|
Jihobbyist
Jarret Brachman is an American terrorism expert, the author of ''Global Jihadism: Theory and Practice'' and a consultant to several government agencies about terrorism. Education and career Brachman graduated from Augustana College (BA, 2000) and University of Delaware (MA, 2002; PhD, 2006). He is a former graduate fellow at the Central Intelligence Agency (2003), and the former director of research at West Point's Combating Terrorism Center (2004–08). Brachman, now managing director of Cronus Global LLC and a civilian scholar on the faculty of North Dakota State University, regularly briefs government officials on terrorism issues. In 2013, Brachman joined Wells Fargo's Emergency Incident Management Team. "Jihobbyist" Brachman coined the phrase "jihobbyist" (portmanteau of ''jihad'' and ''hobbyist'') in his 2008 book ''Global Jihadism: Theory and Practice''. He explains in his introduction to the book that he coined the new term to describe people who, without the suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nidal Malik Hasan
Nidal Malik Hasan (born September 8, 1970) is an American former United States Army major, physician, and mass murderer convicted of killing 13 people and injuring 32 others in the Fort Hood mass shooting on November 5, 2009. Hasan, an Army Medical Corps psychiatrist, admitted to the shootings at his court-martial in August 2013. During the six years Hasan was a medical intern and resident at the Walter Reed Army Medical Center, concerns were raised about his job performance and behavior, specifically comments described by colleagues as "anti-American." Hasan was described as socially isolated, stressed by his work with soldiers, and upset about their accounts of warfare. Two days before the shooting, less than a month before he was due to deploy to Afghanistan, Hasan gave away many of his belongings to a neighbor. Prior to the shooting, an investigation conducted by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) concluded Hasan's email correspondence with the late Imam Anwar al-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Extremism
Islamic extremism refers to extremist beliefs, behaviors and ideologies adhered to by some Muslims within Islam. The term 'Islamic extremism' is contentious, encompassing a spectrum of definitions, ranging from academic interpretations of Islamic supremacy to the notion that all ideologies other than Islam have failed and are inferior. Islamic extremism is different from Islamic fundamentalism or Islamism. Islamic fundamentalism refers to a movement among Muslims advocating a return to the fundamental principles of an Islamic state in Muslim-majority countries. Meanwhile, Islamism constitutes a form of political Islam. However, both Islamic fundamentalism and Islamism can also be classified as subsets of Islamic extremism. Acts of violence committed by Islamic terrorists and jihadists are often associated with these extremist beliefs. Definitions Academic definition The academic definition of radical Islam consists of two parts: * The first being: Islamic thought tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustana University Alumni
Augustana may refer to: In religion: * The ''Augustana'' or Augsburg Confession, which gives its name to several Lutheran institutions * Augustana Evangelical Lutheran Church, a Lutheran religious body from the 1860 until 1962 * Augustana Lutheran Church (Sioux City, Iowa), listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Swedish Evangelical Lutheran Augustana Church In education: * Augustana Academy, a former educational institute in South Dakota * Augustana College (Illinois), a liberal arts college in Illinois * Augustana University (South Dakota), a liberal arts college in South Dakota * Augustana University College, a formerly Lutheran college in Alberta * The University of Alberta Augustana Faculty of the University of Alberta, the present incarnation of the former Augustana University College after its merger with the University of Alberta * Augustana Divinity School (Neuendettelsau), a divinity school of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Bavaria in Neuendettel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
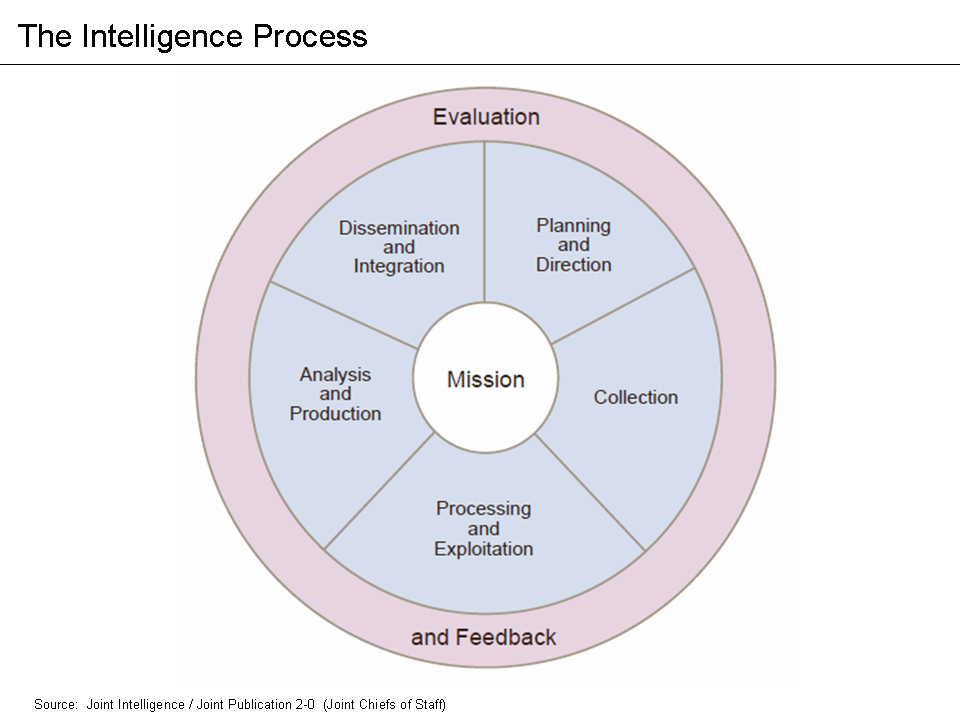
Intelligence Analysts
Intelligence analysis is the application of individual and collective cognitive methods to weigh data and test hypotheses within a secret socio-cultural context. The descriptions are drawn from what may only be available in the form of deliberately deceptive information; the analyst must correlate the similarities among deceptions and extract a common truth. Although its practice is found in its purest form inside national intelligence agencies, its methods are also applicable in fields such as business intelligence or competitive intelligence. Overview Intelligence analysis is a way of reducing the ambiguity of highly ambiguous situations. Many analysts prefer the middle-of-the-road explanation, rejecting high or low probability explanations. Analysts may use their own standard of proportionality as to the risk acceptance of the opponent, rejecting that the opponent may take an extreme risk to achieve what the analyst regards as a minor gain. The analyst must avoid the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamification
Gamification is the process of enhancing systems, services, organisations and activities through the integration of game design elements and principles in non-game contexts. The goal is to increase user engagement, motivation, competition and participation through the use of game mechanics such as points, badges, leaderboards and rewards. It is a component of system design, and it commonly employs game design elements to improve user engagement, organizational productivity, flow, learning, crowdsourcing, knowledge retention, employee recruitment and evaluation, usability, usefulness of systems, physical exercise, tailored interactions and icebreaker activities in dating apps, traffic violations, voter apathy, public attitudes about alternative energy, and more. A collection of research on gamification shows that a majority of studies on gamification find it has positive effects on individuals. However, individual and contextual differences exist. Gamification can be achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Policy
Foreign policy, also known as external policy, is the set of strategies and actions a State (polity), state employs in its interactions with other states, unions, and international entities. It encompasses a wide range of objectives, including defense and security, economic benefits, and humanitarian assistance. The formulation of foreign policy is influenced by various factors such as domestic considerations, the behavior of other states, and geopolitical strategies. Historically, the practice of foreign policy has evolved from managing short-term crises to addressing long-term international relations, with diplomatic corps playing a crucial role in its development. The objectives of foreign policy are diverse and interconnected, contributing to a comprehensive approach for each state. Defense and security are often primary goals, with states forming military alliances and employing soft power to combat threats. Economic interests, including trade agreements and foreign aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Dichotomy
A false dilemma, also referred to as false dichotomy or false binary, is an informal fallacy based on a premise that erroneously limits what options are available. The source of the fallacy lies not in an invalid form of inference but in a false premise. This premise has the form of a disjunction, disjunctive claim: it asserts that one among a number of alternatives must be true. This disjunction is problematic because it oversimplifies the choice by excluding viable alternatives, presenting the viewer with only two absolute choices when, in fact, there could be many. False dilemmas often have the form of treating two contraries, which may both be false, as contradictories, of which one is necessarily true. Various inferential schemes are associated with false dilemmas, for example, the constructive dilemma, the destructive dilemma or the disjunctive syllogism. False dilemmas are usually discussed in terms of deductive reasoning, deductive arguments, but they can also occur as de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The International Centre For The Study Of Radicalisation And Political Violence
The International Centre for the Study of Radicalisation and Political Violence (ICSR) is a non-profit, non-governmental think tank based in the Department of War Studies at King's College London whose mission is to educate the public and help policymakers and practitioners find solutions to radicalisation and political violence. It obtains some of its funding through the European Union. The organisation is a partnership of five academic institutions: King's College London, the University of Pennsylvania, the Interdisciplinary Center Herzliya (Israel), the Jordan Institute of Diplomacy, and Georgetown University. Since summer 2020, the ISCR is a member of the Global Network on Extremism and Technology together with the Peace Research Institute Frankfurt, the George Washington University's Program on Extremism (PoE), the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies' Centre of Excellence for National Security (CENS) and the Lowy Institute. Launch and role ICSR was launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Haganah
Internet Haganah is a "global intelligence network dedicated to confronting Internet activities by Islamists and their supporters, enablers and apologists." Internet Haganah also is an activist organization which attempts to convince businesses not to provide web-based services to such groups, and collects intelligence to store and pass on to government organizations. It was formed by Aaron Weisburd, an American computer programmer from Illinois, in 2002, and became part of a collection of private anti-terrorist web monitoring companies, including "Terrorism Research Center", "Search for International Terrorist Entities Institute", and "Northeast Intelligence Network". Weisburd is the only full-time employee of Internet Haganah, which is run primarily from his home office, with the help of many online associates. The organization ''Haganah'' is a Hebrew word meaning 'defense'. Haganah is also the name of the early Zionist militia originally formed to defend Jewish settlers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
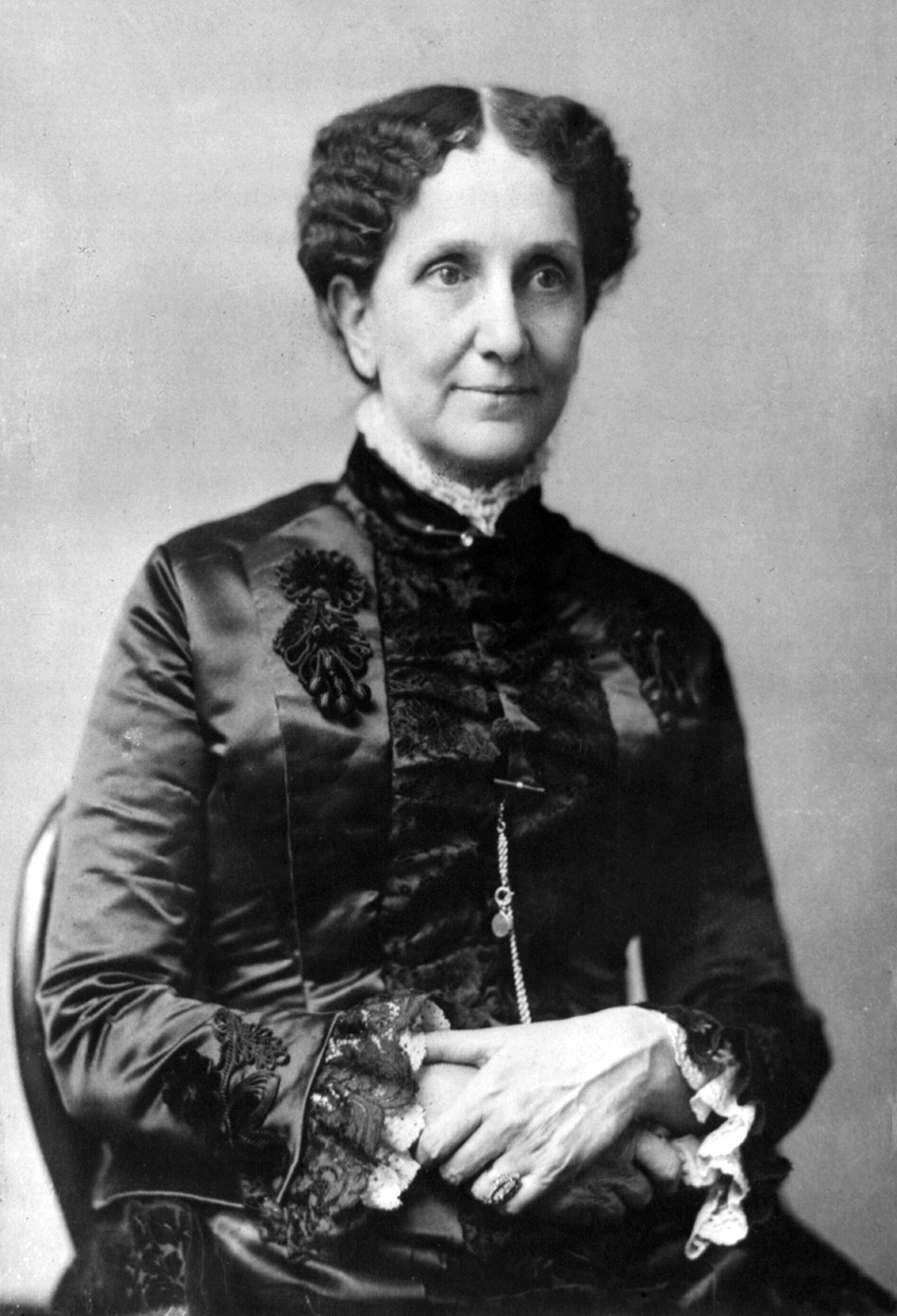
The Christian Science Monitor
''The Christian Science Monitor'' (''CSM''), commonly known as ''The Monitor'', is a nonprofit news organization that publishes daily articles both in Electronic publishing, electronic format and a weekly print edition. It was founded in 1908 as a daily newspaper by Mary Baker Eddy, founder of the new religious movement Christian Science, Church of Christ, Scientist. Since its founding, the newspaper has been based in Boston. Over its existence, seven ''Monitor'' journalists have been awarded the Pulitzer Prize, including Edmund Stevens (1950), John Hughes (editor), John Hughes (1968), Howard James (1968), Robert Cahn (1969), Richard Strout (1978), David S. Rohde (1996), and Clay Bennett (cartoonist), Clay Bennett (2002)."Pulitzer Prizes" at ''The Christian Science Monitor'' official website H ...
|