|
John Eladas
John Eladas ( el, Ἰωάννης ὁ Ἐλαδᾶς; died 914) was a senior member of the Byzantine court and regent in the early 10th century. Life He is first mentioned during the reign of Leo VI the Wise (), when he held the title of ''patrikios'' and was tasked with collecting money (possibly in exchange for commuting military service Military service is service by an individual or group in an army or other militia, air forces, and naval forces, whether as a chosen job ( volunteer) or as a result of an involuntary draft ( conscription). Some nations (e.g., Mexico) requ ...) from the European ''themata''. Under Leo VI's brother and successor, Alexander (Byzantine emperor), Alexander () he bore the supreme non-imperial title, that of ''magistros'', which he may have received already under Leo. In June 913, shortly before his death, Alexander appointed him as guardian and member of a regency council for Leo's underage son, Constantine VII (), along with the Patriarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Navy
The Byzantine navy was the naval force of the East Roman or Byzantine Empire. Like the empire it served, it was a direct continuation from its Imperial Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its earlier iteration. While the fleets of the unified Roman Empire faced few great naval threats, operating as a policing force vastly inferior in power and prestige to the legions, the sea became vital to the very existence of the Byzantine state, which several historians have called a "maritime empire". The first threat to Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean was posed by the Vandals in the 5th century, but their threat was ended by the wars of Justinian I in the 6th century. The re-establishment of a permanently maintained fleet and the introduction of the dromon galley in the same period also marks the point when the Byzantine navy began departing from its late Roman roots and developing its own characteristic identity. This p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Regents
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
914 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 914 ( CMXIV) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Empress Zoe Karbonopsina leads a palace coup at Constantinople and, with the support of the ''magistros'' John Eladas, overthrows Patriarch Nicholas Mystikos as regent over her son, Emperor Constantine VII. She allows Nicholas to remain as patriarch, repudiates the title granted to Simeon I of Bulgaria (see 913) and nullifies the marriage plans (with a Bulgarian princess) made for her son by Nicholas. * Summer – Byzantine–Bulgarian War: Simeon I, with the Bulgarian army, invades the themes of Thrace and Macedonia. Simultaneously, the Bulgarian troops penetrate into the regions of Dyrrhachium and Thessalonica to the west. Thrace's largest and most important city, Adrianople (modern Turkey), is besieged and captured. However, the Byzantines promptly regain the city in exchange for a huge ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Births
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Palace Of Constantinople
The Great Palace of Constantinople ( el, Μέγα Παλάτιον, ''Méga Palátion''; Latin: ''Palatium Magnum''), also known as the Sacred Palace ( el, Ἱερὸν Παλάτιον, ''Hieròn Palátion''; Latin: ''Sacrum Palatium''), was the large imperial Byzantine palace complex located in the south-eastern end of the peninsula now known as Old Istanbul (formerly Constantinople), in modern Turkey. It served as the main imperial residence of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine emperors until 1081 and was the centre of imperial administration for over 690 years. Only a few remnants and fragments of its foundations have survived into the present day. History When Constantine I refounded Byzantium as Constantinople in 330, he planned out a palace for himself. The palace was located between the Hippodrome and Hagia Sophia. The complex of palaces was rebuilt and expanded several times during its history. Much of the complex was destroyed during the Nika riots of 532 and was reb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoe Karbonopsina
Zoe Karbonopsina, also Karvounopsina or Carbonopsina, ( el, Ζωὴ Καρβωνοψίνα, translit=Zōē Karbōnopsina), was an empress and regent of the Byzantine empire. She was the fourth spouse of the Byzantine Emperor Leo VI the Wise and the mother of Constantine VII, serving as his regent from 913 until 919. Early life Zoe Karbonopsina was born into a Greek family. She was a relative of the chronicler Theophanes the Confessor and a niece of the admiral Himerios. Empress Desperate to sire a son, Leo VI married his mistress Zoe on 9 January 906, only after she had given birth to the future Constantine VII at the end of 905. However, this constituted his fourth marriage and was therefore un- canonical in the eyes of the Eastern Orthodox Church, which had already been reluctant to accept his third marriage to Eudokia Baïana, who died in childbirth in 901. Although the Patriarch Nicholas Mystikos reluctantly baptized Constantine, he forbade the emperor from marryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Blachernae
The Palace of Blachernae ( el, ). was an imperial Byzantine residence in the suburb of Blachernae, located in the northwestern section of Constantinople (today located in the quarter of Ayvansaray in Fatih, Istanbul, Turkey). The area of the palace is now mostly overbuilt, and only literary sources are available as to its description. History The Palace of Blachernae was constructed on the northern slopes of the Sixth Hill of the city in circa 500. The hill itself was partially remodelled, particularly in later times, and a number of terraces created to support the various buildings comprising the palace complex. Although the main imperial residence during the 4th–11th centuries was the Great Palace at the eastern end of the city, the Blachernae palace was used at times, and is attested in the ceremonial protocols contained in the 10th-century ''De Ceremoniis'', or Explanation of the Order of the Palace, Chapters I.27, I.34, II.9, II.12) of Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
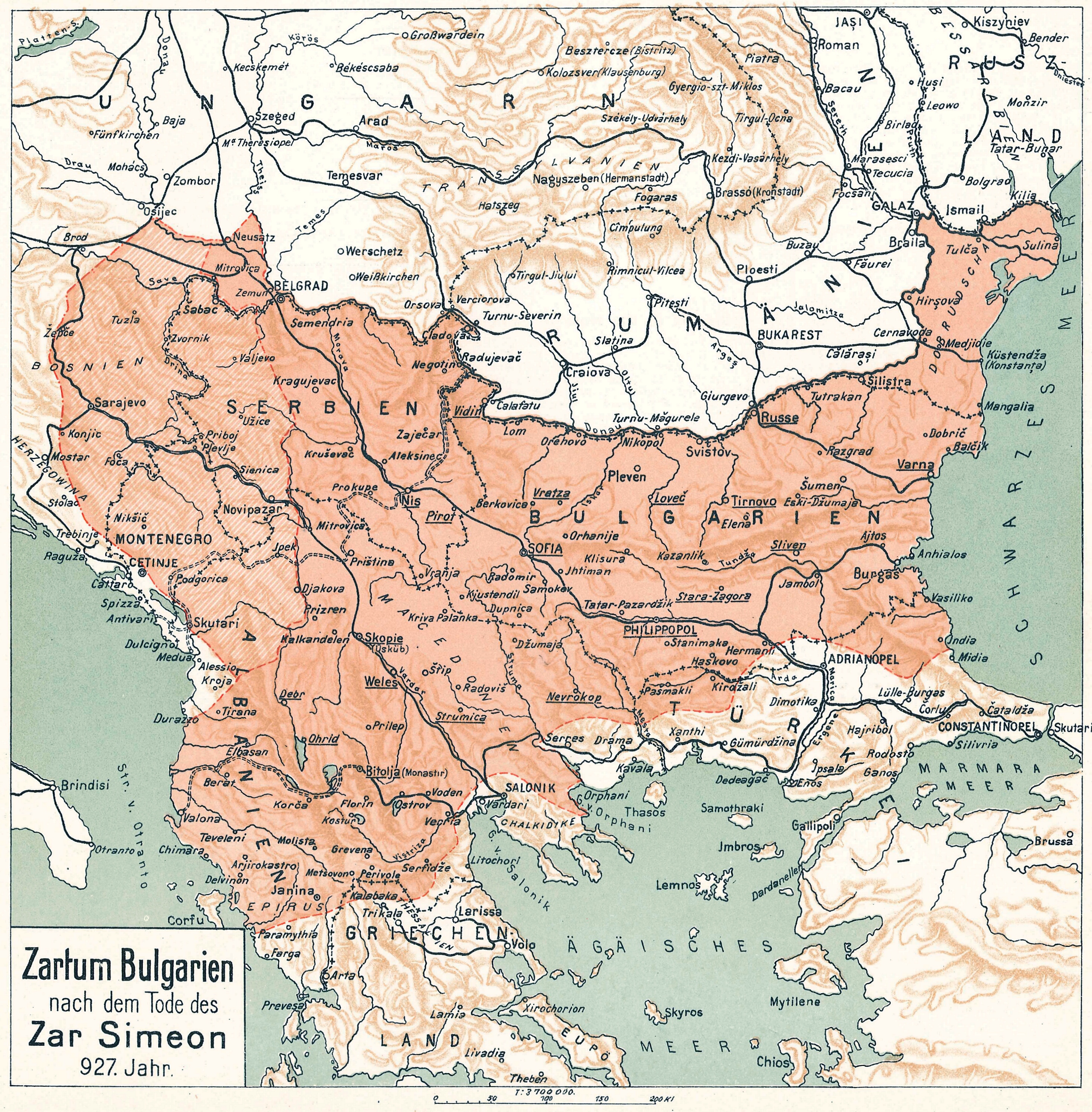
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeatingpossibly with the help of local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. It became the foremost cultural and spiritual centre of south Slavic Europe throughout most of the Middle Ages. As the state solidified its position in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalke Gate
The Chalke Gate ( el, ), was the main ceremonial entrance (vestibule) to the Great Palace of Constantinople in the Byzantine period. The name, which means "the Bronze Gate", was given to it either because of the bronze portals or from the gilded bronze tiles used in its roof. The interior was lavishly decorated with marble and mosaics, and the exterior façade featured a number of statues. Most prominent was an icon of Christ which became a major iconodule symbol during the Byzantine Iconoclasm, and a chapel dedicated to the ''Christ Chalkites'' was erected in the 10th century next to the gate. The gate itself seems to have been demolished in the 13th century, but the chapel survived until the early 19th century. History The gate lay on the southeastern corner of the Augustaion, the main ceremonial plaza of the city, with the Hagia Sophia cathedral on the northern side and the Baths of Zeuxippos and the Hippodrome of Constantinople on the southern and western sides. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |