|
John Clay (chaplain)
John Clay (1796–1858) was an English cleric and prison chaplain. His reporting on inmates of the prison at Preston, Lancashire made him a national figure. Early life John Clay was born in Liverpool on 10 May 1796, the fifth son of Thomas Clay, a ship and anchor smith who died in 1821, and his wife Mary, daughter of Ralph Lowe of Williamson Square, Liverpool, tanner. His father was in the electoral list of 1806 as an ironmonger, resident in Moor Street. His sister Mary married Anthony Swainson, brother of Charles Swainson of Preston, in 1811, and her sister Jane then married Charles Inman in 1817. Clay received a commercial education and his son's memoir states that he attended just one school, with Mr Wylie. This was the Roscoe Street "commercial and classical academy" run by the minister David Stewart Wylie on the corner of Leece Street, where his "rudiments of Latin" mentioned in the memoir could have been obtained. He had training on bookkeeping. Clay then entered a mercha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Chaplain
Prison religion includes the religious beliefs and practices of prison inmates, usually stemming from or including concepts surrounding their imprisonment and accompanying lifestyle. "Prison Ministry" is a larger concept, including the support of the spiritual and religious needs of prison guards and staff, whose work in an often demanding and brutal environment often creates a special need for pastoral care, similar to the care that is extended to the military, police officers and fire fighters. History Many religious groups often supply scripture and reading material, organize programs and worship, and train chaplains for work in prisons. Members of religious groups also engage in missionary activity, as there have been many instances of conversion throughout history. For instance, one of the earliest introductions of Islam into Eastern Europe was through the work of an early 11th-century Muslim prisoner who was captured by the Byzantines during their war against Muslims. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph John Gurney
Joseph John Gurney (2 August 1788 – 4 January 1847) was a banker in Norwich, England and a member of the Gurney family of that city. He became an evangelical minister of the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), whose views and actions led, ultimately, to a schism among American Quakers. Biography Gurney was born at Earlham Hall near Norwich (now part of the University of East Anglia), the tenth child of John Gurney (1749–1809) of Gurney's Bank. He was always called Joseph John. He was the brother of Samuel Gurney, Elizabeth Fry (née Gurney), a prison and social reformer, and Louisa Hoare (née Gurney), a writer on education, and also the brother-in-law – through his sister the campaigner Hannah Buxton – of Thomas Fowell Buxton, who was also an anti-slavery campaigner. He was educated by a private tutor at Oxford, members of non-conformist religious groups being ineligible to matriculate in his day at the English universities. In 1817 Gurney joined his siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Ashworth (nonconformist)
Henry Ashworth (4 September 1794 – 17 May 1880) was an English cotton manufacturer, friend of Richard Cobden, and founding member of the Anti-Corn Law League. Early life and business career Henry Ashworth was born on 4 September 1794 into a prominent Quaker farming family at Birtenshaw, then an outlying hamlet to the north of Bolton, Lancashire. His father was John Ashworth, who supplemented his income by buying cotton and selling it to local cottage weavers, buying back the finished cloth to sell in Manchester and who in 1793 had built the water powered New Eagley cotton spinning mill on the banks of the Eagley brook. He was sent to Ackworth School run by the Society of Friends and in 1808 became involved at the New Eagley mill, taking over its management in 1818. He was joined by his younger brother Edmund in 1821. The partnership of the two brothers expanded both the mill and the business and by 1831 they had 260 employees. In 1832 they bought the partially completed Egerton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preston Strike Of 1853–1854
The Preston strike of 1853–1854 was a strike of English weavers which took place between 1853 and 1854 in Preston, Lancashire. The strike lasted seven months and paralyzed the cotton industry in the city of Preston. The primary leaders were George Cowell and Mortimer Grimshaw. It inspired two contemporary novelists. Charles Dickens spent several days in Preston in January 1854. Although he does not describe a strike in ''Hard Times'', whose publication began in April 1854 in ''Household Words'', he was inspired by Mortimer Grimshaw in creating the character of the union leader, Slackbridge, and the intransigence of the bosses inspired the character of Bounderby. Elizabeth Gaskell, in '' North and South'', was inspired by the Preston strike in depicting one that takes place in Manchester Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Fry
Elizabeth Fry (née Gurney; 21 May 1780 – 12 October 1845), sometimes referred to as Betsy Fry, was an English prison reformer, social reformer, philanthropist and Quaker. Fry was a major driving force behind new legislation to improve the treatment of prisoners, especially female inmates, and as such has been called the "Angel of Prisons". She was instrumental in the 1823 Gaols Act which mandated sex-segregation of prisons and female warders for female inmates to protect them from sexual exploitation. Fry kept extensive diaries in which the need to protect female prisoners from rape and sexual exploitation is explicit. She was supported in her efforts by Queen Victoria and by Emperors Alexander I and Nicholas I of Russia and was in correspondence with both, their wives and the Empress Mother. In commemoration of her achievements she was depicted on the Bank of England £5 note, in circulation between 2002 and 2016. Background and early life Elizabeth Fry was born in Gurney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Fowell Buxton
Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, 1st Baronet (1 April 1786Olwyn Mary Blouet, "Buxton, Sir Thomas Fowell, first baronet (1786–1845)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online ed., May 201accessed 25 April 2013 – 19 February 1845) was an English Member of Parliament, brewer, abolitionist and social reformer. He had connections with the Gurney family. Early life Buxton was born at Castle Hedingham, Essex. His father, also named Thomas Fowell Buxton, died young, leaving three sons and two daughters. His Quaker mother's maiden name was Anna Hanbury. He completed his education at Trinity College Dublin, graduating in 1807. Through his mother's influence Buxton became associated with the Gurney family of Earlham Hall, Norwich, especially with Joseph John Gurney and Gurney's sister, the prison reformer Elizabeth Fry. He married their sister Hannah in May 1807. He lived at Belfield House, Weymouth, Dorset in the constituency he represented as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
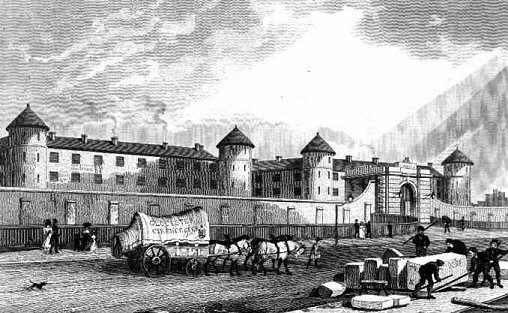
Millbank Penitentiary
Millbank Prison or Millbank Penitentiary was a prison in Millbank, Westminster, London, originally constructed as the National Penitentiary, and which for part of its history served as a holding facility for convicted prisoners before they were transported to Australia. It was opened in 1816 and closed in 1890. Construction The site at Millbank was originally purchased in 1799 from the Marquess of Salisbury for £12,000 by the philosopher Jeremy Bentham, acting on behalf of the Crown, for the erection of his proposed panopticon prison as Britain's new National Penitentiary. After various changes in circumstance, the Panopticon plan was abandoned in 1812. Proposals for the National Penitentiary continued, however, and were given a legislative basis in the Penitentiary House, etc. Act of 1812 (52 Geo. 3 c. 44). An architectural competition for a new prison building on the Millbank site attracted 43 entrants: the winning design was that of William Williams, drawing master at the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Crawford (1788–1847)
William Crawford may refer to: Entertainment * William Broderick Crawford (1911–1986), American film actor * Bill Crawford (cartoonist) (1913–1982), American editorial cartoonist * William L. Crawford (1911–1984), U.S. publisher and editor * William Crawford (knight), character in epic poem about Scottish knight William Wallace Military * William Crawford (soldier) (1732–1782), soldier in American Revolution, burnt at the stake by Native Americans * William Lyne Crawford (1839–1920), American Confederate soldier and lawyer * William J. Crawford (1918–2000), American soldier and Medal of Honor recipient * William Crawford (Royal Navy officer) (1907–2003), British admiral Politics * William Crawford (Pennsylvania politician) (1760–1823), American Representative from Pennsylvania * William Crawford (Virginia politician) (died 1762), politician in Virginia House of Burgesses, founder of Portsmouth, Virginia * William H. Crawford (1772–1834), U.S. Secretary of War an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poacher
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights. Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the hunting privileges of nobility and territorial rulers. Since the 1980s, the term "poaching" has also been used to refer to the illegal harvesting of wild plant species. In agricultural terms, the term 'poaching' is also applied to the loss of soils or grass by the damaging action of feet of livestock, which can affect availability of productive land, water pollution through increased runoff and welfare issues for cattle. Stealing livestock as in cattle raiding classifies as theft, not as poaching. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 15 enshrines the sustainable use of all wildlife. It targets the taking of action on dealing with poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna to ensure their avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scold's Bridle
A scold's bridle, sometimes called a witch's bridle, a gossip's bridle, a brank's bridle, or simply branks, was an instrument of punishment, as a form of public humiliation. It was an iron muzzle in an iron framework that enclosed the head (although some bridles were masks that depicted suffering). A bridle-bit (or curb-plate), about in size, was slid into the mouth and pressed down on top of the tongue, often with a spike on the tongue, as a compress. It functioned to silence the wearer from speaking entirely, and caused extreme pain and physiological trauma to scare and intimidate the wearer into submission. The scold's bridle was overwhelmingly used on women, often at the request of husbands or other family members. This prevented speaking and resulted in many unpleasant side effects for the wearer, including excessive salivation and fatigue in the mouth. For extra humiliation, a bell could also be attached to draw in crowds. The wearer was then led around town by a leash. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treadmill
A treadmill is a device generally used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. Treadmills were introduced before the development of powered machines to harness the power of animals or humans to do work, often a type of mill operated by a person or animal treading the steps of a treadwheel to grind grain. In later times, treadmills were used as punishment devices for people sentenced to hard labor in prisons. The terms ''treadmill'' and ''treadwheel'' were used interchangeably for the power and punishment mechanisms. More recently, treadmills have instead been used as exercise machines for running or walking in one place. Rather than the user powering a mill, the device provides a moving platform with a wide conveyor belt driven by an electric motor or a flywheel. The belt moves to the rear, requiring the user to walk or run at a speed matching the belt. The rate at which the belt moves is the rate of walking or running. Thus, the speed of running ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Batty Addison Clay
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Indiana * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel) 1969 nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |