|
Joseph George Megler
Joseph George Megler (March 10, 1838 – September 10, 1915), generally known as J.G. Megler, was a German-American salmon cannery owner and politician in Washington. He was a member of the Washington House of Representatives for the first legislature in 1889 and five terms thereafter. He was also a member of the Washington State Senate for two terms. During his political career he held the positions of Speaker of the House and President pro tempore of the Senate. He has been described as the father of the salmon hatcheries in Washington. Early life J.G. Megler was born in Berkach, Thuringen, Germany, in 1838, the first child of a schoolteacher.Register of Jewish births, marriages, and deaths for Berkach, Thüringen, Sachsen-Meiningen, Germany, 1831-1875 Left an orphan by the age of 9, he emigrated to the U.S. along with his younger brother and two sisters to join an uncle in New York. Some years later they relocated to Syracuse, where he studied the trade of tin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkach
Berkach is a former municipality in the district Schmalkalden-Meiningen, in Thuringia, Germany. From December 1, 2007, it is part of Grabfeld The Grabfeld is a region in Germany, on the border between Bavaria and Thuringia. It is situated southeast of the Rhön Mountains. Its highest elevation is 679 metres high in the little Gleichberge mountain range. The Grabfeld gave its name to t .... Former municipalities in Thuringia Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen {{SchmalkaldenMeiningen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinsmithing
A tinsmith is a person who makes and repairs things made of tin or other light metals. The profession may sometimes also be known as a tinner, tinker, tinman, or tinplate worker; whitesmith may also refer to this profession, though the same word may also refer to an unrelated specialty of iron-smithing. By extension it can also refer to the person who deals in tinware, or tin plate. Tinsmith was a common occupation in pre-industrial times. Unlike blacksmiths (who work mostly with hot metals), tinsmiths do the majority of their work on cold metal (although they might use a hearth to heat and help shape their raw materials). Tinsmiths fabricate items such as water pitchers, forks, spoons, and candle holders. Training of tinsmiths The tinsmith learned his trade, like many other artisans, by serving an apprenticeship of 4 to 6 years with a master tinsmith. Apprenticeships were considered "indentures" and an apprentice would start first with simply cleaning the shop, polishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brookfield, Washington
Brookfield was a salmon-canning and fishing town located on the Columbia River in Wahkiakum County, Washington, United States, from 1873 to 1957. It was the home of the J.G. Megler Company. History Brookfield was established in 1873, when J.G.Megler built a salmon cannery in the sheltered bay on the Washington side of the Columbia River between Jim Crow Point and the mouth of Jim Crow Creek (then part of Pacific County, later part of Wahkiakum County). He named the cannery "Brookfield Fisheries", after his wife Nellie E. Megler's birthplace of North Brookfield, Massachusetts. The Brookfield post office opened on February 24, 1874 with Joseph G. Megler as postmaster. The majority of the residents were workers at the cannery and fishermen for the cannery. J.G. Megler & Co imported Croatian fishermen from Komiza to fish for them, and these families formed many of the Brookfield residents. The company also hired a Chinese canning crew seasonally to work at the cannery. Arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinook, Washington
Chinook is a census-designated place (CDP) in Pacific County, Washington, United States. The population was 457 at the 2000 census and increased to 466 at the 2010 census. History Chinook was the site of the first court in Pacific County in 1853, as well as the county's first salmon cannery in 1870. Chinook was once a wealthy town based on the salmon harvest. There was no road connection to Ilwaco until 1891, when the bridge was completed across the Chinook River.Hobbs and Lucero, at 10 Later, the Ilwaco Railway and Navigation Company built a narrow gauge railroad from Megler to Ilwaco, passing down the main street of Chinook. The railroad was dismantled in 1931. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 1.0 square miles (2.6 km2), all of it land. The town is located on Baker Bay, on the north side of the Columbia River just behind Cape Disappointment and the mouth of the Columbia. Demographics As of the census of 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific. The Columbia has the 36th greatest discharge of any river in the world. The Columbia and its tributaries have been central to the region's culture and economy for thousands of years. They have been used for transportat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
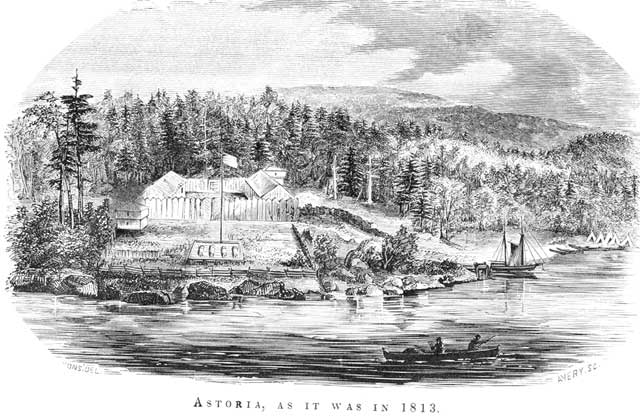
Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is a port city and the seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1811, Astoria is the oldest city in the state and was the first permanent American settlement west of the Rocky Mountains. The county is the northwest corner of Oregon, and Astoria is located on the south shore of the Columbia River, where the river flows into the Pacific Ocean. The city is named for John Jacob Astor, an investor and entrepreneur from New York City, whose American Fur Company founded Fort Astoria at the site and established a monopoly in the fur trade in the early 19th century. Astoria was incorporated by the Oregon Legislative Assembly on October 20, 1876. The city is served by the deepwater Port of Astoria. Transportation includes the Astoria Regional Airport. U.S. Route 30 and U.S. Route 101 are the main highways, and the Astoria–Megler Bridge connects to neighboring Washington across the river. The population was 10,181 at the 2020 census. History Prehist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorable Discharge
A military discharge is given when a member of the armed forces is released from their obligation to serve. Each country's military has different types of discharge. They are generally based on whether the persons completed their training and then fully and satisfactorily completed their term of service. Other types of discharge are based on factors such as the quality of their service, whether their service had to be ended prematurely due to humanitarian or medical reasons, whether they had been found to have drug or alcohol dependency issues and whether they were complying with treatment and counseling, and whether they had demerits or punishments for infractions or were convicted of any crimes. These factors affect whether they will be asked or allowed to re-enlist and whether they qualify for benefits after their discharge. United Kingdom There are several reasons why someone may be discharged from the military, including expiration of enlistment, disability, dependency and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensign (rank)
Ensign (; Late Middle English, from Old French (), from Latin (plural)) is a junior rank of a commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries, normally in the infantry or navy. As the junior officer in an infantry regiment was traditionally the carrier of the ensign flag, the rank acquired the name. This rank has generally been replaced in army ranks by second lieutenant. Ensigns were generally the lowest-ranking commissioned officer, except where the rank of subaltern existed. In contrast, the Arab rank of ensign, لواء, '' liwa''', derives from the command of units with an ensign, not the carrier of such a unit's ensign, and is today the equivalent of a major general. In Thomas Venn's 1672 ''Military and Maritime Discipline in Three Books'', the duties of ensigns are to include not only carrying the color but assisting the captain and lieutenant of a company and in their absence, have their authority. "Ensign" is ''enseigne'' in French, and '' chorąży'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
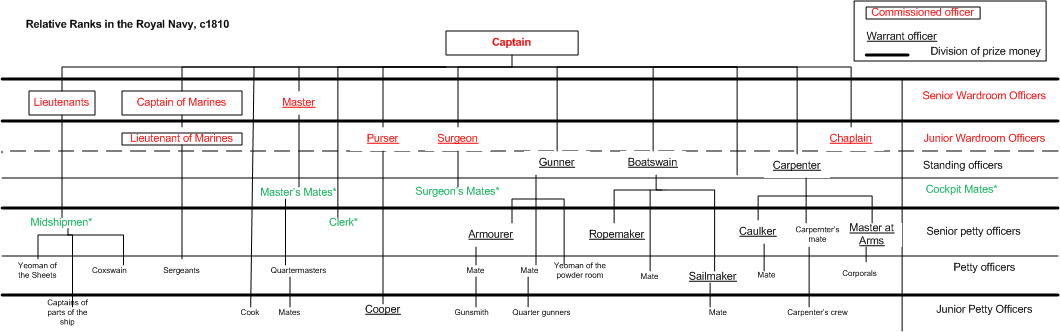
Master's Mate
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the Royal Navy, United States Navy and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer who assisted the master. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of Sub-Lieutenant in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers. Royal Navy Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted the master but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a superior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a first rate, three on a third rate, and two on most frigates. Duties Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected from the ranks of the quartermasters, who they supervised, or from the ranks of midshipmen who wanted more respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
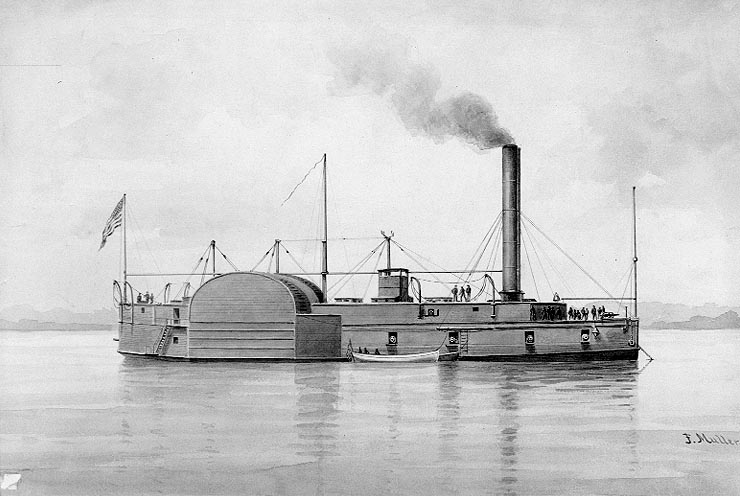
USS Lexington (1861)
The third USS ''Lexington'' was a timberclad gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. Purchase and conversion ''Lexington'' was built as a sidewheel steamer at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, in 1861 and was purchased by the War Department and converted into a gunboat at Cincinnati, Ohio, under the direction of Commander John Rodgers. The gunboat, operated by the navy, joined the army's Western Flotilla at Cairo, Illinois, 12 August 1861. On 22 August, she seized steamer ''W. B. Terry'' at Paducah, Kentucky, and on 4 September, with , she engaged Confederate gunboat ''Jackson'' and southern shore batteries at Hickman and Columbus, Kentucky. On 6 September, the two gunboats spearheaded General Ulysses S. Grant's drive to seize strategic Paducah and Smithland, Kentucky, at the mouths of the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers. In his first use of strength afloat, Grant countered a Confederate move into the state, helping preserve Kentucky for the Union and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paymaster
A paymaster is someone appointed by a group of buyers, sellers, investors or lenders to receive, hold, and dispense funds, commissions, fees, salaries (remuneration) or other trade, loan, or sales proceeds within the private sector or public sector. Specific titles within the British government are Paymaster of the Forces, Paymaster-General and Paymaster of Pensions. Purpose The primary purpose of a paymaster is to receive fees in escrow by buyers in a large transaction, and disburse to the sellers and brokers on the transaction. A paymaster is usually, but not required to be, a lawyer (also known as a 'lawyer paymaster'). When dealing with commission payments on contracts dealing with large amounts of money (such as Oil, Gas, Steel, Iron, Gold, MTN's, VG's, T-Strips, and other instruments), most banks in the United States are very wary of handling such large amounts of money. In addition, most buyers and sellers of such transactions want to place the money with a neutral thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |