|
Joseachal
Joseachal was a Quinault man who lived in the early 19th century. Notably he was the sole survivor of the '' Tonquin'', a trading vessel owned by the Pacific Fur Company (PFC) that was destroyed near Vancouver Island. He was hired to act an interpreter for the vessel in negotiations with various Nuu-chah-nulth peoples. Enraged at the prices that the Tla-o-qui-aht insisted upon, captain Jonathan Thorn struck an elder with a pelt. After purchasing PFC blades, the Tla-o-qui-aht attacked and killed the crew. Only Joseachal survived to reach Fort Astoria to inform the PFC officers of the ''Tonquin's'' destruction. Battle of Woody Point Near Destruction Island he was recruited by Thorn to act as an interpreter. He had a sister married to a Tla-o-qui-aht man, a factor that has been attributed to his later survival on Vancouver Island. While at Clayoquot Sound in June 1811, the ''Tonquin'' hosted members of the neighboring Tla-o-qui-aht nation. They boarded the ship in large numbers to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonquin (1807)
''Tonquin'' was a 290-ton American merchant ship initially operated by Fanning & Coles and later by the Pacific Fur Company (PFC), a subsidiary of the American Fur Company (AFC). Its first commander was Edmund Fanning, who sailed to the Qing Empire for valuable Chinese trade goods in 1807. The vessel was outfitted for another journey to China and then was sold to German-American entrepreneur John Jacob Astor. Included within his intricate plans to assume control over portions of the lucrative North American fur trade, the ship was intended to establish and supply trading outposts on the Pacific Northwest coast. Valuable animal furs purchased and trapped in the region would then be shipped to China, where consumer demand was high for particular pelts. ''Tonquin'' left New York City for the Columbia River in late 1810. From there the vessel sailed across the Atlantic Ocean until reaching the Falkland Islands in December. Captain Jonathan Thorn marooned eight PFC employees there, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
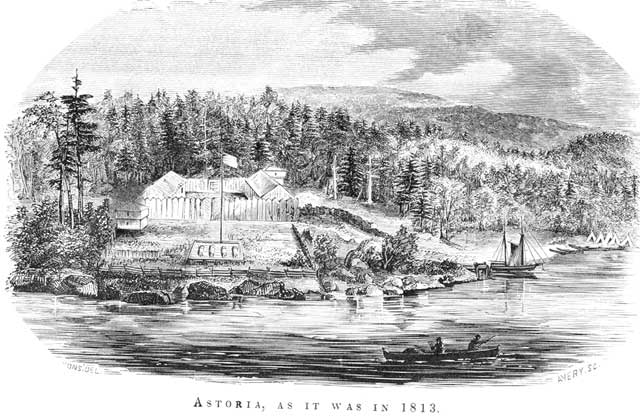
Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the '' Tonquin'', while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America. The inhabitants of the fort differed greatly in background and position, and were structured into a corporate hierarchy. The fur trading partners of the company were at the top, with clerks, craftsmen, hunters, and laborers in descending order. Nationalities included Americans, Scots, French Canadian voyageurs, Native Hawaiian Kanakas, and various indigenous North Americans, including Iroquois and others from Eastern Canada. They found life quite monotonous, with the fish and vegetable diet boring. Venereal diseases were pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Thorn
Jonathan Thorn (8 January 1779 – 15 June 1811) was a career officer of the United States Navy in the early 19th century. Early life and Naval career Born on 8 January 1779 at Schenectady, New York, during the Revolutionary War, Thorn was the eldest of fifteen children of Samuel Thorn and Helena Van Slyck Thorn. He was appointed a midshipman at age 21 on 28 April 1800. His brother Robert Livingston also served in the U.S. Navy as a surgeon on the frigate during the War of 1812. His other brother, Herman, was purser on the USS Wasp and the USS Peacock. Jonathon Thorn served in the Navy during the Tripolitan War, and volunteered to take part in the hazardous expedition to destroy the captured frigate ''Philadelphia'', which was moored beneath the guns of the defended Tripoli harbor. On 16 February 1804, Lieutenant Stephen Decatur led a party of these volunteers in the ketch ''Intrepid'' into Tripoli and burned the American ship so it could not be used by the enemy. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clayoquot Sound
, image = Clayoquot Sound - Near Tofino - Vancouver Island BC - Canada - 08.jpg , image_size = 260px , alt = , caption = , image_bathymetry = Vancouver clayoquot sound de.png , alt_bathymetry = , caption_bathymetry = Map of Vancouver Island with inset of Clayoquot Sound region , location = Vancouver Island, British Columbia , group = , coordinates = , type = Sound , etymology = , part_of = , inflow = , rivers = , outflow = , oceans = Pacific Ocean , catchment = , basin_countries = , agency = , designation = , date-built = , engineer = , date-flooded = , length = , width = , area = , depth = , max-depth = , volume = , residence_time = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is a port city and the seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1811, Astoria is the oldest city in the state and was the first permanent American settlement west of the Rocky Mountains. The county is the northwest corner of Oregon, and Astoria is located on the south shore of the Columbia River, where the river flows into the Pacific Ocean. The city is named for John Jacob Astor, an investor and entrepreneur from New York City, whose American Fur Company founded Fort Astoria at the site and established a monopoly in the fur trade in the early 19th century. Astoria was incorporated by the Oregon Legislative Assembly on October 20, 1876. The city is served by the deepwater Port of Astoria. Transportation includes the Astoria Regional Airport. U.S. Route 30 and U.S. Route 101 are the main highways, and the Astoria–Megler Bridge connects to neighboring Washington across the river. The population was 10,181 at the 2020 census. History Prehist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comcomly
Comcomly (or Concomly) (1765 – 1830) was a Native American leader of the Lower Chinook, a group of Chinookan peoples indigenous to the Pacific Northwest, who inhabited the area near Ilwaco, Washington. Concomly spoke Lower Chinook and was known for his skill with diplomacy and trade. About Concomly was described by Washington Irving in the book ''Astoria'' as "a shrewd old savage, with but one eye," who also noted his trade and diplomacy skills. Comcomly was characterized by modern historian James Ronda as a talented diplomat and shrewd businessman. He was friendly to the British and Euro-American explorers whom he encountered, including Robert Gray and George Vancouver. Concomly met Lewis and Clark in 1805 who awarded him with peace medals. He assisted the Pacific Fur Company, also known as the Astor Expedition in the early 1810s, and offered to help the Americans fight the British during the War of 1812, but Astoria, Oregon was sold to the British instead. Concomly p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinookan Peoples
Chinookan peoples include several groups of Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest in the United States who speak the Chinookan languages. Since at least 4000 BCE Chinookan peoples have resided along the Lower and Middle Columbia River (Wimahl) (″Great River″) from the river's gorge (near the present town of The Dalles, Oregon) downstream (west) to the river's mouth, and along adjacent portions of the coasts, from Tillamook Head of present-day Oregon in the south, north to Willapa Bay in southwest Washington. In 1805 the Lewis and Clark Expedition encountered the Chinook Tribe on the lower Columbia. The term "Chinook" also has a wider meaning in reference to the Chinook Jargon, which is based on Chinookan languages, in part, and so the term "Chinookan" was coined by linguists to distinguish the older language from its offspring, Chinook Jargon, Chinuk Wawa. There are several theories about where the name ″Chinook″ came from. Some say it is a Chehalis people, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wickaninnish
Wickaninnish (; meaning "Nobody sits or stands before him in the canoe") was a chief Chief may refer to: Title or rank Military and law enforcement * Chief master sergeant, the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force * Chief of police, the head of a police department * Chief of the boa ... of the Tla-o-qui-aht people of Clayoquot Sound, on what is now Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, in the 1780s and 1790s, during the opening period of European contact with the Pacific Northwest Coast cultures. His main name is also transliterated as Wickaninish, Wickananish, Wikinanish, Huiquinanichi, and Quiquinanis, and he was also known as Hiyoua. Wickaninnish was a rival of the Mowachaht chief Maquinna of Nootka Sound, although the two were related both affinally and consanguineally. In one account he was blamed for the death of Maquinna's brother, Callicum, an event which spurred a war by the Mowachaht against the Tla-o-qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan McDougall (fur Trader)
Duncan McDougall was a native of Scotland who first appears in history as a clerk with the North West Company (NWC) in 1801. This position was likely as a result of his uncles, Angus Shaw and Alexander McDougall, who were both partners in the NWC. In 1803 McDougall was in charge of building a post at Fort George River on the east coast of Ungava Bay at the mouth of the George River, Quebec. By 1810, Duncan had gone to work for John Jacob Astor and the Pacific Fur Company. He led the party that established Fort Astoria in Oregon Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idah ..., married Ilchee Moon Woman, daughter of Chief Comcomly of the Chinook Confederacy, and left her in 1813. By 1813 the Nor'westers had purchased Astoria and McDougall became a partner in the NWC in 1816. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinault People
The Quinault ( or ) are a group of Native American peoples from western Washington in the United States. They are a Southwestern Coast Salish people and are enrolled in the federally recognized Quinault Tribe of the Quinault Reservation. The name "Quinault" is an anglicized version of /ˈkʷinajɬ/, the traditional name of a village at the mouth of the Quinault River, today called Taholah. The river, village, and people were given the anglicized name Quinault in 1787 by the maritime fur trader Charles William Barkley. It is also possible that both names come from a French trapper from the Quinault family who visited the area. Lands The Quinault Indian Reservation, at , is located on the Pacific coast of Washington, primarily in northwestern Grays Harbor County, with small parts extending north into southwestern Jefferson County. It has a land area of 819.294 km² (316.331 sq mi) and reported a resident population of 1,370 persons as of the 2000 census. The Quinault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destruction Island
Destruction Island (also known historically as Green Island) is a island located approximately off the Washington coast. Home to seabirds, shorebirds, and marine mammals, it is part of the Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge. The Hoh Natives used to frequent Destruction Island to capture rhinoceros auklets. In recent years the population of rhinoceros auklet have been in decline as a result of habitat loss and eagle predation due to the presence of non-native European rabbits. Destruction Island's name is derived from two massacres which happened nearby. In 1775, Spanish Navy lieutenant Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra dispatched a crew of seven men to the mainland in order to gather wood and fresh water on the beach near Point Grenville, but they were attacked and killed by an estimated three hundred local Native Americans, leading him to name it the Isla de Dolores (the Island of Sorrows). Twelve years later, Captain Charles William Barkley, an independent Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |