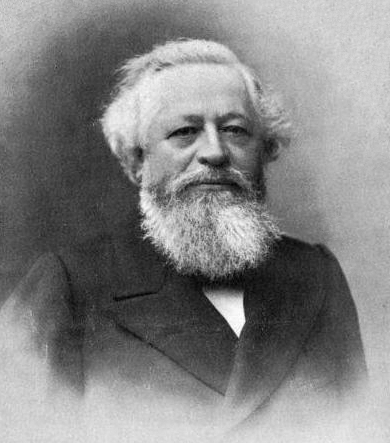|
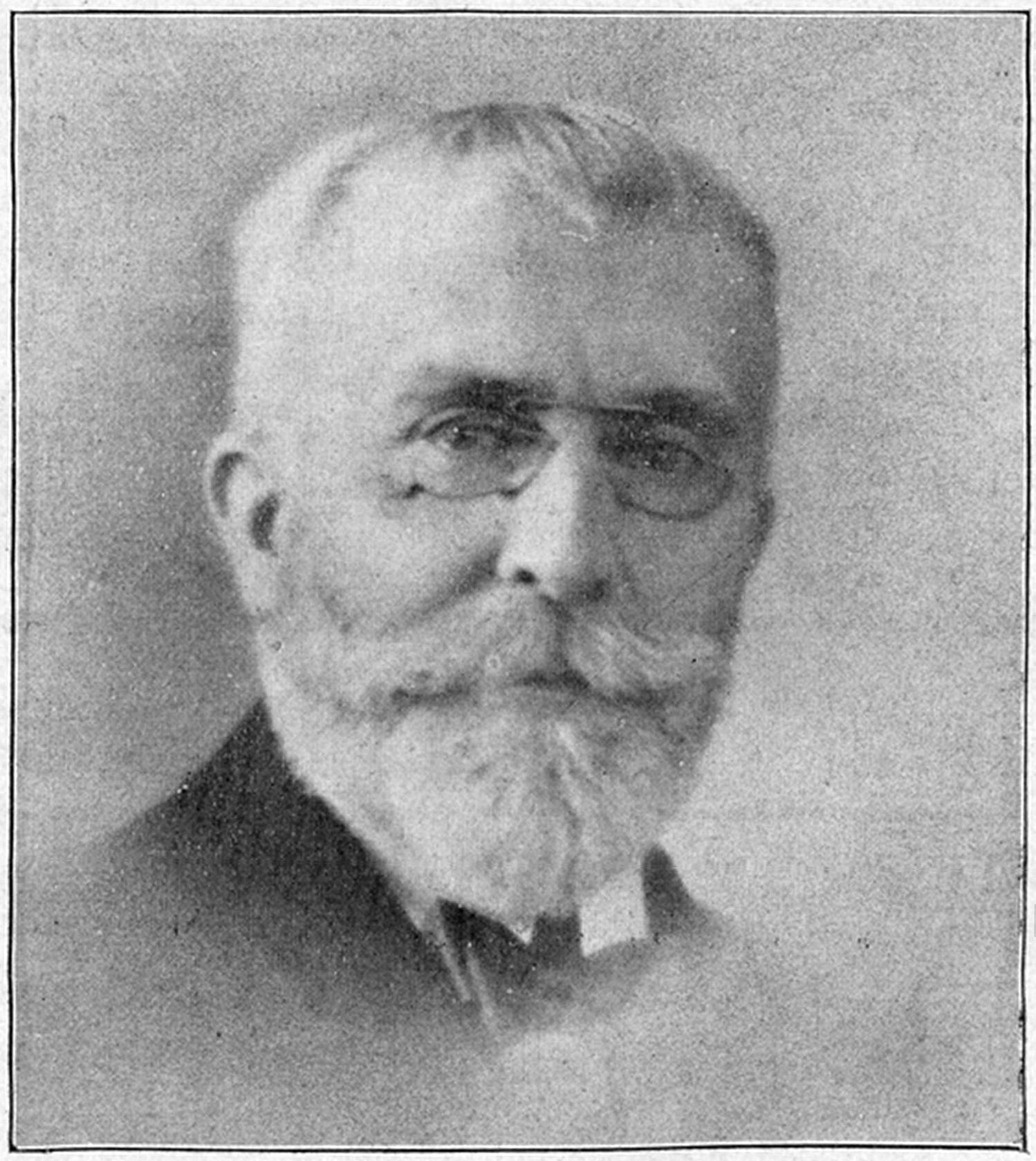
Joseph Boulnois
Joseph Boulnois (28 January 1884 – 20 October 1918) was a French organist and composer. Biography Boulnois attended the Conservatoire de Paris, where he studied counterpoint with Georges Caussade and organ with Louis Vierne. In 1906, he married the pianist Jane Chevalier, and they had a son the following year, Michel Boulnois, who also became a composer and organist. In 1908, he was appointed to the organ of the , in the 3rd arrondissement of Paris. He stayed there a short time and was appointed to the organ of the in the 9th arrondissement. In 1909, he was singing conductor at the Opéra-Comique. He remained very active as a soloist, notably as co-founder with Marc de Ranse, of the Concerts spirituels de Saint-Louis d'Antin. He also played in the Opéra-Comique and performed in the church in the 14th arrondissement. After the beginning of the First World War, Boulnois was mobilised at the Février Hospital of Châlons-sur-Marne, where he was a nurse from 1 January 1915. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistice Of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices had been agreed with Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. It was concluded after the German government sent a message to American president Woodrow Wilson to negotiate terms on the basis of a recent speech of his and the earlier declared "Fourteen Points", which later became the basis of the German surrender at the Paris Peace Conference, which took place the following year. Also known as the Armistice of Compiègne (french: Armistice de Compiègne, german: Waffenstillstand von Compiègne) from the place where it was officially signed at 5:45 a.m. by the Allied Supreme Commander, French Marshal Ferdinand Foch, it came into force at 11:00 a.m. Central European Time (CET) on 11 November 1918 and marked a vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théodore De Banville
Théodore Faullain de Banville (14 March 1823 – 13 March 1891) was a French poet and writer. His work was influential on the Symbolist movement in French literature in the late 19th century. Biography Banville was born in Moulins in Allier, Auvergne, the son of a captain in the French navy. His boyhood, by his own account, was cheerlessly passed at a ''lycée'' in Paris; he was not harshly treated, but took no part in the amusements of his companions. On leaving school with but slender means of support, he devoted himself to letters, and in 1842 published his first volume of verse (''Les Cariatides''), which was followed by ''Les Stalactites'' in 1846. The poems encountered some adverse criticism, but secured for their author the approbation and friendship of Alfred de Vigny and Jules Janin. From then on, Banville's life was steadily devoted to literary production and criticism. He printed other volumes of verse, among which the ''Odes funambulesques'' (1857) received unstint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marceline Desbordes-Valmore
Marceline Desbordes-Valmore (20 June 1786 – 23 July 1859) was a French poet and novelist. She was born in Douai. Following the French Revolution, her father's business was ruined, and she traveled with her mother to Guadeloupe in search of financial help from a distant relative. Marceline's mother died of yellow fever there, and the young girl somehow made her way back to France. At age 16, back in Douai, she began a career on stage. In 1817 she married her husband, the "second-rate" actor Prosper Lanchantin-Valmore. She published ''Élégies et Romances'', her first poetic work, in 1819. In 1821 she published the narrative work ''Veillées des Antilles''. It includes the novella ''Sarah'', a contribution to the genre of slave stories in France. Marceline appeared as an actress and singer in Douai, Rouen, the Opéra-Comique in Paris, and the Théâtre de la Monnaie in Brussels, where she notably played Rosine in Beaumarchais's '' Le Barbier de Séville''. She retired from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Rollinat
Maurice Rollinat (December 29, 1846 in Châteauroux, Indre – October 26, 1903 in Ivry-sur-Seine) was a French poet and musician. Early works His father represented Indre in the National Assembly of 1848, and was a friend of George Sand, whose influence is very marked in young Rollinat's first volume, ''Dans les brandes'' (1877), and to whom it was dedicated. Brief fame After its publication, he abandoned realism and worked in a very different manner. He joined a literary circle that called themselves '' Les Hydropathes'', founded by Émile Goudeau, an anti-clerical group with ties to the decadent literary movement. Under their influence wrote the poems that made his reputation. In ''Les Névroses'', with the sub-title ''Les Âmes, Les Luxures, Les Refuges, Les Spectres, Les Ténèbres'', he showed himself as a disciple of Charles Baudelaire. He constantly returns in these poems to the physical horrors of death, and is obsessed by unpleasant images. Less outre in sentime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gérard Hekking
Gérard Hekking (24 August 1879 – 5 June 1942) was a French cellist. Born in Nancy, he served as first cellist of the Concertgebouw Orchestra from 1903 until 1914. In 1912 Alphons Diepenbrock composed his Berceuse (''Le Seigneur a dit à son enfant'') for him and his wife, a soprano. Among the works premiered by Hekking were Fauré's First and Second Cello Sonatas, in 1917 and 1921 respectively. Hekking composed some works, including ''Villageoise, Joujou mécanique, Danse pour les Sakharoff'' and ''Danse campagnarde'', all for cello and piano. From 1927 until his death Hekking taught cello at the Paris Conservatoire. Among his students were Pierre Fournier, Maurice Gendron and Paul Tortelier. ''Grove Music Online'', Oxford University Press, retrieved 2 March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Mignan
Édouard Charles Octave Mignan (17 March 1884 - 17 September 1969) was a French organist and composer. He was born in Orléans and 14 years old he became the organist of église Saint Paterne. He studied organ in Paris with Alexandre Guilmant and Louis Vierne and won the Grand Prix de Rome in 1912. He was organist at Saint-Thomas-d'Aquin from 1917 to 1935. He succeeded Henri Dallier as organist of la Madeleine in 1935 and held that post until 1962. He died in Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ... at the age of 85. References 1884 births 1969 deaths Musicians from Orléans French classical organists French male organists Prix de Rome for composition 20th-century French male musicians Male classical organists {{organist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Vidal
Paul Antonin Vidal (16 June 1863 – 9 April 1931) was a French composer, conductor and music teacher mainly active in Paris.Charlton D. Paul Vidal. In: ''The New Grove Dictionary of Opera.'' Macmillan, London and New York, 1997. Life and career Paul Vidal was born in Toulouse, and studied at the conservatoires there and in Paris, under Jules Massenet at the latter. He won the Prix de Rome in 1883, one year before Claude Debussy. On 8 January 1886, in Rome, Vidal and Debussy performed Franz Liszt's '' Faust Symphony'' at two pianos for Liszt himself, an after-dinner performance that Liszt apparently slept through. The following day they played Emmanuel Chabrier's ''Trois valses romantiques'' for Liszt. Vidal conducted at the Opéra National de Paris where he made his first appearance directing '' Gwendoline'' in 1894 (he had coached the singers for the Paris premiere in 1893), and later conducted the first performance of ''Ariane'' and the Paris premieres of ''Roma'' by Massene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accompaniment
Accompaniment is the musical part which provides the rhythmic and/or harmonic support for the melody or main themes of a song or instrumental piece. There are many different styles and types of accompaniment in different genres and styles of music. In homophonic music, the main accompaniment approach used in popular music, a clear vocal melody is supported by subordinate chords. In popular music and traditional music, the accompaniment parts typically provide the "beat" for the music and outline the chord progression of the song or instrumental piece. The accompaniment for a vocal melody or instrumental solo can be played by a single musician playing an instrument such as piano, pipe organ, or guitar. While any instrument can in theory be used as an accompaniment instrument, keyboard and guitar-family instruments tend to be used if there is only a single instrument, as these instruments can play chords and basslines simultaneously (chords and a bassline are easier to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lenepveu
Charles-Ferdinand Lenepveu (4 October 1840 – 16 August 1910), was a French composer and teacher. Destined for a career as a lawyer, he defied his family and followed a musical career. He studied at the Paris Conservatoire, and won France's top musical award, the Prix de Rome in 1867. Much of Lenepveu's career was as a professor at the Conservatoire from 1880. He was known as a strict conservative, hostile to musical innovation, as was much of the French musical Establishment of the time. He was expected to succeed Théodore Dubois as director of the Conservatoire in 1905, but his chances evaporated when he was implicated in an attempt to rig the results of that year's Prix de Rome in favour of his own pupils. Life and career Early years Lenepveu was born in Rouen (Seine-Maritime), the son of Charles-François Lenepveu, a prominent lawyer, and his wife Marie-Françoise-Armande, ''née'' Petit. The young Lenepveu received a traditional education in his home town, while at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fugue
In music, a fugue () is a contrapuntal compositional technique in two or more voices, built on a subject (a musical theme) that is introduced at the beginning in imitation (repetition at different pitches) and which recurs frequently in the course of the composition. It is not to be confused with a '' fuguing tune'', which is a style of song popularized by and mostly limited to early American (i.e. shape note or "Sacred Harp") music and West Gallery music. A fugue usually has three main sections: an exposition, a development and a final entry that contains the return of the subject in the fugue's tonic key. Some fugues have a recapitulation. In the Middle Ages, the term was widely used to denote any works in canonic style; by the Renaissance, it had come to denote specifically imitative works. Since the 17th century, the term ''fugue'' has described what is commonly regarded as the most fully developed procedure of imitative counterpoint. Most fugues open with a short m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre Guilmant
Félix-Alexandre Guilmant (; 12 March 1837 – 29 March 1911) was a French organist and composer. He was the organist of La Trinité from 1871 until 1901. A noted pedagogue, performer, and improviser, Guilmant helped found the Schola Cantorum de Paris. He was appointed as Professor of Organ at the Paris Conservatoire in 1896. Biography Guilmant was born in Meudon. A student first of his father Jean-Baptiste and later of the Belgian master Jacques-Nicolas Lemmens, he became an organist and teacher in his place of birth. In 1871 he was appointed to play the organ regularly at la Trinité church in Paris, and this position, ''organiste titulaire'', was one he held for 30 years.Ochse, Orpha Caroline (1994), ''Organists and Organ Playing in Nineteenth-Century France and Belgium'', Indiana University Press, pp. 195–96, Guilmant was known for his improvisations, both in the concert and church setting. His inspiration came from gregorian chants, and he was greatly noted amongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)