|
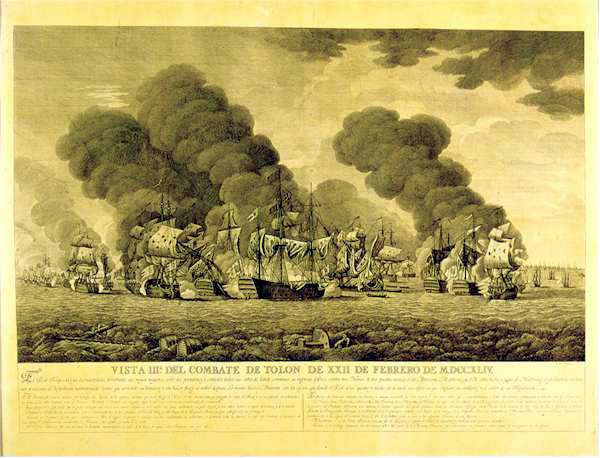
John Forbes (admiral)
Admiral of the Fleet John Forbes (17 July 1714 – 10 March 1796) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. After taking part in an expedition to Lisbon to support the Portuguese in the face of a Spanish threat, he saw action as captain of the third-rate HMS ''Norfolk'' at the Battle of Toulon during the War of the Austrian Succession. He was one of the few captains who really bore down on the enemy. Forbes went on to serve as a Lord Commissioner of the Admiralty under successive governments. In that role, he was convinced of the illegality of the sentence of death on Vice-Admiral John Byng and refused to sign Byng's death warrant. He also served as Member of Parliament for St Johnstown and then as Member of Parliament for Mullingar in the Parliament of Ireland. Early career Born the second son of George Forbes, 3rd Earl of Granard and Mary (the eldest daughter of William Stewart, 1st Viscount Mountjoy), Forbes joined the Royal Navy in the 70-gun third-rate HMS ''Burf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral Of The Fleet (Royal Navy)
Admiral of the Fleet (ADMF) is a Five-star rank, five-star naval officer rank and the highest rank of the Royal Navy, formally established in 1688. The five-star NATO rank code is OF-10, equivalent to a Field Marshal (UK), field marshal in the British Army or a marshal of the Royal Air Force. Apart from honorary appointments, no new admirals of the fleet have been named since 1995, and no honorary appointments have been made since 2014. History The origins of the rank can be traced back to John de Beauchamp, 1st Baron Beauchamp de Warwick, who was appointed 'Admiral of the South, North and West, Admiral of the King's Southern, Northern and Western Fleets' on 18 July 1360. The appointment gave the command of the English navy to one person for the first time; this evolved into the post of admiral of the fleet. In the days of sailing ships the Admiral (Royal Navy), admiral distinctions then used by the Royal Navy included distinctions related to the fleet being divided into thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Spain (1700–1808)
The Kingdom of Spain () entered a new era with the death of Charles II of Spain, Charles II, the last Habsburg Spain, Spanish Habsburg monarch, who died childless in 1700. The War of the Spanish Succession was fought between proponents of a House of Bourbon, Bourbon prince, Philip V of Spain, Philip of Anjou, and the Austrian House of Habsburg, Habsburg claimant, Archduke Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles. After the wars were ended with the Peace of Utrecht, Philip V of Spain, Philip V's rule began in 1715, although he had to renounce his place in the succession of the French throne. Spain entered a period of reform. Ideas of the Age of Enlightenment entered Spain and Spanish America during the eighteenth century. The invasion of the Iberian Peninsula by Napoleon Bonaparte in the Peninsular War upended the stability of the Spanish state and Spanish Empire, empire and although France was defeated, the turmoil in Spain led to the Spanish American wars of independence of 1808 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Stewart (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Charles Stewart (1681 – 5 February 1741) was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the Nine Years' War, and the Wars of the Spanish Succession, Quadruple Alliance and Austrian Succession. He embarked on a political career, and was a Member of Parliament for the Parliaments of Ireland and Great Britain. Stewart was born into the nobility, raised the younger son of a viscount. He entered the navy at an early age, but suffered a severe wound at the beginning of his career, losing his right hand. He recovered, and prospered in the service, rising to command several ships in the frequent wars of the early eighteenth century. He also had an interest in politics, representing County Tyrone from 1715. By 1720 he had risen high enough in the navy to be entrusted with a squadron to take action against Mediterranean piracy, particularly the dangerous Salé Rovers. He had the dual commission of acting as minister plenipotentiary to Morocco, and managed to suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Burford (1722)
HMS ''Burford'' was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Deptford Dockyard to the 1719 Establishment, and launched on 19 July 1722. ''Burford'' was notably the early posting of both John Forbes (admiral), John Forbes and John Byng,RN Museum, John Byng. both of whom rose to become admirals. She was in commission as the flagship of Vice Admiral Edward Hopson during Anglo-Spanish War (1727-1729), War with Spain in 1727 to 1729 and was repaired in 1737–1738. She served as the flagship of Edward Vernon at the capture of Puerto Bello in 1739 during the War of Jenkins' Ear under the command of Captain Thomas Watson, before returning to Britain for repairs in 1741/42. Her next active duty was in the West Indies from 1742 to 1744 during which she took part in operations at La Guayra and Porto Cabello in 1743 (where she lost two captains in succession) before being stationed in the Mediterranean from 1744 to 1748. After her final decommissioning in 1748, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with second rates having between 90 and 98 guns, while first rates had 100 guns or more, and fourth rates between 48 and 60 guns. By the latter half of the 18th century, they carried between 500 and 720 men. This designation became especially common because it included the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Stewart, 1st Viscount Mountjoy
William Stewart, 1st Viscount Mountjoy (1653–1692), was an Anglo-Irish soldier. Early life William Stewart was born in 1653, the son of Sir Alexander Stewart, 2nd Baronet, of Ramelton. His family was from Donegal, Ulster Scots, and Protestant. Career He was appointed master-general of the ordnance and colonel of a regiment of foot. In 1682 Charles II created him Viscount Mountjoy and Baron Stewart in the Peerage of Ireland. In 1686 Mountjoy served the Holy League (1684) in Hungary at the Siege of Buda, where he was twice dangerously wounded. On his return to Ireland, he was made a brigadier-general. Macaulay styled him "a brave soldier, an accomplished scholar". In Dublin he was the centre of a small circle of learned and ingenious men, who had, under his presidency, formed themselves into a Royal Society. In 1685 Charles II died and King James II acceded to the throne. James started replacing Protestants in Ireland with Catholics. In 1687 James appointed a new vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Forbes, 3rd Earl Of Granard
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland () was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until the end of 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chambers: the Irish House of Commons, House of Commons and the Irish House of Lords, House of Lords. The Lords were members of the Peerage of Ireland, Irish peerage ('Lords Temporal, lords temporal') and Bishop, bishops ('Lords Spiritual, lords spiritual'; after the Reformation, Church of Ireland bishops). The Commons was directly elected, albeit on a very restricted Suffrage, franchise. Parliaments met at various places in Leinster and Munster, but latterly always in Dublin: in Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin, Christ Church Cathedral (15th century),Richardson 1943 p.451 Dublin Castle (to 1649), Chichester House (1661–1727), the The King's Hospital, Blue Coat School (1729–31), and finally a purpose-built Parliament House, Dublin, Parliament House on College G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullingar (Parliament Of Ireland Constituency)
Mullingar was a constituency represented in the Irish House of Commons from 1612 to 1800. Borough The constituency represented the parliamentary borough of Mullingar. Members of Parliament * 1560 Nicholas Casey and James Reling * 1585 Richard Casey and Redmond Pettit * 1613–1615: Nicholas Casey and John Hammond * 1634–1635: Edward Pettit and James Christabel * 1639–1649: Edward Pettit (died and replaced 1642 by Sir Richard Kennedy, 2nd Baronet) and Alexander Hope (died and replaced 1642 by Oliver Wheeler) * 1661–1666: Arthur Forbes, 1st Earl of Granard (sat for Tyrone and replaced by Sir Robert Newcomen) and James Leighe 1689–1801 Notes References * {{Coord missing, County Westmeath 1612 establishments in Ireland 1800 disestablishments in Ireland Constituencies established in 1612 Constituencies disestablished in 1800 Constituencies of the Parliament of Ireland (pre-1801) Historic constituencies in County Westmeath Mullingar, Ireland Parliament Constitue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Johnstown (County Longford) (Parliament Of Ireland Constituency)
St Johnstown was a borough constituency for Ballinalee or Saintjohnstown County Longford represented in the Irish House of Commons The Irish House of Commons was the lower house of the Parliament of Ireland that existed from 1297 until the end of 1800. The upper house was the Irish House of Lords, House of Lords. The membership of the House of Commons was directly elected, ... until 1800. Members of Parliament Notes References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Johnstown Longford Historic constituencies in County Longford Constituencies of the Parliament of Ireland (pre-1801) 1800 disestablishments in Ireland Constituencies disestablished in 1800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Execution Warrant
An execution warrant (also called a death warrant or a black warrant) is a writ that authorizes the Capital punishment, execution of a capital punishment, condemned person. United States In the United States, either a judicial or executive official designated by law issues an execution warrant. This is done when a person, in trial court proceedings, has been sentenced to death, after trial (law), trial and conviction (law), conviction, and usually after appeals are exhausted. Normally when a death warrant is signed and an execution date is set, the condemned person is moved from his or her death row cell to a death watch cell, which is typically located adjacent to the execution chamber. Usually, the government agency tasked with carrying out the execution, normally the state's Department of Corrections or the Federal Bureau of Prisons in federal cases, has a limited time frame, normally about 60 days, from the date the warrant is signed, to complete the execution process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |