|
John Graudenz
Wolfgang Kreher Johannes "John" Graudenz (12 November 1884 – 22 December 1942) was a German journalist, press photographer, industrial representative and German resistance to Nazism, resistance fighter against the Nazi regime. Graudenz was most notable for being an important member of the Berlin-based anti-fascist resistance group that would later be named by the Gestapo as the Red Orchestra (espionage), Red Orchestra and was responsible for the technical aspect of the production of leaflets and pamphlets that the group produced. Family Graudenz was the son of a wikt:saddler, saddler, and came from a large family with 10 siblings. Graudenz was married three times and also had an illegitimate daughter. In 1925, he married Antonie Wasmuth (died 1985), his third wife. She was the daughter of art publisher Ernst Wasmuth Verlag, Ernst Wasmuth. Together they had two children, Silva and Karin. Life In 1901, aged 16 or 17, Graudenz left the family home after a quarrel with the fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdańsk lies at the mouth of the Motława River and is situated at the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay, close to the city of Gdynia and the resort town of Sopot; these form a metropolitan area called the Tricity, Poland, Tricity (''Trójmiasto''), with a population of approximately 1.5 million. The city has a complex history, having had periods of Polish, German and self rule. An important shipbuilding and trade port since the Middle Ages, between 1361 and 1500 it was a member of the Hanseatic League, which influenced its economic, demographic and #Architecture, urban landscape. It also served as Poland's principal seaport and was its largest city since the 15th century until the early 18th century when Warsaw surpassed it. With the Partition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga River
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of .«Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge at delta – between and – and of . It is widely regarded as the national river of |
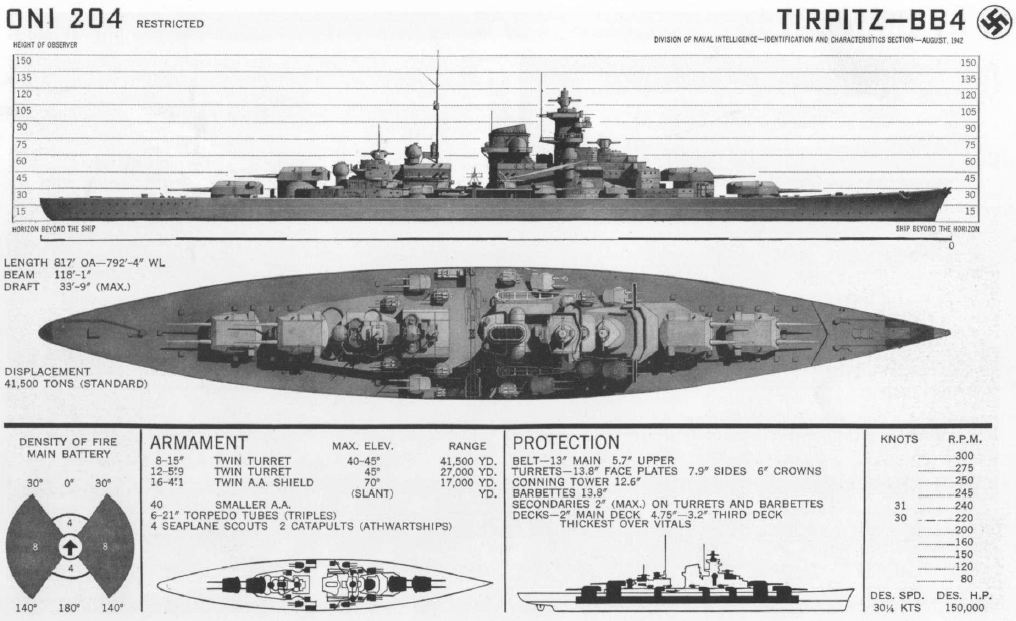
German Battleship Tirpitz
() was the second of two s built for Nazi Germany's (navy) prior to and during the Second World War. Named after Grand Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, the architect of the (Imperial Navy), the ship was laid down at the in Wilhelmshaven in November 1936 and her Hull (watercraft), hull was launched two and a half years later. Work was completed in February 1941, when she was commissioned into the German fleet. Like her sister ship, , was armed with a main battery of eight 38 cm SK C/34 naval gun, guns in four twin Gun turret, turrets. After a series of wartime modifications she was 2000 tonnes heavier than , making her the heaviest battleship ever built by a European navy. After completing sea trials in early 1941, briefly served as the centrepiece of the Baltic Fleet, which was intended to prevent a possible break-out attempt by the Soviet Baltic Fleet#Great Patriotic War, Soviet Baltic Fleet. In early 1942, the ship sailed to Norway to act as a deterrent against an Allied in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Navy submarines were also known as U-boats. U-boats are most known for their unrestricted submarine warfare in both world wars, trying to Commerce raiding, disrupt merchant traffic towards the UK and force the UK out of the war. In World War I, Germany intermittently waged unrestricted submarine warfare against the United Kingdom, UK: a first campaign in 1915 was abandoned after strong protests from the US but in 1917 the Germans, facing deadlock on the continent, saw no other option than to resume the campaign in February 1917. The renewed campaign failed to achieve its goal mainly because of the introduction of Convoys in World War I, convoys. Instead the campaign ensured final defeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German rearmament, German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War, non-intervention, but in reality supporting the Francoist Spain, Nationalists against the Second Spanish Republic, Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding programme, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the United Kingdom, British Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial German Navy, Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk (air base), Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the Luftwaffe's existence was publicly acknowledged and officially established on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a Luftwaffe detachment sent to aid Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown. In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation. Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimeograph
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator or stencil machine) is a low-cost duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a copy made by the process is a mimeograph. Mimeographs, along with spirit duplicators and hectographs, were common technologies for printing small quantities of a document, as in office work, classroom materials, and church bulletins. For even smaller quantities, up to about five, a typist would use carbon paper. Early fanzines were printed by mimeograph because the machines and supplies were widely available and inexpensive. Beginning in the late 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, photocopying gradually displaced mimeographs, spirit duplicators, and hectographs. Origins Use of stencils is an ancient art, butthrough chemistry, papers, and pressestechniques advanced rapidly in the late nineteenth century: Papyrograph A description of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libertas Schulze-Boysen
Libertas Viktoria "Libs" Schulze-Boysen ( Haas-Heye; 20 November 1913 – 22 December 1942) was a German noblewoman and resistance fighter against the Nazis. From the early 1930s to 1940, she attempted to build a literary career, first as a press officer and later as a writer and journalist. Initially sympathetic to the Nazis, she changed her mind after meeting and marrying Luftwaffe officer Harro Schulze-Boysen. As an aristocrat, Schulze-Boysen had contact with many different people in different strata of German society. Starting in 1935, she utilized her position to recruit left-leaning Germans into discussion groups which she hosted at her and Harro's apartment, where they sought to influence their guests. Through these discussions, resistance to the Nazi regime grew, and by 1936, she and Harro began to actively resist the Nazis. During the early 1940s, whilst working as a censor for the German Documentary Film Institute, Schulze-Boysen began to document atrocities committed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Krauss
Anna Krauss ( Friese; 27 October 1884, Bogen, Germany, Bogen – 5 August 1943, Plötzensee Prison, Berlin) was a German Clairvoyance, clairvoyant, fortune-teller and businesswomen who became a German resistance to Nazism, resistance fighter against the Nazi regime, through her association with a Berlin-based anti-fascist German resistance to Nazism, resistance group that was later called the Red Orchestra (espionage), Red Orchestra ("Rote Kapelle") by the Abwehr, during the Nazi regime. Life Krauss was a daughter of a farmer, Johann Friese. In 1911, Krauss married Hungarian Josef Krauss and had a son, Rudolf (born 1914). Josef Krauss was killed in World War I, leaving her a widow. Krauss had a sister, Magda Friese, who lived in an apartment at Parkallee 10, Stahnsdorf. Krauss and her son lived in Berlin from 1920. To earn a living, she became a seamstress to eventually owning a sewing workshop. Since 1936, Krauss, who had undergone commercial training in her youth, had become th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clairvoyance
Clairvoyance (; ) is the claimed ability to acquire information that would be considered impossible to get through scientifically proven sensations, thus classified as extrasensory perception, or "sixth sense". Any person who is claimed to have such ability is said to be a clairvoyant () (). Claims for the existence of paranormal and psychic abilities such as clairvoyance have not been supported by scientific evidence.Robert Todd Carroll, Carroll, Robert Todd. (2003)"Clairvoyance" Retrieved 2014-04-30. Parapsychology explores this possibility, but the existence of the paranormal is not accepted by the scientific community. The scientific community widely considers parapsychology, including the study of clairvoyance, a pseudoscience. Usage Pertaining to the ability of clear-sightedness, clairvoyance refers to the paranormal ability to see persons and events that are distant in time or space. It can be divided into roughly three classes: precognition, the ability to perceive o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortune-telling
Fortune telling is the spiritual practice of predicting information about a person's life. Melton, J. Gordon. (2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena''. Visible Ink Press. pp. 115–116. The scope of fortune telling is in principle identical with the practice of divination. The difference is that divination is the term used for predictions considered part of a religious ritual, invoking deities or spirits, while the term fortune telling implies a less serious or formal setting, even one of popular culture, where belief in occult workings behind the prediction is less prominent than the concept of suggestion, spiritual or practical advisory or affirmation. Historically, Pliny the Elder describes use of the crystal ball in the 1st century CE by soothsayers (''"crystallum orbis"'', later written in Medieval Latin by scribes as ''orbuculum''). Contemporary Western images of fortune telling grow out of folkloristic reception of Renaissance magic, specifically ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |