|
Jesús Arango Cano
Jesús Arango Cano (21 June 1915 – 9 January 2015) was a Colombian economist, diplomat, anthropologist, archaeologist and writer. Biography Arango Cano was born in La Tebaida, Quindío, La Tebaida, Colombia, a village that his father, archaeologist Luis Arango Cardona, founded a year after his birth. He attended the Rutgers Preparatory School in New Brunswick, New Jersey and studied Economy at the University of California and later International Relations at Columbia University, New York. In the 1940s Arango Cano became consul (representative), consul for Colombia in São Paulo, Brazil and Undersecretary of International Relations. Arango Cano has written more than fifty books of which 40 are published. His first two books were ''Inmigración para Colombia'', published in 1951, and ''Inmigración y Colonización en la Gran Colombia'' in 1953. In 1965 Arango published his book ''Mitos, leyendas y dioses chibchas'', about the Muisca mythology, myths, legends and Muisca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tebaida, Quindío
La Tebaida () is a municipality in the western part of the department of Quindío, Colombia. It's located 17 km southwest of the departmental capital Armenia. History La Tebaida was founded by Luis Arango Cardona, born in Manizales, Caldas on February 19, 1879. He was one of the first people to undertake systematic archaeological studies of the indigenous tombs (''guacas'') in Quindío. His research led to the publication in 1924 of his two-volume book ''Recuerdos de la guaquería en el Quindío'', the first study of its type in Colombia. In 1899, Arango and his brother had started a farm with an area of 6.7 km² in the south of Armenia. They named their farm La Tebaida, the name of a region in Egypt where Christian monks had sought solitude for contemplation and prayer. In order to increase the productivity of their land, they divided it into 10 hectare blocks. The brothers distributed these to approximately 60 families, who paid the owners with a proportion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consul (representative)
A consul is an official representative of a government who resides in a foreign country to assist and protect citizens of the consul's country, and to promote and facilitate commercial and diplomatic relations between the two countries. A consul is generally part of a government's diplomatic corps or Diplomatic service, foreign service, and thus enjoys certain privileges and protections in the host state, albeit without full diplomatic immunity. Unlike an ambassador, who serves as the single representative of one government to another, a state may appoint several consuls in a foreign nation, typically in major cities; consuls are usually tasked with providing assistance in bureaucratic issues to both citizens of their own country traveling or living abroad and to the citizens of the country in which the consul resides who wish to travel to or trade with the consul's country. Origin and history Antecedent: the classical Greek ''proxenos'' In classical Greece, some of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
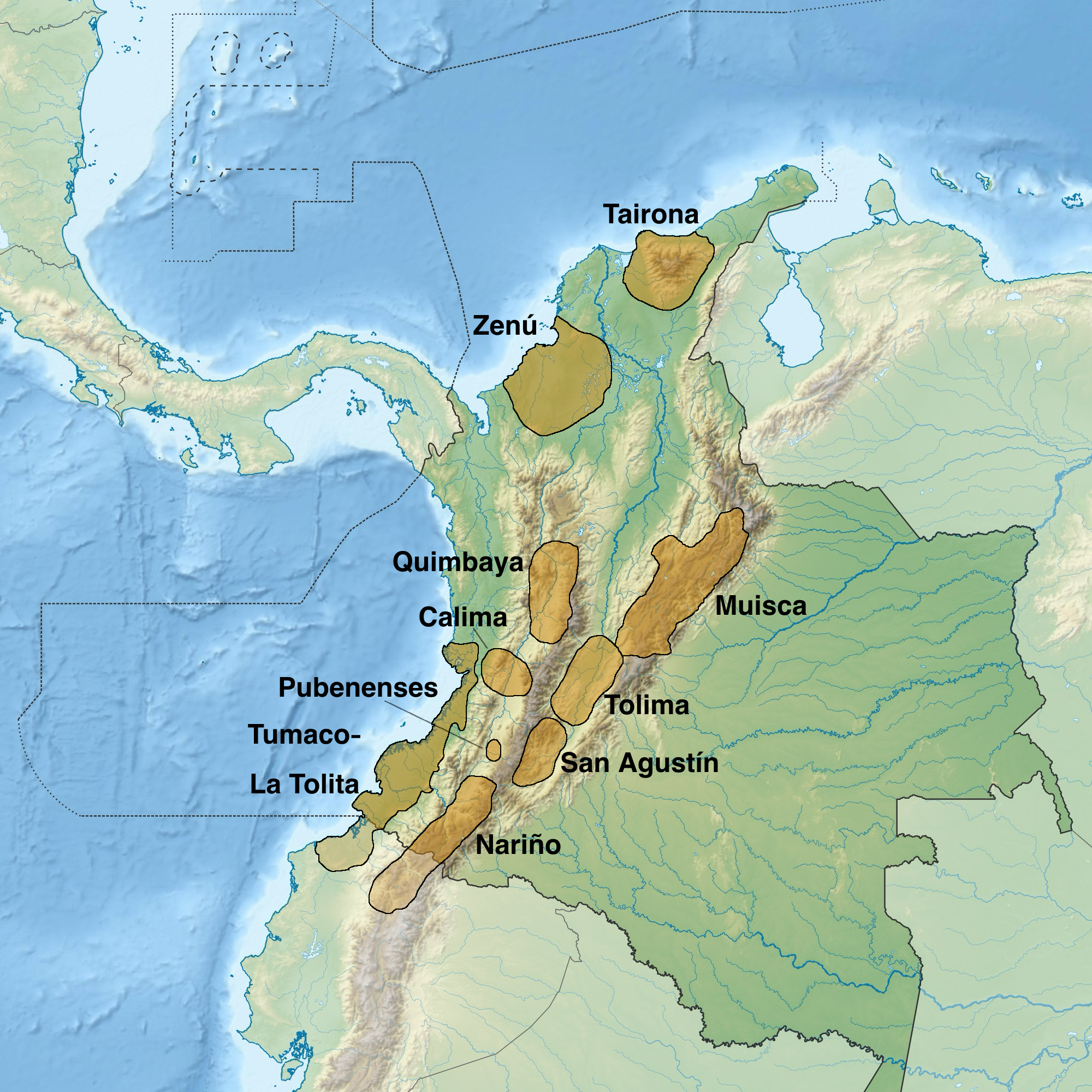
Muzo People
The Muzo people are a Cariban languages, Cariban-speaking Indigenous group who inhabited the western slopes of the eastern Colombian Andes. They were a highly war-like tribe who frequently clashed with their neighbouring Indigenous groups, especially the Muisca. The Muzo inhabited the right banks of the Magdalena River in the lower elevations of western Boyacá Department, Boyacá and Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and were known as the Emerald People, thanks to their exploitation of the gemstone in Muzo. During the time of Spanish conquest of the Muisca, conquest, they resisted heavily against the Spanish invaders taking twenty years to submit the Muzo. Knowledge about the Muzo people has been provided by List of Muisca and pre-Muisca scholars, chroniclers Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Pedro Simón, Juan de Castellanos, Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita and others. Muzo territory The Muzo were inhabiting the lower-elevation northwestern areas of the Cundinamarca departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially available. There are also various coffee substitutes. Typically served hot, coffee has the highest sales in the world market for hot drinks. Coffee production begins when the seeds from coffee cherries (the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits) are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The "beans" are roasted and then ground into fine particles. Coffee is brewed from the ground roasted beans, which are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often added to mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Coffee Growing Axis
The Coffee Axis () is a geographic, cultural, economic and ecological region of Colombia, located in the departments of Caldas, Risaralda and Quindío, as well as the regions of northwestern Tolima, northern and eastern Valle del Cauca and southwestern Antioquia, including the capital cities of the first four departments mentioned (Manizales, Pereira, Colombia, Pereira, Armenia, Colombia, Armenia and Ibagué, respectively). History of coffee Coffee was first grown commercially in Colombia in Salazar de las Palmas, north of Santander, and over the twentieth century grew to be Colombia's primary export. When coffee was first brought into the country, the leaders tried to push the farming of coffee beans, but was met with resistance from the people because it takes about 5 years until the first harvest of the bean. In 1999 coffee revenues represented 3.7% of gross domestic product (gdp) and 37% of agricultural employment. The main coffee-producing departments are: Nariño, Norte de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Civilization
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco (altepetl), Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of Colombia
Indigenous Colombians (), also known as Native Colombians (), are the ethnic groups who have inhabited Colombia before the Spanish colonization of Colombia, in the early 16th century. Estimates on the percentage of Colombians who are indigenous vary, from 3% or 1.5 million to 10% or 5 million. According to the 2018 Colombian census, they comprise 4.4% of the country's population, belonging to 115 different tribes, up from 3.4% in the 2005 Colombian census. However, a Latinobarómetro survey from the same year found that 10.4% of Colombian respondents self-identified as indigenous. The most recent estimation of the number of indigenous peoples of Colombia places it at around 9.5% of the population. This places that Colombia as having the seventh highest percentage of Indigenous peoples in the Americas with Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador, Guatemala, Peru, and Panama having a higher estimated percentage of Indigenous peoples than Colombia. The percentage of Indigenous peoples has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calima Culture
Calima culture (200 BCE–400 CE) is a series of Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia, pre-Columbian cultures from the Valle del Cauca in Colombia."Calima Darién Archaeological Museum: 10,000 Years of History." ''Colombia''. (retrieved 1 Dec 2011) The four societies that successively occupied the valley and make up Calima culture are the Ilama, Yotoco, Sonso, and Malagana, Malagana cultures. The Calima Darién Archaeological Museum and the Calima Gold Museum feature artifacts from the Calima culture. Ilama culture By 1500 BCE the Ilama culture, the first Agricultural-Pottery society, appeared along the Calima River, near ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quimbaya Culture
The Quimbaya () were a small, ancient indigenous group in present-day Colombia noted for their gold work characterized by technical accuracy and detailed designs. The majority of the gold work is made in ''tumbaga'' alloy, with 30% copper, which colours the pieces. History The Quimbaya inhabited the areas corresponding to the modern departments of Quindío, Caldas and Risaralda in Colombia, around the valley of the Cauca River. There is no clear data about when they were initially established; the current best guess is around the 1st century BCE. The name "quimbaya" has become a traditional generic term to refer to many of the productions and objects found in this geographical area, even if they cannot technically be traced to this same ethnic group and can be dated to different epochs in time. The Quimbaya people reached their zenith during the 4th to 7th century CE period known as The Quimbaya Classic. The culture's most emblematic piece comes from this period, a form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca People
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are indigenous peoples in Colombia and were a Pre-Columbian culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The Muisca speak Muysccubun, a language of the Chibchan language family, also called ''Muysca'' and ''Mosca''. The first known contact with Europeans in the region was in 1537 during the Spanish conquest of New Granada. In New Spain, Spanish clerics and civil officials had a major impact on the Muisca, attempting to Christianize and incorporate them into the Spanish Empire as subjects. Postconquest Muisca culture underwent significant changes due to the establishment of the New Kingdom of Granada. Sources for the Muisca are far less abundant than for the Aztec Empire of Mesoamerica or the Inca Empire and their incorporation to the Spanish Empire during the colonial era. In the New Kingdom of Granada and into the colonial era, the Muisca became " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |