|
Joanna (opera)
''Joanna'' is an opéra comique in two acts by the French composer Étienne Méhul. It premiered at the Opéra-Comique The Opéra-Comique is a Paris opera company which was founded around 1714 by some of the popular theatres of the Parisian fairs. In 1762 the company was merged with – and for a time took the name of – its chief rival, the Comédie-Italienn ..., Paris on 23 November 1802. The libretto, by Benoît-Joseph Marsollier, is a revision of the same author's ''Emma, ou Le soupçon'', set by Étienne Fay in 1799. The piece was not a success and only enjoyed eight performances. Roles Synopsis ''Scene: Madras in India'' By marrying Amélie, the son of Lord Hervey has brought disgrace on his family and is forced to leave the country. Under the assumed name Charles, he works as a carpenter in Madras and Amélie lives with him under the name Joanna. However, Charles becomes jealous of a young army officer Édouard. Believing Édouard is trying to seduce his wife, Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1802 Operas
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album ''Burnout'' * " I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas By Étienne Méhul
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as '' Singspiel'' and ''Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratonice (opera)
''Stratonice'' is a one-act ''opéra comique'' by Étienne Méhul to a libretto by François-Benoît Hoffman, first performed at the Théâtre Favart in Paris, on 3 May 1792. The plot is taken from '' De Dea Syria'' ("On the Syrian Goddess", attributed to Lucian) concerning an incident from the history of the Seleucid dynasty which ruled much of the Middle East during the Hellenistic era of the ancient world. Performance history ''Stratonice'' was a popular opera, receiving over 200 performances during Méhul's lifetime. On 6 June 1792 a parody, ''Nice'', by Jean-Baptiste Desprez and Alexandre de Ségur, appeared at the Théâtre du Vaudeville. In 1821 Méhul's nephew Joseph Daussoigne-Méhul wrote new recitatives for the opera's revival in Paris at the Académie Royale de Musique. Roles Synopsis Antiochus, the son of King Seleucus, is pining away yet he would rather die than name the cause of his disease to his father. The doctor, Erasistratus, suspects love is behind Anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaveaux
Pierre Gaveaux (9 October 1761 – 5 February 1825) was a French operatic tenor and composer, notable for creating the role of Jason in Cherubini's ''Médée'' and for composing '' Léonore, ou L’amour conjugal'', the first operatic version of the story that later found fame as ''Fidelio''. Early life Gaveaux was born in Béziers and sang in the cathedral choir there from the age of seven. Although intending to enter the priesthood, he also took lessons in composition. He next became first tenor at the Basilica of Saint-Seurin in Bordeaux, studying with Franz Ignaz Beck, and subsequently decided to follow a career in music, becoming a conductor at the Grand Théâtre de Bordeaux as well as continuing to sing. Career as a singer After a period in Montpellier, he moved to Paris where, on 26 January 1789, he took part in a performance of Giacomo Tritto's ''Le Avventure Amorose'', which marked the inauguration of the Théâtre de Monsieur company in the Salle des Machin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Pierre Solié
Jean-Pierre Solié (also Soulier, Solier, Sollié; 1755 in Nîmes – 6 August 1812 in Paris) was a French cellist and operatic singer. He began as a tenor, but switched and became well known as a baritone. He sang most often at the Paris Opéra-Comique. He also became a prolific composer, writing primarily one-act comic operas.Letailleur, Paulette. "Solié olier, Sollié, Soulié, Soulier Jean-Pierre" in Sadie (1992) 4: 446. Career as a singer His father was a cellist with the orchestra at the theatre in Nîmes, and Solié likewise learned to play the cello. But he also learned to sing and play the guitar, and became a choirboy in the cathedral. As he got older he began traveling to nearby towns in southern France, where he played cello in local theatre orchestras and supplemented his income by giving lessons in guitar and singing. In 1778 in Avignon he was called upon to replace an ailing tenor in André Grétry's ''La Rosière de Salency'' and made such a good impressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
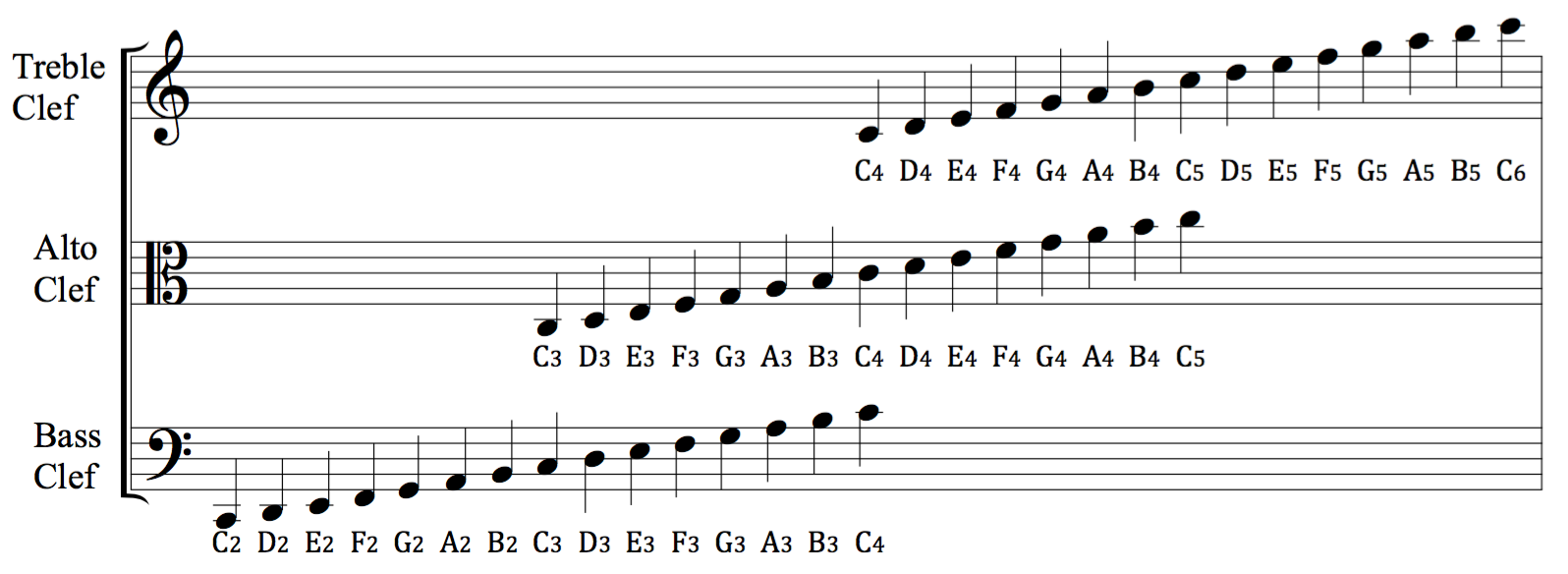
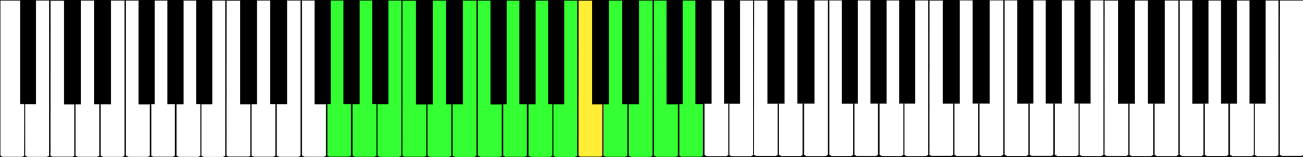
Bass Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the G-clef, F-clef, and C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space instead of a line, but this is rare. The use of different clefs makes it possible to write music for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the G-clef, F-clef, and C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space instead of a line, but this is rare. The use of different clefs makes it possible to write music for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass-baritone
A bass-baritone is a high-lying bass or low-lying "classical" baritone voice type which shares certain qualities with the true baritone voice. The term arose in the late 19th century to describe the particular type of voice required to sing three Wagnerian roles: the title role in '' Der fliegende Holländer'', Wotan/Der Wanderer in the '' Ring Cycle'' and Hans Sachs in ''Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg''. Wagner labelled these roles as ''Hoher Bass'' ("high bass")—see fach for more details. The bass-baritone voice is distinguished by two attributes. First, it must be capable of singing comfortably in a baritonal tessitura. Secondly, however, it needs to have the ripely resonant lower range typically associated with the bass voice. For example, the role of Wotan in '' Die Walküre'' covers the range from F2 (the F at the bottom of the bass clef) to F4 (the F above middle C), but only infrequently descends beyond C3 (the C below middle C). Bass-baritones are typically divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opéra Comique
''Opéra comique'' (; plural: ''opéras comiques'') is a genre of French opera that contains spoken dialogue and arias. It emerged from the popular '' opéras comiques en vaudevilles'' of the Fair Theatres of St Germain and St Laurent (and to a lesser extent the Comédie-Italienne), M. Elizabeth C. Bartlet and Richard Langham Smith"Opéra comique" '' Grove Music Online''. Oxford Music Online. 19 November 2009 which combined existing popular tunes with spoken sections. Associated with the Paris theatre of the same name, ''opéra comique'' is not necessarily comical or shallow in nature; '' Carmen'', perhaps the most famous ''opéra comique'', is a tragedy. Use of the term The term ''opéra comique'' is complex in meaning and cannot simply be translated as "comic opera". The genre originated in the early 18th century with humorous and satirical plays performed at the theatres of the Paris fairs which contained songs ('' vaudevilles''), with new words set to already existing musi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)