|
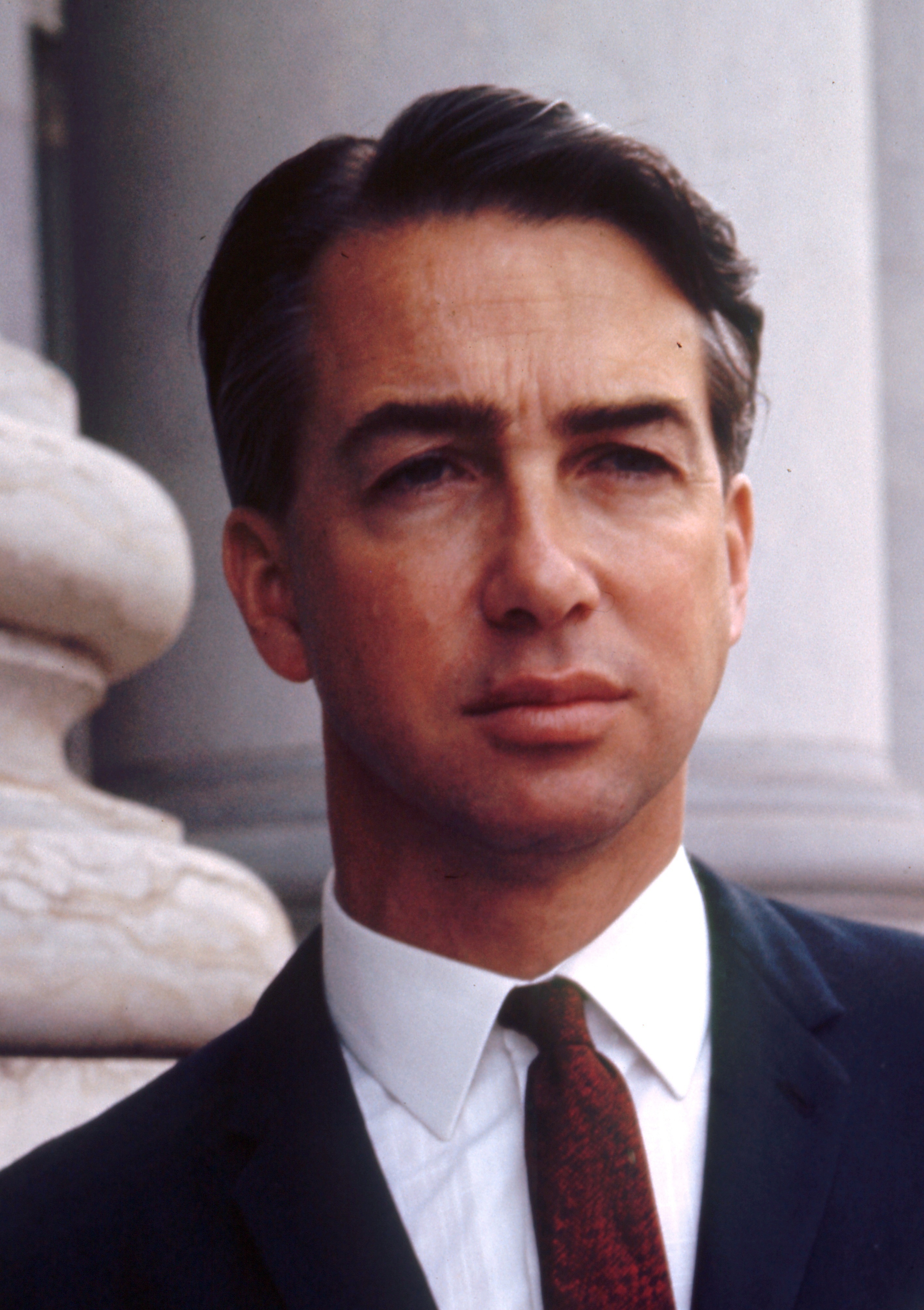
John Bannon
John Charles Bannon (7 May 1943 – 13 December 2015) was an Australian politician and academic. He was the 39th Premier of South Australia, leading the Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch), South Australian Branch of the Australian Labor Party from a single term in opposition back to government at the 1982 South Australian state election, 1982 election. At the 1985 South Australian state election, 1985 election Bannon's government was re-elected with an increased majority, but it was reduced to minority government status at the 1989 South Australian state election, 1989 election. In 1992 Bannon became List of Premiers of South Australia by time in office, Labor's longest-serving and South Australia's second longest-serving Premier. As a result of the State Bank of South Australia, State Bank collapse, he resigned as Premier in 1992, and from parliament at the 1993 South Australian state election, 1993 election landslide. He was also an academic and the Head of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premier Of South Australia
The premier of South Australia is the head of government in the state of South Australia, Australia. The Government of South Australia follows the Westminster system, with a Parliament of South Australia acting as the legislature. The premier is appointed by the governor of South Australia, and by modern convention holds office by virtue of their ability to command the support of a majority of members of the lower house of Parliament, the South Australian House of Assembly, House of Assembly. Peter Malinauskas is the current premier, having served since 21 March 2022. History The office of premier of South Australia was established upon the commencement of responsible government with the passage of the ''Constitution Act 1856''. The role was based upon that of the prime minister of the United Kingdom, with the premier requiring the support of a majority of the members of the lower house to remain head of government. For the early years of responsible government, the office was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Honourable
''The Honourable'' (Commonwealth English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific Style (manner of address), style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general, consuls and honorary consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners only. Africa Democratic Republic of the Congo In the Democrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Bank Of South Australia
The State Bank of South Australia was a bank created in 1896 and owned by the Government of South Australia. The bank became the subject of a two-year South Australian Royal Commission upon its collapse in 1991. The surviving part of the bank now exists as BankSA. History Early history The State Bank of South Australia was founded in 1896 as the outcome of an Act of Parliament, The Advances Bill, which provided for setting up of the bank which could benefit the State's primary producers and other industries by providing loans guaranteed by the Government at preferential conditions. A Bill based on a failed Victorian proposal was introduced by the Kingston-Holder government in 1894 but lapsed, then revived with clarifications by Frederick Holder (later Sir Frederick) in 1895. The Bill passed both houses of parliament in December 1895, and five Trustees were appointed: H. M. Addison (Chairman), J. B. Spence, J. Angas Johnson, S. Stanton and G. Inglis. :Addison resigned 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 25 November 1989. All 47 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Australian Labor Party led by Premier of South Australia John Bannon defeated the Liberal Party of Australia led by Leader of the Opposition John Olsen. Labor won 22 out of 47 seats, and secured a majority of 24 with the support of two Independent Labor members. Background Parliamentary elections for both houses of the Parliament of South Australia were held in South Australia in 1989. John Bannon's Labor government had initially presided over an economic boom, but at the time of the election the economy had slowed due to the late 1980s recession. The Liberals' campaign accused Bannon of inaction during the poor economic conditions, capitalising on the fact that he was national president of Australian Labor Party at the time. Outcome The Liberals gained five seats (Adelaide, Bright, Fisher, Hayward and Newland), but Labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minority Government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in the legislature. It is sworn into office, with or without the formal support of other parties, enabling a government to be formed. Under such a government, legislation can only be passed with the support or consent of enough other members of the legislature to provide a majority, encouraging multi-partisanship. In bicameral legislatures, the term relates to the situation in the chamber whose confidence is considered most crucial to the continuance in office of the government (generally, the lower house). A minority government tends to be less stable than a majority government because, if they can unite, opposing parliamentary members have sufficient numbers to vote against legislation, or even bring down the government with a vote of no c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1985 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 7 December 1985. All 47 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch), Australian Labor Party led by Premiers of South Australia, Premier of South Australia John Bannon increased its majority, and defeated the Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division), Liberal Party of Australia led by Leader of the Opposition (South Australia), Leader of the Opposition John Olsen. Background Parliamentary elections for both houses of the Parliament of South Australia were held in South Australia on 7 December 1985, which saw John Bannon and the Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch), Australian Labor Party win a second successive term, against the Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division), Liberal Party of Australia opposition led by John Olsen. Labor won the election with an increased majority–at the time, the biggest major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1982 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 6 November 1982. All 47 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Party of Australia led by Premier of South Australia David Tonkin was defeated by the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition John Bannon. A referendum on daylight saving was held on the same day, and was passed. Background Parliamentary elections for both houses of the Parliament of South Australia were held in South Australia in 1982, which saw John Bannon and the Australian Labor Party defeat the incumbent Liberal Party of Australia led by David Tonkin, after one term in power. As Premier, Tonkin combined fiscal conservatism with socially progressive reforms. In the former, Tonkin made significant cuts to the public service, earning him the enmity of the unions, while an example of the latter was the passage of the land rights bill and the return to the Pitjantjatjara people of 10 per cent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flinders University
Flinders University, established as The Flinders University of South Australia is a public university, public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia, with a footprint extending across a number of locations in South Australia and the Northern Territory. The main campus is in Bedford Park, South Australia, Bedford Park, about south of the Adelaide city centre. Other campuses include Tonsley, South Australia, Tonsley, Adelaide central business district, Renmark, South Australia, Renmark, Alice Springs, and Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin. Founded in 1966, it was named in honour of British navigator Matthew Flinders, who explored and surveyed the Australian and South Australian coastline in the early 19th century. In 2022, there were 25,247 students enrolled at the university. History Origins and construction By the late 1950s, the University of Adelaide's North Terrace campus was approaching capacity. In 1960, Premier Thomas Playford IV, Thomas Playford announ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Adelaide
The University of Adelaide is a public university, public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia. Established in 1874, it is the third-oldest university in Australia. Its main campus in the Adelaide city centre includes many Sandstone universities, sandstone buildings of historical and architectural significance, such as Bonython Hall. Its royal charter awarded by Queen Victoria in 1881 allowed it to become the University of London, second university in the English-speaking world to confer degrees to women. It Adelaide University, plans to merge with the neighbouring University of South Australia, is adjacent to the Australian Space Agency headquarters on Lot Fourteen and is part of the Adelaide BioMed City research precinct. The university was founded at the former South Australian Society of Arts, Royal South Australian Society of Arts by the Union College and studies were initially conducted at its State Library of South Australia, Institute Building. The soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre; the demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, traditional owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna, with the name referring to the area of the city centre and surrounding Adelaide Park Lands, Park Lands, in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bendigo
Bendigo ( ) is an Australian city in north-central Victoria. The city is located in the Bendigo Valley near the geographical centre of the state and approximately north-west of Melbourne, the state capital. As of 2022, Bendigo has a population of 103,818 making it Australia's 19th-largest city by population. Bendigo is the fourth-largest inland city in Australia and the fourth-most populous city in Victoria. Bendigo is administered by the City of Greater Bendigo, formerly the City of Bendigo. The council area encompasses roughly 3,000 square kilometres. The city is surrounded by smaller towns such as Castlemaine, Heathcote, Kyneton, Maryborough, Elmore, Rochester, Goornong and Axedale. The traditional owners of the area are the Dja Dja Wurrung (Djaara) people. The discovery of gold on Bendigo Creek in 1851 transformed the area from a sheep station into one of colonial Australia's largest boomtowns. News of the finds intensified the Victorian gold rush, brin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |