|
Ji Ru
Jiru () was a trusted personal servant of Emperor Gaozu, the founder of China's Han dynasty. Louis Crompton claims that Jiru was Gaozu's pillow companion, or homosexual lover, and that Jiru had more access to the emperor than did ministers.Louis Crompton, ''Homosexuality and Civilization'' (Cambridge, MA and London, Harvard University Press, 2003) Citing . Jiru was documented by Sima Qian in the ''Records of the Grand Historian The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st ce ...'': Gaozu's example of effectively elevating a male lover to the top of the administration would be followed by nine more rulers of the Han dynasty. This relationship was especially noted because Gaozu was a former brigand with coarse manners, while Jiru was considered elegant. References 2nd-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (surname 籍)
Jí is the Mandarin pinyin romanization of the Chinese surname written in Chinese character. It is romanized as Chi in Wade–Giles, and Zik in Cantonese. Ji is listed 275th in the Song dynasty classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. It is not among the 300 most common surnames in China. Origin According to the '' Zuo Zhuan'' and the Song dynasty encyclopedia '' Tongzhi'', the surname Ji 籍 originated from Bo Yan ( 伯黡), a chief minister of the state of Jin, a major power of the Spring and Autumn period. Boyan was in charge of government records, and was commonly referred to as Ji Yan (''ji'' 籍 means record). His descendants adopted Ji as their surname. During the Chu–Han Contention, many people surnamed Ji 籍 changed their surname to Xi 席 because of naming taboo of Xiang Yu, the Hegemon-King of Western Chu, whose given name was Ji 籍. Notable people *Bo Yan (伯黡) or Ji Yan, chief minister of the state of Jin *Ji Yan or Ji You ( 籍偃, fl. 6th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
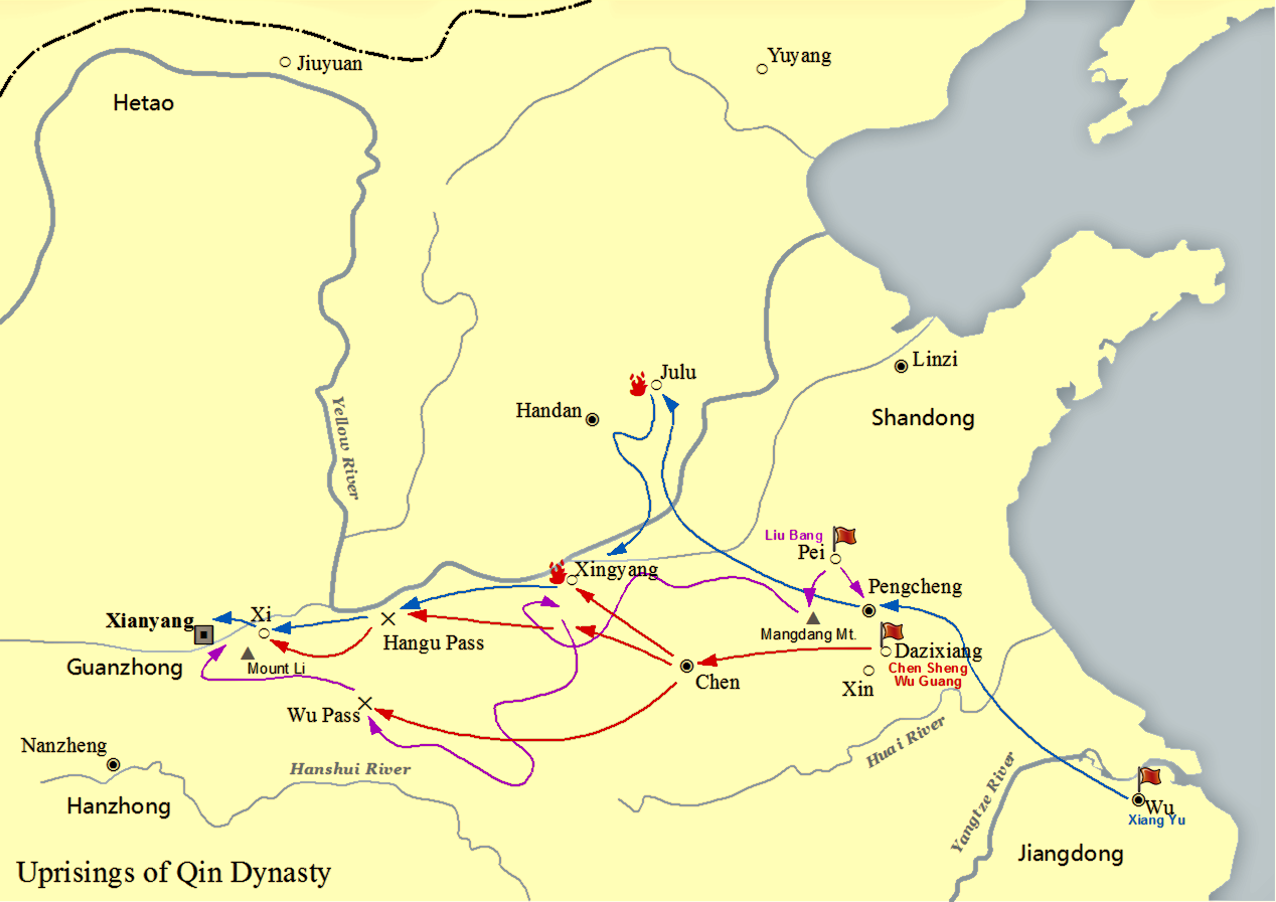
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one of the greatest emperors in history, credited with establishing the first Pax Sinica, one of China's longest golden ages. Liu Bang was among the few dynastic founders to have been born in a peasant family. He initially entered the Qin dynasty bureaucracy as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town in Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. During the political chaos following the death of Qin Shi Huang, who had been the first emperor in Chinese history, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became a rebel leader, taking up arms against the Qin dynasty. He outmanoeuvred rival rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland and forced the surrender of the Qin ruler Ziying in 206 BC. After the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Crompton
Louis Crompton (April 5, 1925 – July 11, 2009) was a Canadian scholar, professor, author, and pioneer in the instruction of queer studies. Biography Born to Master Mariner Clarence and Mabel Crompton, Crompton received an M.A. in mathematics from the University of Toronto in 1948 and a Ph.D. in English from the University of Chicago in 1954. After teaching mathematics at the University of British Columbia and the University of Toronto, he joined the English department at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln in 1955, retiring in 1989. During his career, he gained an international reputation as a scholar of the works of George Bernard Shaw. In 1970, Crompton taught a gay studies class at UNL, the Proseminar in Homophile Studies, the second such course offered in the United States, an action that raised LGBTQ awareness in academia, Nebraska, and the nation. The course provoked one Nebraska state legislator into introducing a bill that would ban any teaching on homosexuality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is an academic publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University. It is a member of the Association of University Presses. Its director since 2017 is George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint (trade name), imprint, which it inaugurated in May 1954 with the publication of the ''Harvard Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China covering more than two thousand years from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and formation of the first Chinese polity to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, during which Sima wrote. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Shiji'' served as a model for official histories for subsequent dynasties across the Sinosphere until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father, Sima Tan, first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill his father's dying wish of composing and putting together th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC by the Han dynasty historian Sima Qian, building upon work begun by his father Sima Tan. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Shiji'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and Qin Shi Huang, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Shiji'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historiographical conventions, the ''Shiji'' does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Hui Of Han
Emperor Hui of Han (; 210 BC – 26 September 188 BC), born Liu Ying (), was the second emperor of the Han dynasty. He was the second son of Emperor Gaozu, the first Han emperor, and the only son of Empress Lü from the powerful Lü clan. Emperor Hui is generally remembered as a somewhat weak character dominated and terrorized by his mother, Empress Lü, who became Empress Dowager after she encouraged her husband to command personally the war against Ying Bu, in which he died eventually from an arrow wound sustained during the war. Huidi was personally kind and well-intentioned, simple, hesitant, soft-hearted and generous, unable to escape the impact of his mother's viciousness. He tried to protect his younger half-brother Ruyi, Prince Yin of Zhao from being murdered by Empress Dowager Lü, but failed. After that, he indulged himself in drinking and sex, gave up government affairs to his mother, and died at a relatively young age. Emperor Hui's wife was Empress Zhang Yan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Ru
Hong Ru (閎孺) (also Hong Yu, Hong Jiru) (fl. c. 190 BCE) was the favorite companion of the Chinese Emperor Hui of Han. He and the emperor were also reputed to possibly be lovers. Hong Ru had much influence with the emperor, and his dress and cosmetics were imitated by other courtiers in an attempt to impress the emperor. These noblemen began wearing feathers in their hats, powdering their faces, and dangling sea shells from their clothes. Hong Yu was documented by China's Grand Historian Sima Qian. Sources *''Homosexuality and Civilization'' by Louis Crompton Louis Crompton (April 5, 1925 – July 11, 2009) was a Canadian scholar, professor, author, and pioneer in the instruction of queer studies. Biography Born to Master Mariner Clarence and Mabel Crompton, Crompton received an M.A. in mathemati ... References LGBTQ people from Imperial China Male lovers of royalty 2nd-century BC Chinese people {{China-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosexuality In China
Homosexuality has been documented in China since ancient times. According to one study by Bret Hinsch, for some time after the fall of the Han dynasty, homosexuality was widely accepted in China but this has been disputed. Several early Chinese emperors are speculated to have had homosexual relationships accompanied by heterosexual ones. There exists a dispute among sinologists as to when negative views of homosexual relationships became prevalent among the general Chinese population, with some scholars arguing that it was common by the time of the Ming dynasty, established in the 14th century, following homophobia entrenched in the Mongol empire and the Yuan dynasty, and others arguing that anti-gay attitudes became entrenched during the Westernization efforts of the late Qing dynasty and the early Republic of China in the 19th and 20th centuries. For most of the 20th century homosexuality in China had been legal, except for a period between 1979 and 1997 where male anal sex wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBTQ People From Imperial China
LGBTQ people are individuals who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or questioning. Many variants of the initialism are used; LGBTQIA+ people incorporates intersex, asexual, aromantic, agender, and other individuals. The group is generally conceived as broadly encompassing all individuals who are part of a sexual or gender minority, including all sexual orientations, romantic orientations, gender identities, and sex characteristics that are not heterosexual, heteroromantic, cisgender, or endosex, respectively. Scope and terminology A broad array of sexual and gender minority identities are usually included in who is considered LGBTQ. The term ''gender, sexual, and romantic minorities'' is sometimes used as an alternative umbrella term for this group. Groups that make up the larger group of LGBTQ people include: * People with a sexual orientation that is non-heterosexual, including lesbians, gay men, bisexual people, and asexual people * People who are trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |