|
John P. Hatch
John Porter Hatch (January 9, 1822 – April 12, 1901) was a career American soldier who served as general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He received a Medal of Honor for gallantry in action at the September 1862 Battle of South Mountain during the Maryland Campaign. Early life and career Hatch was born in Oswego, N. Y., a son of Moses Porter and Hannah (Reed) Hatch. He graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1845, ranking 17th in his class. He experienced his first active field service as a second lieutenant in the 3rd U.S. Infantry during the Mexican War. In May 1846, he served under General Zachary Taylor at Palo Alto and Resaca de la Palma. He was transferred later to serve under Winfield Scott in the Mounted Rifles. He was brevetted as a first lieutenant for gallant service in the subsequent battles of Contreras and Churubusco, and captain for bravery at Chapultepec. When the war ended, Hatch was assigned to various posts on the frontier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswego, New York
Oswego () is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Oswego County, New York, United States. The population was 16,921 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Oswego is situated at the mouth of the Oswego River (New York), Oswego River on the southeastern shore of Lake Ontario in Upstate New York, about northwest of Syracuse, New York, Syracuse and east-northeast of Rochester, New York, Rochester by road. The city promotes itself as "The Port City of Central New York". The first European settlement at Oswego was a British trading post established in 1722, and it was first incorporated as a village in 1828 before becoming a city in 1848. British forces briefly captured the city during the War of 1812, but were defeated nearby later that same month. The canalization of the Oswego River was a major boon to Oswego, attracting settlement and investment; this was later bolstered by its status as a rail hub for much of the 19th and 20th centuries, though this status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Cavalry Regiment (United States)
The 4th Cavalry Regiment is a United States Army cavalry regiment, whose lineage is traced back to the mid-19th century. It was one of the most effective units of the Army against American Indians on the Texas frontier. Today, the regiment exists as separate squadrons within the U.S. Army. Presently, 1st Squadron, 4th Cavalry and 5th Squadron, 4th Cavalry are parts of the 1st Infantry Division's 1st Brigade and 2nd Brigade combat teams, respectively. 1st Squadron, 4th Cavalry's official nickname is "Quarterhorse", which alludes to its "1/4 Cav" designation.The 3rd Squadron, 4th Cavalry, official nicknamed "Raiders," serves as part of the 25th Infantry Division. The 4th Squadron, 4th Cavalry officially was stood up in September 2009 at Fort Riley, Kansas as part of 1st Infantry Division. It was inactivated in October 2015. The 6th Squadron, 4th Cavalry served as part of the recently inactivated 3rd Brigade Combat Team, 1st Infantry Division, at Fort Knox, Kentucky. Origin an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
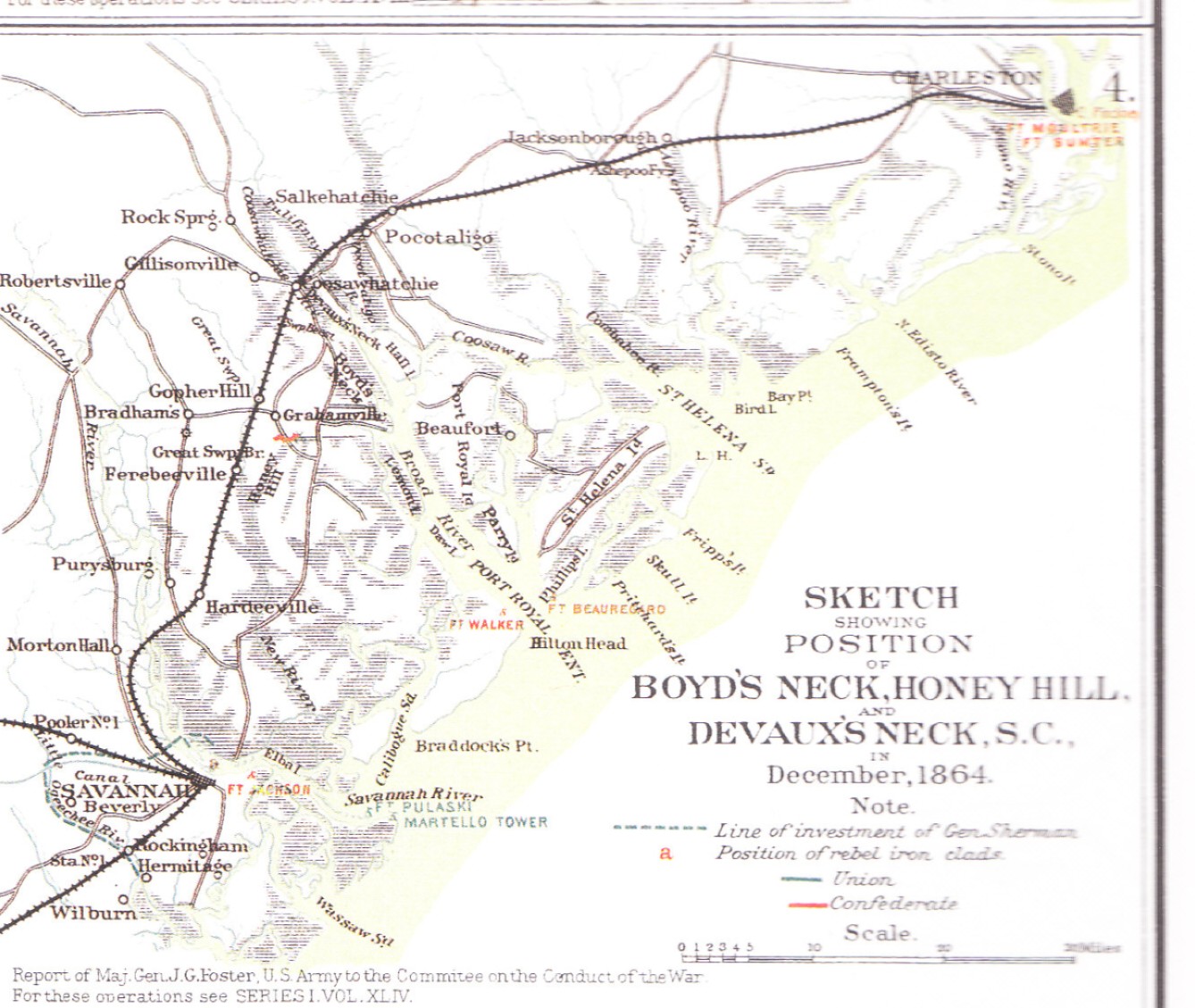
Battle Of Honey Hill
The Battle of Honey Hill was the third battle of Sherman's March to the Sea, fought November 30, 1864, during the American Civil War. It did not involve Major General William T. Sherman's main force, marching from Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia, but was a failed Union Army expedition under Brig. Gen. John P. Hatch that attempted to cut off the Charleston and Savannah Railroad in support of Sherman's projected arrival in Savannah. Engagement Hatch's expeditionary force left Hilton Head, South Carolina, for Boyd’s Neck (above Beaufort) on November 28. It consisted of 5,000 men—two brigades of the Coast Division of the Department of the South, one naval brigade, and portions of three batteries of light artillery. They steamed up the Broad River in transports to cut the Charleston and Savannah Railroad near Pocotaligo. Due to a heavy fog the troops were not disembarked from the transports until late the following afternoon, and Hatch immediately started forward to cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of South Mountain
The Battle of South Mountain, known in several early Southern United States, Southern accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap, was fought on September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland campaign of the American Civil War. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain (Maryland and Pennsylvania), South Mountain passes: Crampton's Gap, Crampton's, Turner's Gap, Turner's, and Fox's Gaps. Major general (United States), Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, commanding the Union Army, Union Army of the Potomac, needed to pass through these gaps in his pursuit of Confederate States Army, Confederate General Robert E. Lee's precariously divided Army of Northern Virginia. Although the delay bought at South Mountain would allow him to reunite his army and forestall defeat in detail, Lee considered termination of the Maryland Campaign at nightfall. Background South Mountain (Maryland and Pennsylvania), South Mountain is the name given to the continuation of the Blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Bull Run
The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederate States Army, Confederate General (CSA), Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia against Union Army, Union Major General (CSA), Maj. Gen. John Pope (general), John Pope's Army of Virginia, and a battle of much larger scale and numbers than the First Battle of Bull Run (or First Manassas) fought on July 21, 1861, on the same ground. Following a wide-ranging Flanking maneuver, flanking march, Confederate Maj. Gen. Stonewall Jackson, Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson captured the Union supply depot at Manassas, Virginia, Manassas Junction, threatening Pope's line of communications with Washington, D.C. Withdrawing a few miles to the northwest, Jackson took up strong concealed defensive positions on Stony Ridge and awaited the arrival of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Winchester
The First Battle of Winchester, fought on May 25, 1862, in and around Frederick County, Virginia, and Winchester, Virginia, was a major victory in Confederate Army Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's Campaign through the Shenandoah Valley during the American Civil War. Jackson enveloped the right flank of the Union Army under Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks and pursued it as it fled across the Potomac River into Maryland. Jackson's success in achieving force concentration early in the fighting allowed him to secure a more decisive victory which had escaped him in previous battles of the campaign. Background Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks learned on May 24, 1862, that the Confederates had captured his garrison at Front Royal, Virginia, and were closing on Winchester, turning his position. He ordered a hasty retreat down the Valley Pike from Strasburg. His columns were attacked at Middletown and again at Newtown ( Stephens City) by Jackson's converging forces. The Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Bull Run
The First Battle of Bull Run, called the Battle of First Manassas . by Confederate States Army, Confederate forces, was the first major battle of the American Civil War. The battle was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, just north of what is now the city of Manassas, Virginia, Manassas and about thirty miles west-southwest of Washington, D.C. The Union Army was slow in positioning themselves, allowing Confederate reinforcements time to arrive by rail. Each side had about 18,000 poorly trained and poorly led troops. The battle was a Confederate victory and was followed by a disorganized post-battle retreat of the Union forces. Just months after the start of the war at Battle of Fort Sumter, Fort Sumter, the northern public clamored for a march against the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
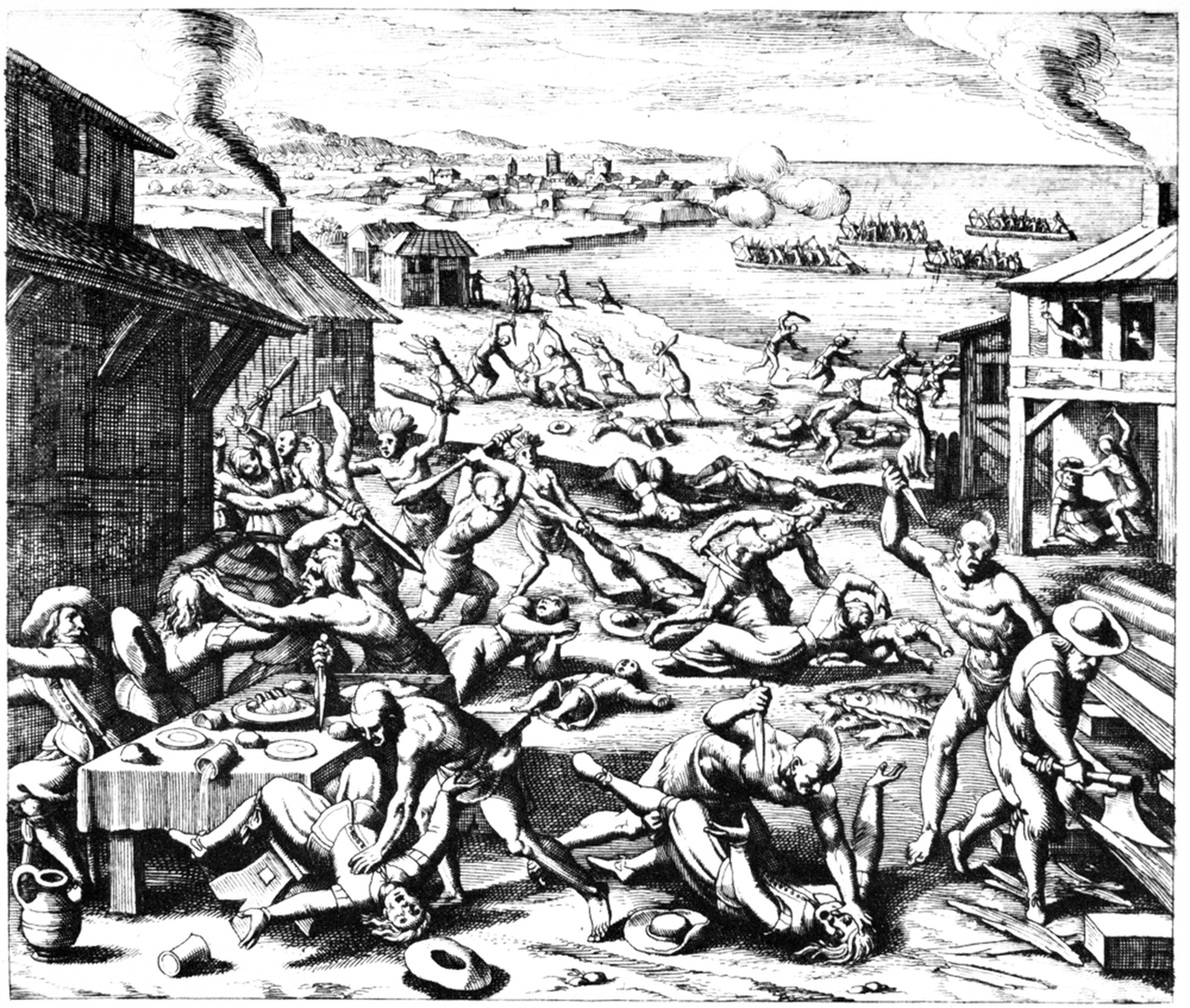
American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, was a conflict initially fought by European colonization of the Americas, European colonial empires, the United States, and briefly the Confederate States of America and Republic of Texas against various Tribe (Native American), American Indian tribes in North America. These conflicts occurred from the time of the earliest colonial settlements in the 17th century until the end of the 19th century. The various wars resulted from a wide variety of factors, the most common being the desire of settlers and governments for Indian tribes' lands. The European powers and their colonies enlisted allied Indian tribes to help them conduct warfare against each other's colonial settlements. After the American Revolution, many conflicts were local to specific states or regions and frequently involved disputes over land use; some entailed cycles of violent reprisal. As American pioneer, American settlers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
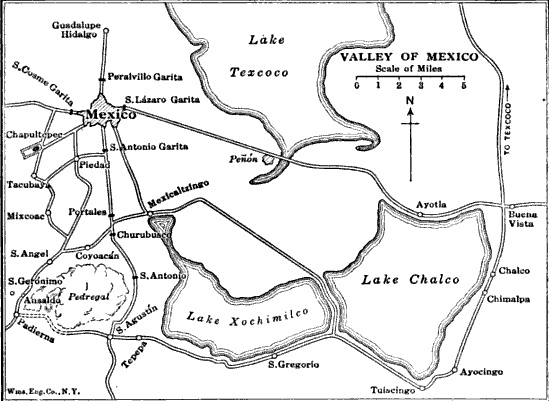
Battle Of Chapultepec
The Battle of Chapultepec took place between U.S. troops and Mexican forces holding the strategically located Chapultepec Castle on the outskirts of Mexico City on the 13th of September, 1847 during the Mexican–American War. The castle was built atop a hill in 1783, and in 1833 it was converted into a military academy and a gunpowder storage facility. The hill was surrounded by a wall 1,600 yards long. The battle was one of the most pivotal battles during the Mexican–American War as it paved the way to seize Mexico City and led to a decisive American victory. On the U.S. side the army was headed by General Winfield Scott, who led a force totaling 7,200 men. The Mexican side was led by General Antonio López de Santa Anna, commander of the Mexican army, had formed an army of approximately 25,000 men. Chapultepec Castle was defended by General Nicholas Bravo and his infantry of approximately 832 men, including military cadets of the Heroic Military Academy (Mexico), Military A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, while Santa Anna's army was in retreat from the Battle of Contreras or Battle of Padierna during the Mexican–American War. It was the battle where the San Patricio Battalion, made up largely of US deserters, made their last stand against U.S. forces. The U.S. Army was victorious, outnumbering more than six-to-one the defending Mexican troops. After the battle, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles (8 km) away from Mexico City. 50 Saint Patrick's Battalion members were officially executed by the U.S. Army, all but two by hanging. Collectively, this was the largest mass execution in United States history. Background Following their defeats at Contreras, Antonio López de Santa Anna ordered Major General Nicolás Bravo Rueda with the Army of the Center, to retreat from San Antonio to Churubusco.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846-1848'', New York:Macmillan, Santa Anna also ordered Major General Manuel Rincón t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place on 19–20 August 1847, in one of the final encounters of the Mexican–American War, as invading U.S. forces under Winfield Scott approached the Mexican capital. American forces surprised and then routed the Mexican forces of General Gabriel Valencia, who had disobeyed General Antonio López de Santa Anna's orders for his forces' placement. Although the battle was an overwhelming victory for U.S. forces, there are few depictions of it in contemporary popular prints. The armies re-engaged the next day in the Battle of Churubusco. Background General Gabriel Valencia's army of the north was part of the forces that fought at the Battle of Buena Vista in February 1847, in which Santa Anna retreated before giving a crushing blow to the forces of Zachary Taylor. The Mexican forces were then divided in two, with one sent to Cerro Gordo and the other to San Luis Potosí. General Valencia was given the command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |