|
Jens Toller Rosenheim
Jens Toller Rosenheim (born 1636 in Christiania, died in 1690 in Dublin), was a Norwegian nobleman, jurist and official. Family and marriage Jens Toller was the son of Niels Toller (1592-1642), who was Mayor of Christiania (now Oslo) and one of the leading merchants in the city. His father had originally come from Haderslev. Upon his father's death, Jens and his brother Niels inherited a large fortune. Jens Toller attended the University of Copenhagen (1652) and the University of Leiden (1658). He married in 1666 Anne Hansdatter Lilienskiold (d. ca 1680), the daughter of Hans Hansen Lilienskiold (1610-1681) who was the Mayor of Bergen. General history Jens Toller became lawyer in 1666. He was in 1676 ennobled under the surname Rosenheim. In 1679, he became the judge of the Supreme Court. In 1676 he became a deputy in the Danish Chancellery. In 1677, he became a county governor in Lister and Mandal county, a post he held until 1681. He also temporarily served as a stewart (act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of in 2019, and the metropolitan area had an estimated population of in 2021. During the Viking Age the area was part of Viken. Oslo was founded as a city at the end of the Viking Age in 1040 under the name Ánslo, and established as a ''kaupstad'' or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada. The city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 reduced its influence. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in honour of the king. It became a municipality (''formannskapsdistrikt'') on 1 January 1838. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vest-Agder
Vest-Agder (; "West Agder") was one of 18 counties (''fylker'') in Norway up until 1 January 2020, when it was merged with Aust-Agder to form Agder county. In 2016, there were 182,701 inhabitants, around 3.5% of the total population of Norway. Its area was about . The county administration was located in its largest city, Kristiansand. Vest-Agder was a major source of timber for Dutch and later English shipping from the 16th century onwards. Historically, the area exported timber, wooden products, salmon, herring, ships, and later nickel, paper, and ferrous and silica alloys. Compared to other counties of Norway, today's exports-intensive industry produces shipping and offshore equipment (National Oilwell Varco), cranes (Cargotec), ships (Umoe Mandal, Flekkefjord Slip), wind turbine equipment, nickel ( Glencore), and solar industry microsilica ( Elkem). A major tourist attraction is Kristiansand Dyrepark. Vest-Agder grew to political prominence with the decision of King Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Danielsen Knoff
Daniel Danielsen Knoff (1614–1687) was a Dano-Norwegian civil servant and politician. He served as the County Governor of three different counties: Romsdalen county from 1680 until 1681, Lister og Mandal county from 1681 until 1683, and in Stavanger county from 1683 until his death in 1687. Knoff was born in Roskilde in Denmark. He was a Norwegian businessman and customs administrator. In 1649, he was employed as a customs officer at Bragernes, working as the general customs administrator over the southern part of Norway from 1655 to 1670 and 1673–80. He built a large farm at Strømsø and owned several ironworks and farms in the area. Knoff played an important role in the fight for market town rights for Strømsø and Bragernes (later they merged to form the town of Drammen Drammen () is a city and municipality in Viken (county), Viken, Norway. The port and river city of Drammen is centrally located in the south-eastern and most populated part of Norway. Drammen mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hamilton (Norwegian Governor)
Robert Thomas Hamilton (died 1677) was a military officer who served in Denmark and Norway. He served as the first County Governor of Lister og Mandal county from 1671 until around 1675. Robert Hamilton was born in Scotland. He began as an officer for army for the Kingdom of Denmark-Norway in 1657, serving in the cavalry. This was during a time of an alliance between the House of Stuart who ruled in Britain and the House of Oldenburg who ruled in Denmark-Norway. He was promoted to captain in Norway in 1658 and became a colonel watchmaster in 1660. Hamilton's promotion continued and he made lieutenant colonel in 1661 due to a commendation by King Charles II. He was also named a Knight of the Elephant the same year. In 1668, King Frederik III of Denmark-Norway ordered the Governor-general of Norway to pay 2000 rigsdaler of the army's money to Hamilton in advance of his wages. In 1670, Hamilton left the cavalry and became commander of Kronborg Castle and was also appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
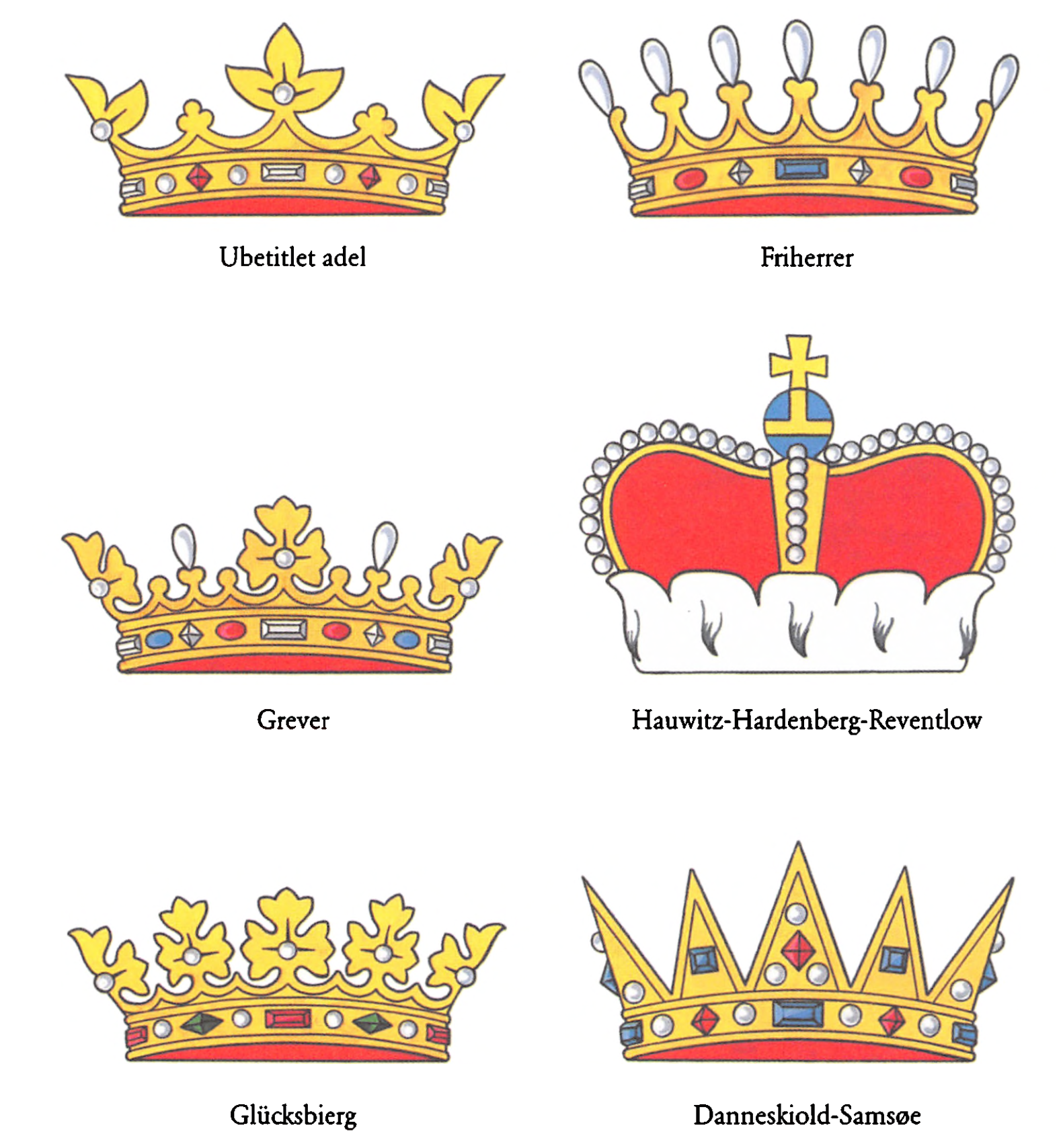
Danish Nobility
Danish nobility is a social class and a former estate in the Kingdom of Denmark. The nobility has official recognition in Denmark, a monarchy. Its legal privileges were abolished with the constitution of 1849. Some of the families still own and reside in castles or country houses. A minority of nobles still belong to the elite, and they are as such present at royal events where they hold court posts, are guests, or are objects of media coverage, for example Kanal 4's TV-hostess Caroline Fleming née Baroness Iuel-Brockdorff. Some of them own and manage companies or have leading positions within business, banking, diplomacy and NGOs. Historians divide the Danish nobility into two categories: ancient nobility ( da, uradel) and letter nobility ( da, brevadel) based on the way they achieved nobility. Another status based categorization distinguishes between higher and lower nobility ( da, højadel, lavadel). "Ancient nobility" refer to those noble families that are known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crest (heraldry)
A crest is a component of a heraldic display, consisting of the device borne on top of the helm. Originating in the decorative sculptures worn by knights in tournaments and, to a lesser extent, battles, crests became solely pictorial after the 16th century (the era referred to by heraldists as that of "paper heraldry"). A normal heraldic achievement consists of the shield, above which is set the helm, on which sits the crest, its base encircled by a circlet of twisted cloth known as a torse. The use of the crest and torse independently from the rest of the achievement, a practice which became common in the era of paper heraldry, has led the term "crest" to be frequently but erroneously used to refer to the arms displayed on the shield, or to the achievement as a whole. Origin The word "crest" derives from the Latin ''crista'', meaning "tuft" or "plume", perhaps related to ''crinis'', "hair". Crests had existed in various forms since ancient times: Roman officers wore fans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinister (heraldry)
''Dexter'' and ''sinister'' are terms used in heraldry to refer to specific locations in an escutcheon bearing a coat of arms, and to the other elements of an achievement. ''Dexter'' (Latin for 'right') indicates the right-hand side of the shield, as regarded by the bearer, i.e. the bearer's proper right, and to the left as seen by the viewer. ''Sinister'' (Latin for 'left') indicates the left-hand side as regarded by the bearer – the bearer's proper left, and to the right as seen by the viewer. In vexillology, the equivalent terms are '' hoist'' and ''fly''. Significance The dexter side is considered the side of greater honour, for example when impaling two arms. Thus, by tradition, a husband's arms occupy the dexter half of his shield, his wife's paternal arms the sinister half. The shield of a bishop shows the arms of his see in the dexter half, his personal arms in the sinister half. King Richard II adopted arms showing the attributed arms of Edward the Confessor in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexter (heraldry)
''Dexter'' and ''sinister'' are terms used in heraldry to refer to specific locations in an escutcheon bearing a coat of arms, and to the other elements of an achievement. ''Dexter'' (Latin for 'right') indicates the right-hand side of the shield, as regarded by the bearer, i.e. the bearer's proper right, and to the left as seen by the viewer. ''Sinister'' (Latin for 'left') indicates the left-hand side as regarded by the bearer – the bearer's proper left, and to the right as seen by the viewer. In vexillology, the equivalent terms are ''hoist'' and '' fly''. Significance The dexter side is considered the side of greater honour, for example when impaling two arms. Thus, by tradition, a husband's arms occupy the dexter half of his shield, his wife's paternal arms the sinister half. The shield of a bishop shows the arms of his see in the dexter half, his personal arms in the sinister half. King Richard II adopted arms showing the attributed arms of Edward the Confessor in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. He was the last Catholic monarch of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religious tolerance, but it also involved struggles over the principles of absolutism and the divine right of kings. His deposition ended a century of political and civil strife in England by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown. James succeeded to the thrones of England, Ireland, and Scotland following the death of his brother with widespread support in all three countries, largely because the principles of eligibility based on divine right and birth were widely accepted. Tolerance of his personal Catholicism did not extend to tolerance of Catholicism in general, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William III Of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s, and King of England, Ireland, and Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is commemorated by Unionists, who display orange colours in his honour. He ruled Britain alongside his wife and cousin, Queen Mary II, and popular histories usually refer to their reign as that of "William and Mary". William was the only child of William II, Prince of Orange, and Mary, Princess Royal, the daughter of King Charles I of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His father died a week before his birth, making William III the prince of Orange from birth. In 1677, he married h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |