|
Jinping-I Dam
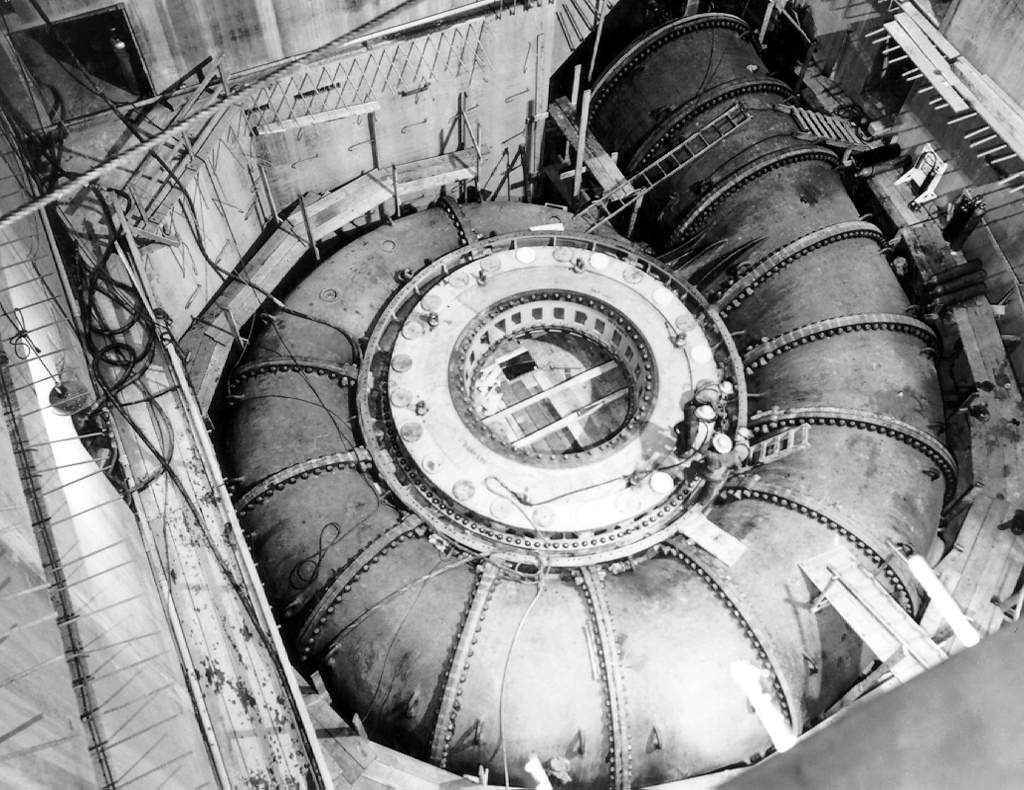
The Jinping-I Dam () also known as the Jinping-I Hydropower Station or Jinping 1st Cascade, is a tall arch dam on the Jinping Bend of the Yalong River (Yalong Jiang) in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Liangshan, Sichuan, People's Republic of China, China. Construction on the project began in 2005 and was completed in 2014. Its power station has a 3,600 MW capacity to produce between 16 and 18 TW·h (billion kW·h) annually. Supplying the power station is a reservoir created by the 305-meter-tall arch dam, the tallest in the world. The project's objective is to supply energy for expanding industrialization and urbanization, improve flood protection, and prevent erosion. History Harnessing hydropower on the Jinping bend of the Yalong River has been in planning for decades. The length of bend around the Jinping Mountains is 150 km but the downstream (northbound) part of the river on the opposite side is only separated by 16 km. Between that distance, there is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalong River
The Yalong River ( zh, 雅砻江, Pinyin, p ''Yǎlóngjiāng'', Wade–Giles, w ''Ya-lung Chiang'', Help:IPA/Mandarin, IPA ), or Nyag Chu (Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: , Tibetan pinyin, z ''Nyag Qu''), is a major tributary river of the Yangtze, Yangtze River in Southwest China. With a length of , the Yalong River flows from north to south through the Hengduan Mountains in western Sichuan, Sichuan Province. Course The Yalong has its source in the Bayan Har Mountains on the Tibetan Plateau, Tibet–Qinghai Plateau in Chindu County, Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Yushu, Qinghai, where it is known as the Za Qu ( zh, 扎曲). Flowing southeasterly, the Yalong gradually turns south at Garzê Town, Garzê and travels between the Shaluli Mountains to the west and the Daxue Mountains to the east. The Yalong River channel runs through a deep gorge for much of its length south of Garzê. The southern China National Highway 318, Sichuan-Tibet Highway crosses t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also mean population growth in urban areas instead of rural ones. It is predominantly the process by which towns and City, cities are formed and become larger as more people begin to live and work in central areas. Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from Urban sprawl, urban growth. Urbanization refers to the ''proportion'' of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the ''absolute'' number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050, about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. This is predicted to generate artificial scarcities of land, lack of dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Dams In China
The tallest dams in China are some of the tallest dams in the world. Nearly 22,000 dams over in height – about half the world's total – have been constructed in China since the 1950s. Many of the tallest are located in the southwestern part of the country (Guizhou, Sichuan, Yunnan) on rivers such as the Mekong, the Yangtze, and its upper stretch (Jinsha River) and tributaries ( Yalong, Dadu, Min and Wu). The Yellow River in the western part of the country also hosts several among the tallest. Purposes for these high structures include flood control, irrigation and, predominantly, hydroelectric power. While beneficial, many throughout the country have been criticized for their effects on the environment, displacement of locals and effect on transboundary river flows. Currently, the country's and world's tallest, Jinping-I Dam, an arch dam high, is located in Sichuan. The tallest embankment dam in China is the Nuozhadu Dam in Yunnan. The country's highest gravity dam is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Dams In The World
This is a list of the tallest dams in the world above in height. The tallest dam in the world is the Jinping-I dam, an arch dam in China at . The tallest embankment dam and the second tallest dam in the world is the Nurek Dam in Tajikistan, built by USSR. The tallest gravity dam is the high Grande Dixence Dam in Switzerland. The tallest natural dam, the Usoi Dam in Tajikistan, is higher than the tallest existing man-made dam. Existing Under construction Gallery File:BarrageDeLaGrandeDixenceFaceValee.JPG, The Grande Dixence Dam in Switzerland File:Enguri Dam, Georgia.jpg, The Inguri Dam in Georgia File:VajontDiga.jpg, The Vajont Dam in Italy File:Tehri dam india.jpg, The Tehri Dam in India File:MicaDam.JPG, The Mica Dam in Canada File:Саяно-Шушенская ГЭС.jpg, The Sayano Shushenskaya Dam in Russia File:OrovilleDam.jpg, The Oroville Dam in the United States File:El Cajon Dam Honduras.jpg, The El Cajón Dam in Honduras File:Bhakra Dam Aug 15 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinping-II Dam
The Jinping-II Dam (), also known as the Jinping-II Hydropower Station, is a gravity dam on the Jinping Bend of the Yalong River (Yalong Jiang) in Sichuan, China. Construction on the project began in 2007 and it was complete in 2014. Its hydroelectric power station has a 4,800 MW installed capacity. While Jinping-I relies on a conventional tall dam and large reservoir to supply water, Jinping-II uses a much smaller dam, located 7.5 km downstream of Jinping-I, to divert water into four 16.6 km long headrace tunnels. These tunnels connect to a downstream point on the same river at a much lower elevation, providing a head of water without flooding a large area of land. History Harnessing hydropower on the Jinping Bend of the Yalong River has been in planning for decades. The river makes a hairpin bend 150 km long around the Jinping Mountains, but the downstream part of the river on the opposite side of the mountain is separated by only 16 km. In that dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinsha River
The Jinsha River (, Classical Tibetan, Tibetan: Dri Chu, འབྲི་ཆུ, ) or Lu river, is the Chinese name for the upper stretches of the Yangtze River. It flows through the provinces of the PRC, provinces of Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan in western China. The river passes through Tiger Leaping Gorge. It is sometimes grouped together with the Lancang River, Lancang (upper Mekong) and Nujiang River, Nu (upper Salween) as the ''Sanjiang'' ("Three Rivers") area, part of which makes up the Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas. The river is important in generating hydroelectric power, and several of the world's List of largest hydroelectric power stations, largest hydroelectric power stations are on the Jinsha river. Name The river was first recorded as the Hei (, ''Hēishuǐ'', lit. "Blackwater") in the Warring States period, Warring States' "Tribute of Yu". It was described as the Sheng (traditional characters, t , simplified characters, s , '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Province
Sichuan is a Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Chengdu, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai and Gansu to the north, Shaanxi and Chongqing to the east, Guizhou and Yunnan to the south, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet to the west. During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of Ba (state), Ba and Shu (kingdom), Shu until their incorporation by the Qin (state), Qin. During the Three Kingdoms era (220–280), Liu Bei's state of Shu Han, Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent Qing dynasty, Manchu conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During World War II, Chongqing served as the temporary capital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
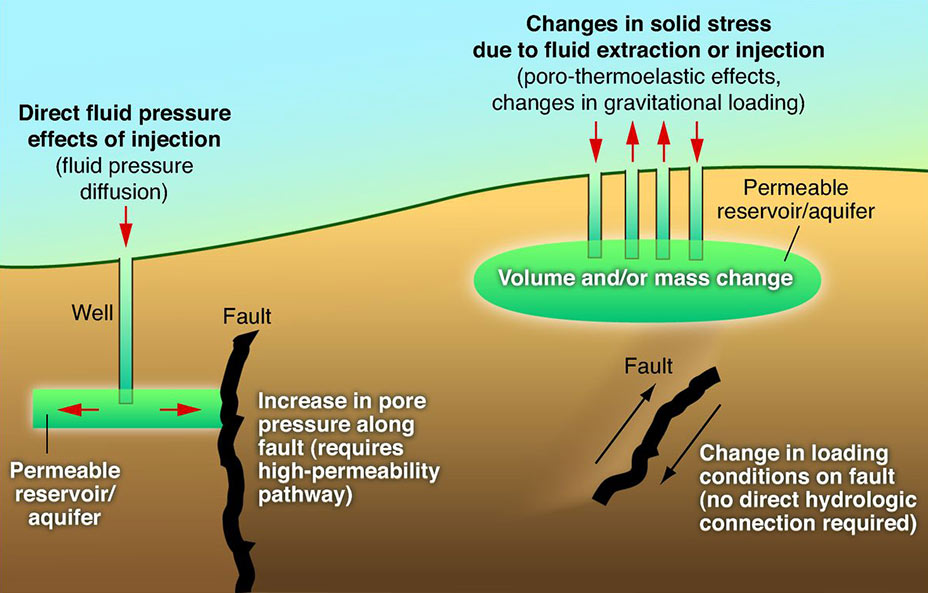
Reservoir-induced Seismicity
Induced seismicity is typically earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The Geysers geothermal plant in California which averaged two M4 events and 15 M3 events every year from 2004 to 2009. The Human-Induced Earthquake Database (''HiQuake'') documents all reported cases of induced seismicity proposed on scientific grounds and is the most complete compilation of its kind. Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of wastewater by the oil industry. A huge number of seismic events in oil and gas extraction states like Oklahoma is caused by increasing the volume of wastewater inje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |