|
Jew (word)
The English term ''Jew'' is originally derived from the Hebrew term '' Yehudi'' (), which passed into Greek as '' Ioudaios'' and into Latin as ''Iudaeus'', in turn evolving into the Old French term ''giu'' after the letter "d" was dropped. A variety of related forms are found in early English from about the year 1000, including ''Iudea'', ''Gyu'', ''Giu'', ''Iuu'', ''Iuw'', and ''Iew'', which eventually developed into the modern English word for the Jews, Jewish people. Etymology ''Yehudi'' in the Hebrew Bible According to the Book of Genesis, Judah (, ''Yehudah'') was the name of the fourth son of the patriarch Jacob. During the Exodus, the name was given to the Tribe of Judah, descended from the patriarch Judah. After the conquest and settlement of the land of Canaan, Judah also referred to the territory allocated to the tribe. After the splitting of the united Kingdom of Israel, the name was used for the southern kingdom of Judah. The kingdom now encompassed the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah (son of Jacob), Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was one of the tribes to take its place in Canaan, occupying its southern part. Jesse (biblical figure), Jesse and his sons, including King David, belonged to this tribe. The Tribe of Judah played a central role in the Deuteronomistic history, which encompasses the books of Book of Deuteronomy, Deuteronomy through Books of Kings, II Kings. After the death of King Solomon, the Tribe of Judah, along with the Tribe of Tribe of Benjamin, Benjamin, the Tribe of Dan, and the Levites formed the Southern Kingdom of Judah, with Jerusalem and Hebron as its capital. The kingdom lasted until its conquest by Babylon in BCE. The tribe's symbol was the lion, which was often represented in Jewish art. After the Babylonian captivity, the distinction between the Tribes was largely lost, but the term "Judah", via ''Ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimei
Shimei ( ''Šīmʿī'') is the name of a number of persons referenced in the Hebrew Bible and Rabbinical literature. *The second son of Gershon and grandson of Levi (; ; ). The family of the Shimeites, as a branch of the tribe of Levi, is mentioned in ; ("Shimei" in verse 9 could be a scribal error''Jewish Encyclopedia'' (1906), "Shimei."); and in Zechariah 12:13. In the New Testament the name occurs in , spelled Semei in the King James Version. * Shimei ben Gera, a Benjamite of Bahurim, son of Gera, "a man of the family of the house of Saul" (; ). He is mentioned as one of David's tormentors during his flight before Absalom, and as imploring and winning David's forgiveness when the latter returned. David, however, in his dying charge to Solomon, bade him avenge the insult (). Jewish scribes say that Solomon's teacher was Shimei (son of Gera), and while he lived, he prevented Solomon from marrying foreign wives. The Talmud says at Ber. 8a: "For as long as Shimei the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordecai
Mordecai (; also Mordechai; , IPA: ) is one of the main personalities in the Book of Esther in the Hebrew Bible. He is the cousin and guardian of Esther, who became queen of Persia under the reign of Ahasuerus (Xerxes I). Mordecai's loyalty and bravery are highlighted in the story as he helps Esther foil the plot of Haman, the king's vizier, to exterminate the Jewish people. His story is celebrated in the Jewish holiday of Purim, which commemorates his victory. One theory frequently discussed in scholarship suggests that the Book of Esther serves as an etiology for Purim, with Mordecai and Esther representing the Babylonian gods Marduk and Ishtar in a historicized Babylonian myth or ritual. The identification of Mordecai in the Book of Esther with a Persian official named "Marduka" mentioned in an inscription from the reign of Xerxes is debated, with some scholars supporting the connection while others find it unconvincing because the name was common. Biblical account Mord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
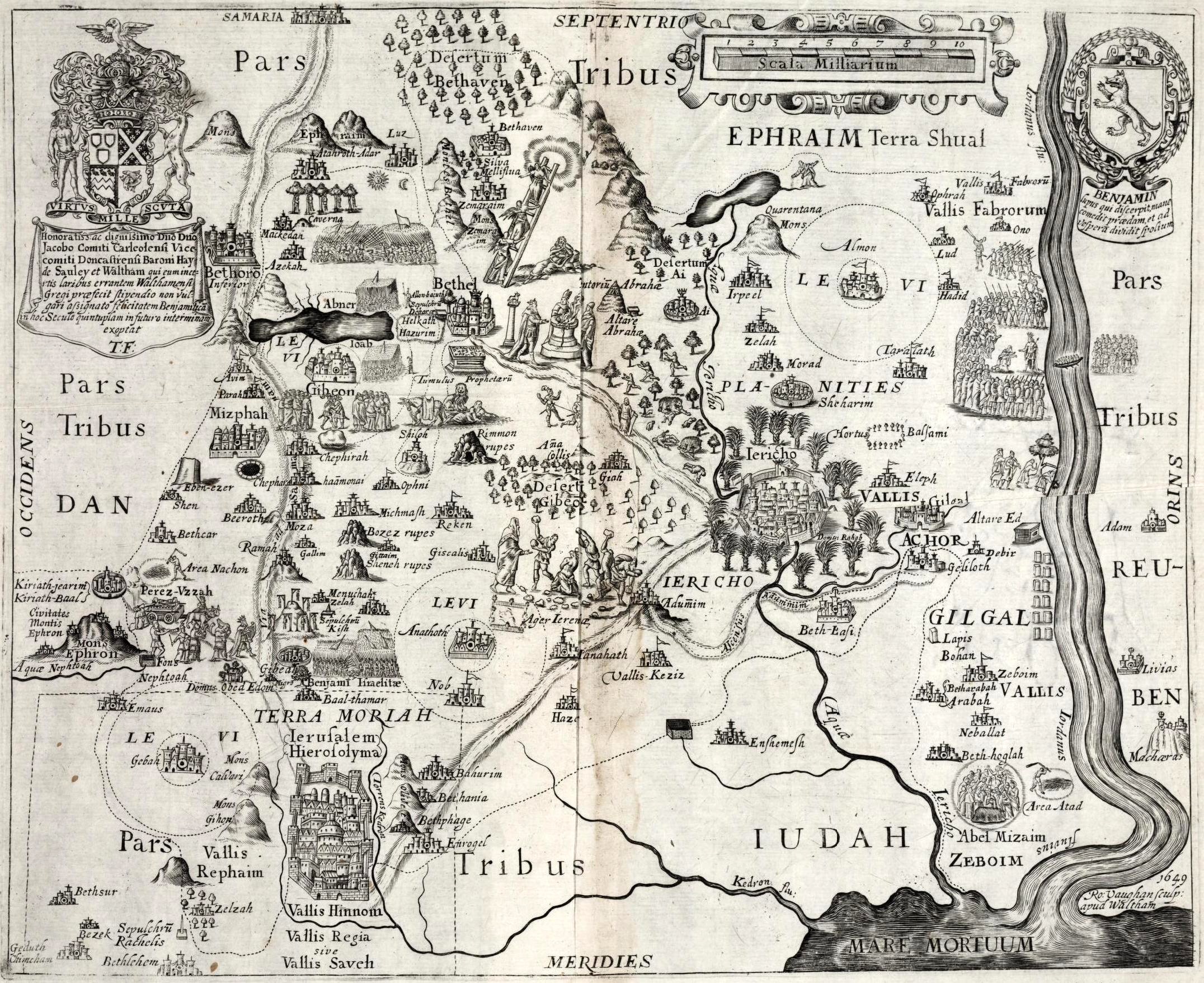
Tribe Of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the Samaritan Pentateuch the name appears as ''Binyamēm'' (Samaritan Hebrew: ). The Tribe of Benjamin, located to the north of the Tribe of Judah but to the south of the later Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel, is significant in biblical narratives as a source of various Israelites, Israelite leaders, including the first Israelite king, Saul, as well as earlier tribal leaders in the period of the Hebrew Bible judges, Judges. In the period of the Judges, they feature in an episode in which a civil war results in their near-extinction as a tribe. After the brief period of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel, Benjamin became part of the southern Kingdom of Judah following the split into two kingdoms. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text (MT or 𝕸; ) is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (''Tanakh'') in Rabbinic Judaism. The Masoretic Text defines the Jewish canon and its precise letter-text, with its vocalization and accentuation known as the ''masora''. Referring to the Masoretic Text, ''masora'' specifically means the diacritic markings of the text of the Jewish scriptures and the concise marginal notes in manuscripts (and later printings) of the Tanakh which note textual details, usually about the precise spelling of words. It was primarily copied, edited, and distributed by a group of Jews known as the Masoretes between the 7th and 10th centuries of the Common Era (CE). The oldest known complete copy, the Leningrad Codex, dates to 1009 CE and is recognized as the most complete source of biblical books in the Ben Asher tradition. It has served as the base text for critical editions such as Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia and Adi. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age. Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations and other peoples.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture ... In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature. Given the information available, one cannot maintain a radical cultural separation between Canaanites and Israelites for the Iron I period." (pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Israel (Samaria)
The Kingdom of Israel ( ), also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. It controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan (region), Transjordan; the former two regions underwent a period in which a large number of new settlements were established shortly after the kingdom came into existence. It had four capital cities in succession: Shiloh (biblical city), Shiloh, Shechem, Tirzah (ancient city), Tirzah, and the Samaria (ancient city), city of Samaria. In the 9th century BCE, it was ruled by the Omrides, Omride dynasty, whose political centre was the city of Samaria. According to the Hebrew Bible, the territory of the Twelve Tribes of Israel was once amalgamated under a Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, which was ruled by the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Levi
According to the Bible, the Tribe of Levi is one of the tribes of Israel, traditionally descended from Levi, son of Jacob. The descendants of Aaron, who was the first High Priest of Israel, were designated as the priestly class, the Kohanim. The Tribe of Levi served particular religious duties for the Israelites and had political responsibilities as well. In return, the landed tribes were expected to give tithes to the Kohanim, the priests working in the Temple in Jerusalem, particularly the first tithe. The Levites who were not Kohanim played music in the Temple or served as guards. Most scholars view the Torah as projecting the origins of the Levites into the past to explain their role as landless cultic functionaries. When Joshua led the Israelites into the land of Canaan, the Levites were the only Israelite tribe that received cities but were not allowed land tenure; Joshua 13:33, "But no portion was assigned by Moses to the tribe of Levi; YHWH God of Israel is their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Simeon
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Simeon (; ''Šīm‘ōn'', "hearkening/listening/understanding/empathizing") was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. The Book of Joshua locates its territory inside the boundaries of the Tribe of Judah (Joshua 19:9). It has been usually counted as one of the ten lost tribes, although its territory was surrounded by and gradually being absorbed by Judah from the start. For any Simeonites to be of the Northern Kingdom of Israel or to be affected by the Assyrian sack of the kingdom (future lost tribes) would imply a northward migration at some point in time, with support perhaps from 2 Chronicles (15:9 and 34:6,7). The biblical narrative has it coming into the Land of Israel following the Exodus, while scholarly reconstructions have offered a variety of opinions as to its origins and early history. From the Book of Genesis until the Babylonian captivity, the Bible provides various details about its history, after which point it disappears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the Samaritan Pentateuch the name appears as ''Binyamēm'' (Samaritan Hebrew: ). The Tribe of Benjamin, located to the north of the Tribe of Judah but to the south of the later Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel, is significant in biblical narratives as a source of various Israelites, Israelite leaders, including the first Israelite king, Saul, as well as earlier tribal leaders in the period of the Hebrew Bible judges, Judges. In the period of the Judges, they feature in an episode in which a civil war results in their near-extinction as a tribe. After the brief period of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel, Benjamin became part of the southern Kingdom of Judah following the split into two kingdoms. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |