|
John Clarke Lee
John Clarke Lee (April 9, 1804 – November 19, 1877) was an American lawyer, merchant, banker and politician who co-founded the prominent stock brokerage firm of Lee, Higginson & Co. Early life Lee was born on April 9, 1804, at Tremont Street, Tremont Place in Boston, Massachusetts, and named after the Rev. John Clarke, D.D. He was the son of Nathaniel Cabot Lee (1772–1806) and Mary Ann ( Cabot family, Cabot) Lee (1784–1809), who were first cousins. After his father's death in Barbados, his mother married Francis Blanchard. His mother died at 25, shortly after giving birth to his only sibling, half-sister Elizabeth Cabot Blanchard, who also died young at age 33 in 1842 after becoming the first wife of U.S. Senator Robert Charles Winthrop and having three children. His maternal grandparents were Anna ( Clarke) Cabot and Francis Cabot (brother of U.S. Senator George Cabot), who lived in Natchez, Mississippi. His paternal grandparents were Capt. Joseph Lee and Elizabeth ( Cabot) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Harding (painter)
Chester Harding (September 1, 1792 – April 1, 1866) was an American portrait Painting, painter known for his paintings of prominent figures in the United States and England. Early life Harding was born in Conway, Massachusetts, on September 1, 1792. He was the fourth of twelve children born to his mother, Olive (née Smith) Harding, and his father, Abiel Harding. He was over 6'3" in height. His family moved to Caledonia, New York, when he was fourteen-years-old. Self-sufficient at a young age, his initial trade was that of a woodturning, woodturner. Career In the War of 1812, he marched as a drummer with the militia to the St. Lawrence County, New York, St Lawrence. He became subsequently chair-maker, peddler, inn-keeper, and house-painter, painting signs in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He worked at this latter occupation a year, when acquaintance with a traveling portrait painter led him to attempt that art. Having succeeded in producing a crude portrait of his wife, he devoted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Pickering
Timothy Pickering (July 17, 1745January 29, 1829) was the third United States Secretary of State, serving under Presidents George Washington and John Adams. He also represented Massachusetts in both houses of United States Congress, Congress as a member of the Federalist Party. In 1795, he was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society. Born in Salem, Massachusetts, Salem in the Province of Massachusetts Bay, Pickering began a legal career after graduating from Harvard College. He won election to the Massachusetts General Court and served as a county judge. He also became an officer in the colonial militia and served in the siege of Boston during the early stages of the American Revolutionary War. Later in the war, he was Adjutant General and Quartermaster General of the United States Army, Quartermaster General of the Continental Army. After the war, Pickering moved to the Wyoming Valley of Pennsylvania and took part in the then colony's 1787 ratifying convention for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Endicott Peabody
Samuel Endicott Peabody (April 19, 1825 – October 31, 1909) was an American merchant and banker who was a partner in the London banking firm of J.S. Morgan & Co. Early life Peabody was born on April 19, 1825, in Salem, Massachusetts. He was a son of Col. Francis Peabody (1801–1867) and Martha ( Endicott) Peabody (1799–1891). His paternal grandparents were Joseph Peabody and Elizabeth ( Smith) Peabody (a daughter of the Rev. Elias Smith and sister of Rev. Elias Smith). Through his mother, he was a direct descendant of Gov. John Endicott of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. His maternal grandparents were Samuel Endicott and Elizabeth ( Putnam) Endicott. Peabody spent one year studying at Harvard College before becoming a merchant. Career After Harvard, he organized the merchant firm of Curtis & Peabody, with offices on India Wharf. He also served as president of the Salem National Bank and was a director of many companies. In 1875, Peabody was invited to become a partner in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Empire Loyalist
United Empire Loyalist (UEL; or simply Loyalist) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the governor of Quebec and governor general of the Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America during or after the American Revolution. At that time, the demonym ''Canadian'' or ''Canadien'' was used by the descendants of New France settlers inhabiting the Province of Quebec. They settled primarily in Nova Scotia and the Province of Quebec. The influx of loyalist settlers resulted in the creation of several new colonies. In 1784, New Brunswick was partitioned from the Colony of Nova Scotia after significant loyalist resettlement around the Bay of Fundy. The influx of loyalist refugees also resulted in the Province of Quebec's division into Lower Canada (present-day Quebec), and Upper Canada (present-day Ontario) in 1791. The Crown gave them land grants of one lot. One lot consisted of per person to encourage their resettle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Paine (physician)
William Paine (June 5, 1750 – April 19, 1833) was a physician and political figure in New Brunswick. He represented Charlotte County in the Legislative Assembly of New Brunswick from 1786 to 1787. Paine was unusual in that he was a United Empire Loyalist who chose to return to the United States. He was born in Worcester, Massachusetts, the son of Timothy Paine and Sarah Chandler. He was educated at Harvard College, then studied medicine with Doctor Edward Augustus Holyoke and set up practice in Worcester in 1771. In 1773, he married Lois Orne. In 1774, he signed a protest against the activities of the pre-revolutionary committees of correspondence. He was censured for his protest and, later that year, travelled to England to continue his medical studies. Paine received an M.D. from Marischal College in Scotland. He returned to North America and served as apothecary for the British forces. In 1782, he was sent to Halifax, Nova Scotia. Paine was granted land near Passamaquo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
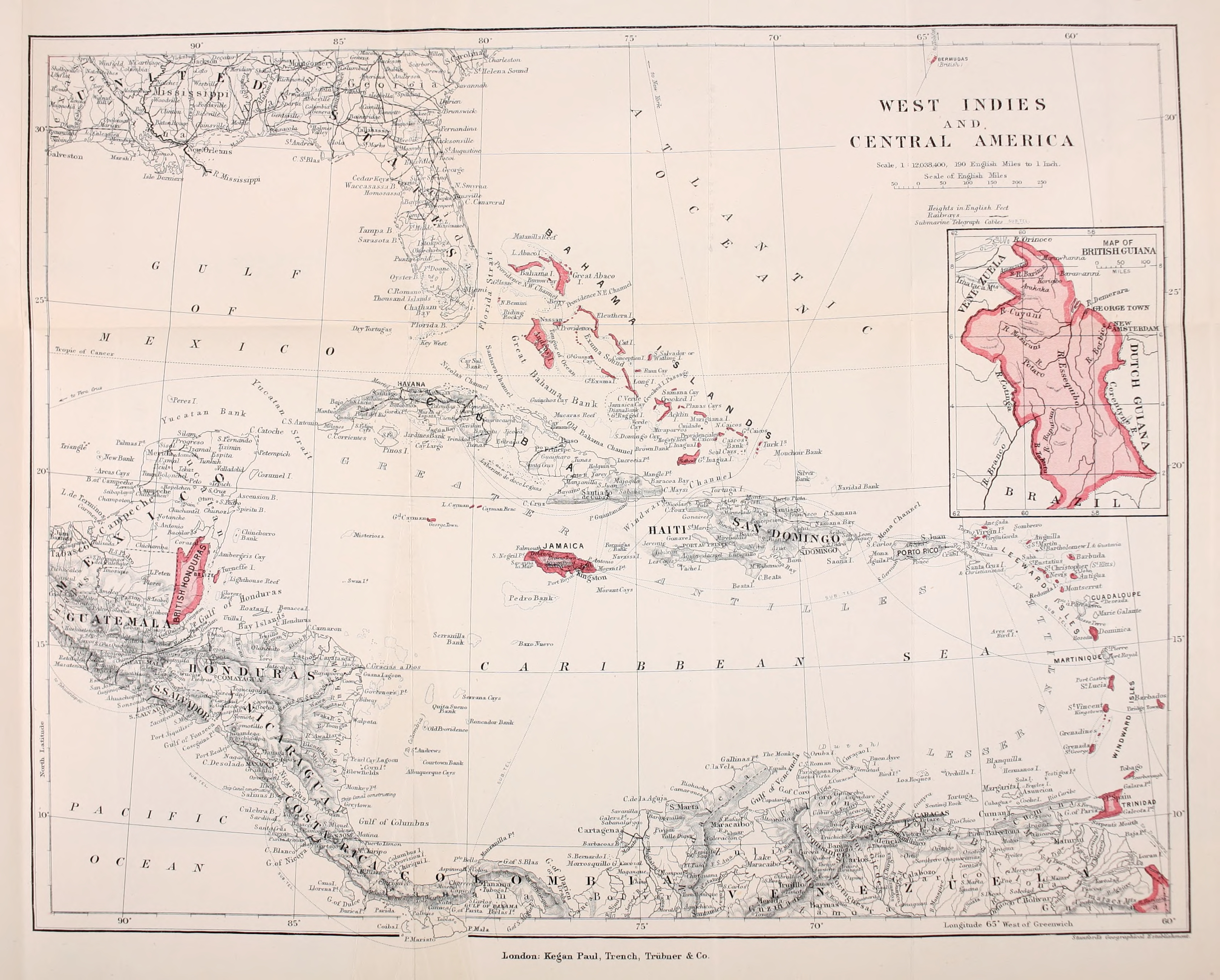
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Honduras, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. The Kingdom of England first English overseas possessions, established colonies in the region during the 17th century. Financed by valuable extractive commodities such as sugar production, the colonies were also at the centre of the Atlantic slave trade, with around 2.3 million slaves being brought to the British West Indies. The colonies also served as bases to project the power of the British Empire through the Royal Navy and Britain's Merchant Marine, and to expand and protect British overseas trade. Before the decolonization of the Americas in the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigua Island
Antigua ( ; ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the local population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the most populous island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Barbuda became an independent state within the Commonwealth of Nations on 1 November 1981. The island's perimeter is roughly and its area . Its population was 83,191 (at the 2011 Census). The economy is mainly reliant on tourism, with the agricultural sector serving the domestic market. Over 22,000 people live in the capital city, St. John's. The capital is situated in the north-west and has a deep harbour which is able to accommodate large cruise ships. Other leading population settlements are All Saints (3,412) and Liberta (2,239), according to the 2001 census. English Harbour on the south-eastern coast provides one of the largest deep water, protected harbors in the Eastern Caribbean. It is the site of UNESCO World Heritage S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harriet Paine Rose Lee (page 432 Crop)
Harriet(t) may refer to: * Harriet (name), a female name ''(includes list of people with the name)'' Places *Harriet, Queensland, rural locality in Australia * Harriet, Arkansas, unincorporated community in the United States * Harriett, Texas, unincorporated community in the United States Ships * ''Harriet'' (1798 ship), built at Pictou Shipyard, Nova Scotia, Canada * ''Harriet'' (1802 EIC ship), East India Company ship * ''Harriet'' (1810 ship), American ship * ''Harriet'' (1813 ship), American ship * ''Harriet'' (1829 ship), British Royal Navy ship * ''Harriet'' (1836 ship), British ship * ''Harriet'' (fishing smack), 1893 British trawler preserved in Fleetwood Museum Other * Harriet (band), an alternative Americana band from Los Angeles * ''Harriet'' (film), a 2019 biographical film about Harriet Tubman * Harriet (novel), a 1976 romance by Jilly Cooper * Harriet (play), 1943 American play * ''Harriet the Spy'' (TV series), a 2021 animated TV series * Harriet (tortoise), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Of France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas et géographie de la France moderne, Flammarion, Paris, 1984. Spain, the Mediterranean Sea and Italy. It includes southern Nouvelle-Aquitaine in the west, Occitania in the centre, the southern parts of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in the northeast, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur in the southeast, as well as the island of Corsica in the southeast. Southern France is generally considered part of southern Europe because of its association with the Mediterranean Sea. The colloquial French name for the region, ''le Midi'', is derived from an Old French compound composed of ''mi'' ("middle") and ''di'' ("day"), meaning literally "midday". Thus, the term is comparable in both origin and meaning to , which to indicates southern Italy, and Romanian whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, largest European island, and the List of islands by area, ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west – these islands, along with over List of islands of the British Isles, 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, comprise the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a land bridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's List of islands by population, third-most-populous islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Historical Society
The Massachusetts Historical Society (MHS) is a major historical archive specializing in early American, Massachusetts, and New England history. The Massachusetts Historical Society was established in 1791 and is located at 1154 Boylston Street in Boston, Massachusetts, and is the oldest historical society in the United States. The society's building was constructed in 1899 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1966. In 2016, the Boston Landmarks Commission designated it a Boston Landmark. History The society was founded on January 24, 1791, by Reverend Jeremy Belknap to collect, preserve, and document items of American history. He and the nine other founding members donated family papers, books, and artifacts to the society to form its initial collection. Its first manuscript was published in 1792, becoming the first historical society publication in the United States. The society incorporated in 1794; signatories included William Baylies, Jeremy Belknap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Lee Higginson
Henry Lee Higginson (November 18, 1834 – November 14, 1919) was an American businessman and philanthropist best known as the founder of the Boston Symphony Orchestra and a patron of Harvard University. Early life Higginson was born in New York City on November 18, 1834, the second child of George Higginson and Mary Cabot Lee.Perry, Bliss, ''Life and Letters of Henry Lee Higginson'' (Boston: Atlantic Monthly Press, 1921) He was a brother of James J. Higginson and a distant cousin of Thomas Wentworth Higginson.Henry Lee Higginson in the North America, Family Histories, 1500-2000. Eight Generation, page 35. Accessed via ancestry.com (paid subscription site) on 18 August 2022. When Higginson was four, his family moved to |