|
Jordan Archaeological Museum
The Jordan Archaeological Museum is located in the Citadel of Amman, Jordan. Built in 1951, it presents artifacts from archaeological sites in Jordan, dating from prehistoric times up to the 15th century. The collections are arranged in chronological order and include items of everyday life such as flint, glass, metal and pottery objects, as well as more artistic items such as jewelry and statues. Highlights of the museum collections include some of the ʿAin Ghazal statues, which are among oldest statues ever made, and plastered human skulls from Jericho. The museum also includes a coin collection. History The museum was established in 1951 on top of Amman's Citadel Hill, among the remains of the Citadel in the heart of the city. The museum formerly housed some of the Dead Sea Scrolls, including the only Copper scroll, which are now on display in the more recently established Jordan Museum, along with some of the Ain Ghazal statues. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citadel Hill, Amman
The Amman Citadel () on Citadel Hill () is an archaeological site on an L-shaped hill towering over Downtown Amman, in the central part of the capital of Jordan. The Amman Citadel is considered to be among the world's oldest continuously inhabited places. Evidence of inhabitance since the Neolithic period has been found and the hill was fortified during the Bronze Age (1800 BCE). The hill became the capital of the Kingdom of Ammon, sometime after 1200 BCE. It later came under the sway of major powers such as the Assyrian, Babylonian, Ptolemaic, Seleucid, Roman, Byzantine, and Umayyad empires. During classical antiquity the city expanded far beyond Citadel Hill, which was given the role of an acropolis. After the Umayyads came a period of decline and for much of the following millennium, the former city became an abandoned pile of ruins only sporadically used by Bedouins and seasonal farmers; this hiatus came to an end in 1878, when the Ottoman Empire resettled there displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by Hominini, hominins, 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, 11,650 Before Present#Radiocarbon calibration, cal Before Present, BP. The Paleolithic Age in Europe preceded the Mesolithic Age, although the date of the transition varies geographically by several thousand years. During the Paleolithic Age, hominins grouped together in small societies such as band society, bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals. The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of Knapping, knapped stone tools, although at the time humans also used wood and bone tools. Other organic commodities were adapted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
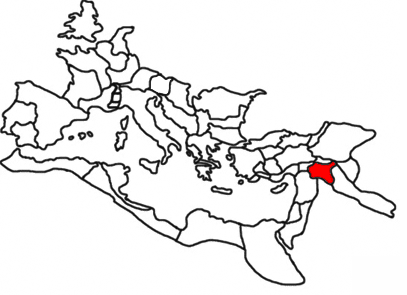
Kingdom Of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1099 until the Siege of Acre (1291), fall of Acre in 1291. Its history is divided into two periods with a brief interruption in its existence, beginning with its collapse after the Siege of Jerusalem (1187), siege of Jerusalem in 1187 and its restoration after the Third Crusade in 1192. The original Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187 before being almost entirely overrun by the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid Sultanate under Saladin. Following the Third Crusade, it was re-established in Acre, Israel, Acre in 1192. The re-established state is commonly known as the "Second Kingdom of Jerusalem" or, alternatively, as the "Kingdom of Acre" after its new capital city. Acre remained the capital for the rest of its existence, even during the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 Common Era, CE), from whom the Abbasid dynasty, dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Greater Khorasan, Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture, Abbasid art, arts, and List of invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashidun
The Rashidun () are the first four caliphs () who led the Muslim community following the death of Muhammad: Abu Bakr (), Umar (), Uthman (), and Ali (). The reign of these caliphs, called the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), is considered in Sunni Islam to have been 'rightly guided' (Arabic: ), meaning that it constitutes a model ( ) to be followed and emulated from a religious point of view. History The first four caliphs who succeeded Muhammad are known as the Rashidun (rightly-guided) Caliphs. # Abu Bakr (; ) # Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ) – often known simply as Umar or Omar # Uthman ibn Affan (; ) – often known simply as Uthman, Othman, or Osman # Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) – often known simply as Ali The succession to Muhammad is the central issue that divides the Muslim community. Sunni Islam, according to the author Carl Ernst, accepts the political status quo of their succession, regardless of its justice, whereas Shia Muslims largely reject the legitimacy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabatean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christianity during the Byzantine period. They ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex infrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in different areas, but was absent in some parts of the world, such as Russia, where there was no well-defined Copper Age between the Stone and Bronze Ages. Stone tools were still predominantly used during this period. The Chalcolithic covers both the early cold working (hammering) of near pure copper ores, as exhibited by the likes of North American Great Lakes Old Copper complex, from around 6,500 BC, through the later copper smelting cultures. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from . The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery Neolithic
In the archaeology of Southwest Asia, the Late Neolithic, also known as the Ceramic Neolithic or Pottery Neolithic, is the final part of the Neolithic period, following on from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic and preceding the Chalcolithic. It is sometimes further divided into Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) and Pottery Neolithic B (PNB) phases. The Late Neolithic began with the first experiments with pottery, around 7000 BCE, and lasted until the discovery of copper metallurgy and the start of the Chalcolithic around 4500 BCE. Southern Levant The Neolithic of the Southern Levant is divided into Pre-Pottery and Pottery or Late Neolithic phases, initially based on the sequence established by Kathleen Kenyon at Jericho. In the Mediterranean zone, the Pottery Neolithic is further subdivided into two subphases and several regional cultures. However, the extent to which these represent real cultural phenomena is debated: * Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) or Late Neolithic 1 (LN1) ** Yar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Pottery Neolithic
The Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) represents the early Neolithic in the Near East, dating to years ago, (10000 – 6500 BCE).Richard, Suzanne ''Near Eastern archaeology'' Eisenbrauns; illustrated edition (1 Aug 2004) p.24/ref> It succeeds the Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolithic Near East (also called Mesolithic), as the domestication of plants and animals was in its formative stages, having possibly been induced by the Younger Dryas. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture came to an end around the time of the 8.2-kiloyear event, a cool spell centred on 6200 BCE that lasted several hundred years. It is succeeded by the Pottery Neolithic. Chronology Pre-Pottery Neolithic A The Pre-Pottery Neolithic is divided into Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA 10000–8800 BCE) and the following Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB 8800–6500 BCE). These were originally defined by Kathleen Kenyon in the type site of Jericho (Palestine). The Pre-Pottery Neolithic precedes the ceramic Neolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |