carrickmore () is a small town in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland. It is situated in the historic barony of Omagh East, the civil parish of Termonmaguirk and the Roman Catholic Parish of Termonmaguirc between Cookstown, Dungannon and Omagh. It had a population of 612 as of the 2001 census. In the 2011 census, 2,330 people lived in the Termon Ward, which covers the Carrickmore and Creggan areas. History The current settlement can trace its origins back thousands of years to the pre-Christian era. A wide range of historic monuments can be found in the Carrickmore area, including cairns, stone circles, standing stones and raths. It lies in the centre of the county on a raised site colloquially called "Carmen". An alias name for Carrickmore village is Termon Rock, Termonn being the first element of the parish name Termonmaguirk (Ir. Tearmann Mhig Oirc ‘McGurk’s sanctuary’) and rock referring to the rocky hill on which the village is situated. The McGurks were the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annie Larsen
The ''Annie Larsen'' was a three-masted schooner that was involved in arms shipment in the so-called " Hindu German Conspiracy" during World War I. ''Annie Larsen'' was built by the Hall Brothers in 1881. She was owned by James Tufts, of San Francisco, and later by Olson & Mahony and sailed in the coastwise lumber trade. In 1915, she was chartered to a shipbroker. The ship came into the spotlight when it was seized on 25 June 1915 by US customs officials at Grays Harbor and found to be carrying large quantities of small arms and ammunitions in violation of the Neutrality Acts. The arms were meant to be transferred to the SS ''Maverick'' at a rendezvous off the coast of Mexico. The Annie Larsen affair was one of the major setbacks to the pro-Indian independence Ghadar Party, and was one of the major charges in the trial, one of the largest and most expensive in American legal history. In 1918, ''Annie Larsen'' stranded on Malden Island Malden Island, sometimes called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fianna Fáil
Fianna Fáil ( ; ; meaning "Soldiers of Destiny" or "Warriors of Fál"), officially Fianna Fáil – The Republican Party (), is a centre to centre-right political party in Ireland. Founded as a republican party in 1926 by Éamon de Valera and his supporters after they split from Sinn Féin in order to take seats in the Oireachtas, which Sinn Féin refused to recognise, since 1927 Fianna Fáil has been one of Ireland's two major parties, along with Fine Gael since 1933; both are seen as centre-right parties, to the right of the Labour Party and Sinn Féin. The party dominated Irish political life for most of the 20th century, and, since its foundation, either it or Fine Gael has led every government. Between 1932 and 2011, it was the largest party in Dáil Éireann, but latterly with a decline in its vote share; from 1989 onwards, its periods of government were in coalition with parties of either the left or the right. Fianna Fáil's vote collapsed in the 2011 ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Boland
Harry Boland (27 April 1887 – 1 August 1922) was an Irish republican politician who served as President of the Irish Republican Brotherhood from 1919 to 1920. He served as a Teachta Dála (TD) from 1918 to 1922. He was elected at the 1918 general election as the MP for Roscommon South, but as with other Sinn Féin candidates, he did not take seat in the British House of Commons, serving instead as a TD in the First Dáil. At the 1921 general election, Boland was elected to the second Dáil as one of the TDs for the Mayo South–Roscommon South. He was re-elected in 1922 as an Anti-Treaty candidate, but was killed two months later in the Irish Civil War. Early life Boland was born at 6 Dalymount Terrace, Phibsborough, Dublin, on 27 April 1887, the son of Irish Republican Brotherhood member James Boland and Kate Woods. He was active in GAA circles in early life, and refereed the 1914 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final. He joined the IRB at the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the forces of the Irish Republic – the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army (IRA) – and The Crown, British Crown forces. The Free State was established as a dominion of the British Empire. It comprised 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland. Northern Ireland, which was made up of the remaining six counties, exercised its right under the Treaty to opt out of the new state. The Irish Free State government consisted of the Governor-General of the Irish Free State, governor-general – the viceregal representative of the King – and the Executive Council of the Irish Free State, Executive Council (cabinet), which replaced both the revolutionary Government of the 2nd Dáil, Dáil Governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Treaty IRA
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty (), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the government of the Irish Republic that concluded the Irish War of Independence. It provided for the establishment of the Irish Free State within a year as a self-governing dominion within the "community of nations known as the British Empire", a status "the same as that of the Dominion of Canada". It also provided Northern Ireland, which had been created by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, an option to opt out of the Irish Free State (Article 12), which was exercised by the Parliament of Northern Ireland. The agreement was signed in London on 6 December 1921, by representatives of the British government (which included Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who was head of the British delegates, and Winston Churchill, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
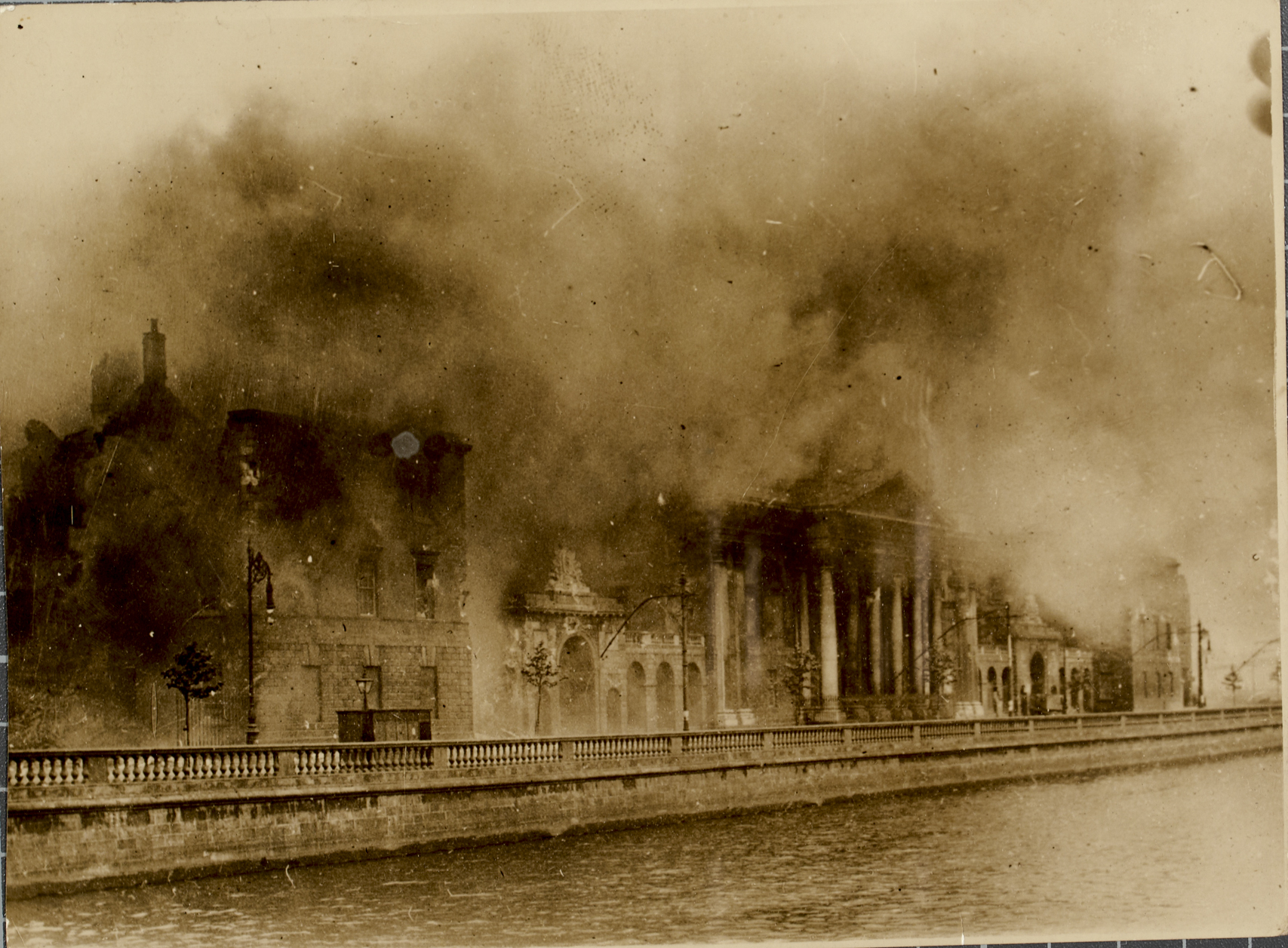
Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War (; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between the Provisional Government of Ireland (1922), Provisional Government of Ireland and the Irish Republican Army (1922–1969), Anti-Treaty IRA over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The Provisional Government (that became the Free State in December 1922) supported the terms of the treaty, while the Anglo-Irish Treaty Dáil vote#Anti-Treaty, anti-Treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic proclaimed during the Easter Rising of 1916. Many of the combatants had fought together against the British in the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army during the War of Independence and had divided after that conflict ended and the Irish Republican Army and the Anglo-Irish Treaty, treaty neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 Irish General Election
The 1922 Irish general election took place in Southern Ireland (1921–1922), Southern Ireland on Friday, 16 June. The election was separately called by a resolution of Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), Dáil Éireann on 19 May and by an order of the Provisional Government of Ireland (1922), Provisional Government on 27 May. The body elected was thus both the Third Dáil and provisional parliament replacing the parliament of Southern Ireland, under the provisions of the 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty to elect a constituent assembly paving the way for the formal establishment of the Irish Free State. From 6 December 1922, it continued as the Dáil Éireann (Irish Free State), Dáil Éireann of the Irish Free State. The election was held under the electoral system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote. It was the first contested general election held in the jurisdiction using the STV system. The election was held in the 128 seats using the Government of Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Collins (Irish Leader)
Michael Collins (; 16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence. During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty (), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the government of the Irish Republic that concluded the Irish War of Independence. It provided for the establishment of the Irish Free State within a year as a self-governing dominion within the "community of nations known as the British Empire", a status "the same as that of the Dominion of Canada". It also provided Northern Ireland, which had been created by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, an option to opt out of the Irish Free State (Article 12), which was exercised by the Parliament of Northern Ireland. The agreement was signed in London on 6 December 1921, by representatives of the British government (which included Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who was head of the British delegates, and Winston Churchill, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel F
Daniel commonly refers to: * Daniel (given name), a masculine given name and a surname * List of people named Daniel * List of people with surname Daniel * Daniel (biblical figure) * Book of Daniel, a biblical apocalypse, "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel" Daniel may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Literature * ''Daniel'' (Old English poem), an adaptation of the Book of Daniel * ''Daniel'', a 2006 novel by Richard Adams * ''Daniel'' (Mankell novel), 2007 Music * "Daniel" (Bat for Lashes song) (2009) * "Daniel" (Elton John song) (1973) * "Daniel", a song from '' Beautiful Creature'' by Juliana Hatfield * ''Daniel'' (album), a 2024 album by Real Estate Other arts and entertainment * ''Daniel'' (1983 film), by Sidney Lumet * ''Daniel'' (2019 film), a Danish film * Daniel (comics), a character in the ''Endless'' series Businesses * Daniel (department store), in the United Kingdom * H & R Daniel, a producer of English porcelain between 1827 and 184 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Devoy
John Devoy (, ; 3 September 1842 – 29 September 1928) was an Irish republican Rebellion, rebel and journalist who owned and edited ''The Gaelic American'', a New York weekly newspaper, from 1903 to 1928. Devoy dedicated over 60 years of his life to the cause of Irish nationalism, Irish independence and was one of the few people to have played a role in the Fenian Rising of 1867, the Easter Rising of 1916 and the Irish War of Independence, Irish War of Independence of 1919–1921. Early life Devoy was born in Kill, County Kildare, on 3 September 1842 the son of a farmer and labourer named William Devoy. After the Great Famine (Ireland), Irish famine of 1845-52, the family moved to Dublin where Devoy's mother obtained a job at Watkins' brewery. Devoy attended night school at the Catholic University before joining the Fenians. In 1861 he travelled to France with an introduction from Timothy Daniel Sullivan to John Mitchel. Devoy joined the French Foreign Legion and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |