|
Jean Barraqué
Jean-Henri-Alphonse Barraqué (17 January 1928 – 17 August 1973) was a French composer and music writer. His relatively small is known for its serialism. Life Barraqué was born in Puteaux, Hauts-de-Seine. In 1931, he moved with his family to Paris. He studied in Paris with Jean Langlais and Olivier Messiaen and, through Messiaen, became interested in serialism. After completing his Piano Sonata in 1952, he suppressed or destroyed his earlier works. A book published by the French music critic André Hodeir, titled ''Since Debussy'', created controversy around Barraqué by claiming this work as perhaps the finest piano sonata since Beethoven. As the work had still not been publicly performed, and only two other works by him had at this time, the extravagant claims made for Barraqué in this book were received with some scepticism. Whilst with hindsight it is clear that Hodeir had accurately perceived the exceptional features of Barraqué's music—notably its searing Romantic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music. Etymology and definition The term is descended from Latin, ''compōnō''; literally "one who puts together". The earliest use of the term in a musical context given by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' is from Thomas Morley's 1597 ''A Plain and Easy Introduction to Practical Music'', where he says "Some wil be good descanters ..and yet wil be but bad composers". "Composer" is a loose term that generally refers to any person who writes music. More specifically, it is often used to denote people who are composers by occupation, or those who work in the tradition of Western classical music. Writers of exclusively or primarily songs may be called composers, but since the 20th century the terms ' songwriter' or ' singer-songwriter' are more often used, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Music
Electronic music broadly is a group of music genres that employ electronic musical instruments, circuitry-based music technology and software, or general-purpose electronics (such as personal computers) in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means (electroacoustic music). Pure electronic instruments depend entirely on circuitry-based sound generation, for instance using devices such as an electronic oscillator, theremin, or synthesizer: no acoustic waves need to be previously generated by mechanical means and then converted into electrical signals. On the other hand, electromechanical instruments have mechanical parts such as strings or hammers that generate the sound waves, together with electric elements including pickup (music technology), magnetic pickups, power amplifiers and loudspeakers that convert the acoustic waves into electrical signals, process them and convert them back into sound waves. Such electromechanical devices in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian and American composer, music theorist, teacher and writer. He was among the first Modernism (music), modernists who transformed the practice of harmony in 20th-century classical music, and a central element of his music was its use of motive (music), motives as a means of coherence. He propounded concepts like developing variation, the emancipation of the dissonance, and the "unified field, unity of musical space". Schoenberg's early works, like ''Verklärte Nacht'' (1899), represented a Brahmsian–Wagnerian synthesis on which he built. Mentoring Anton Webern and Alban Berg, he became the central figure of the Second Viennese School. They consorted with visual artists, published in ''Der Blaue Reiter'', and wrote atonal, expressionist music, attracting fame and stirring debate. In his String Quartets (Schoenberg)#String Quartet No. 2, Op. 10, String Quartet No. 2 (1907–1908), ''Erwartung'' (1909), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alban Berg
Alban Maria Johannes Berg ( ; ; 9 February 1885 – 24 December 1935) was an Austrian composer of the Second Viennese School. His compositional style combined Romantic lyricism with the twelve-tone technique. Although he left a relatively small ''oeuvre'', he is remembered as one of the most important composers of the 20th century for his expressive style encompassing "entire worlds of emotion and structure". Berg was born and lived in Vienna. He began to compose at the age of fifteen. He studied counterpoint, music theory and harmony with Arnold Schoenberg between 1904 and 1911, and adopted his principles of ''developing variation'' and the twelve-tone technique. Berg's major works include the operas '' Wozzeck'' (1924) and ''Lulu'' (1935, finished posthumously), the chamber pieces '' Lyric Suite'' and Chamber Concerto, as well as a Violin Concerto. He also composed a number of songs ('' lieder''). He is said to have brought more "human values" to the twelve-tone system; hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Webern
Anton Webern (; 3 December 1883 – 15 September 1945) was an Austrian composer, conductor, and musicologist. His music was among the most radical of its milieu in its lyric poetry, lyrical, poetic concision and use of then novel atonality, atonal and twelve-tone technique, twelve-tone techniques. His approach was typically rigorous, inspired by his studies of the Franco-Flemish School under Guido Adler and by Arnold Schoenberg's emphasis on structure in teaching composition from the music of Johann Sebastian Bach, the First Viennese School, and Johannes Brahms. Webern, Schoenberg, and their colleague Alban Berg were at the core of what became known as the Second Viennese School. Webern was arguably the first and certainly the last of the three to write music in an Aphorism, aphoristic and Expressionist music, expressionist style, reflecting his instincts and the idiosyncrasy of his compositional process. He treated themes of love, loss, nature, and spirituality, working from his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
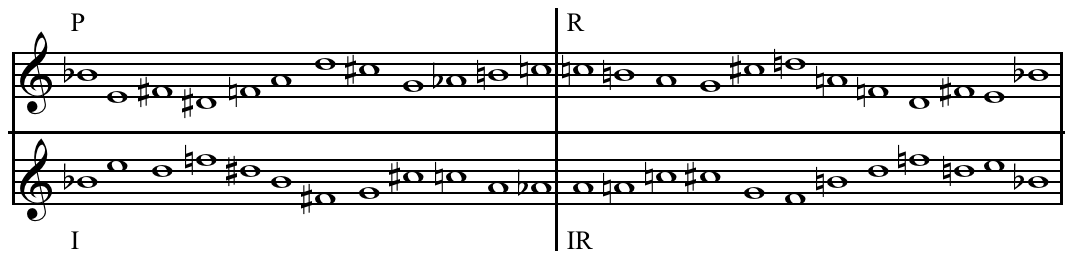
Tone Row
In music, a tone row or note row ( or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found. History and usage Tone rows are the basis of Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique and most types of serial music. Tone rows were widely used in 20th-century contemporary music, like Dmitri Shostakovich's use of twelve-tone rows, "without dodecaphonic transformations." A tone row has been identified in the A minor prelude, BWV 889, from book II of J.S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'' (1742) and by the late eighteenth century it is found in works such as Mozart's C major String Quartet, K. 157 (1772), String Quartet in E-flat major, K. 428, String Quintet in G minor, K. 516 (1790), and the Symphony in G minor, K. 550 (1788). Beethoven also used the technique but, on the whole, "Mozart seems to have employed seria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher. He began his career as a classical philology, classical philologist, turning to philosophy early in his academic career. In 1869, aged 24, Nietzsche became the youngest professor to hold the Chair of Classical Philology at the University of Basel. Plagued by health problems for most of his life, he resigned from the university in 1879, and in the following decade he completed much of his core writing. In 1889, aged 44, he suffered a collapse and thereafter a complete loss of his mental faculties, with paralysis and vascular dementia. He lived his remaining years under the care of his family until his death. Friedrich Nietzsche bibliography, His works and Philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche, his philosophy have fostered not only extensive scholarship but also much popular interest. Nietzsche's work encompasses philosophical polemics, poetry, cultural criticism and fiction, while displaying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concerto (Barraqué)
The Concerto for six instrumental formations and two solo instruments (vibraphone and clarinet) is a work composed by Jean Barraqué, started in 1962 and finished in 1968. History The initial impulse to write the Concerto came when Pierre Boulez wrote to Barraqué asking for a new work for the Domaine musical's 1962–63 season. Barraqué wrote back, suggesting the Concerto, and he began composing it on Easter Monday, 23 April 1962. He did not finish it at that time, however. He resumed work in the summer of 1968 in Perros-Guirec, and completed the score in Florence on 22 October of the same year. It was premiered on 20 November 1968 at the Royal Festival Hall in London, by Hubert Rostaing (clarinet), Tristan Fry (vibraphone), and the BBC Symphony Orchestra conducted by Gilbert Amy. The manuscript score was dedicated on 20 March 1969 to Claude and Hubert Rostaing.; ; . Instrumentation There are two solo instruments, clarinet and vibraphone, accompanied by six instrumental fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Au Delà Du Hasard
Au, AU, au or a.u. may refer to: Science and technology Computing * .au, the internet country code for Australia * Au file format, Sun Microsystems' audio format * Audio Units, a system level plug-in architecture from Apple Computer * Adobe Audition, a sound editor program * Windows Update or Automatic Updates, in Microsoft Windows * Windows 10 Anniversary Update, of August 2016a * Gold, chemical symbol Au * Absorbance unit, a reporting unit in spectroscopy * Atomic units, a system of units convenient for atomic physics and other fields * Ångström unit, a unit of length equal to 10−10 m or 0.1 nanometre. * Astronomical unit, a unit of length used in planetary systems astronomy * Arbitrary unit, a placeholder unit for when the actual value of a measurement is unknown or unimportant Arts and entertainment Music * AU (band), an experimental pop group headed by Luke Wyland * ''Au'', a 2010 release by Scottish rock band Donaldson, Moir and Paterson * ''Au'' a track on Some Time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Temps Restitué
''Le Temps restitué'' (Time Regiven) is a work for mezzo-soprano solo, choir, and orchestra by the French composer Jean Barraqué. It was both the first part to have been begun and the last one to be completed in his projected but unfinished cycle of works based on Hermann Broch's novel, '' The Death of Virgil''. A performance lasts about forty minutes. History In March 1956, Barraqué first formed a plan to set passages, in the French translation by Albert Kohn, from the second book ("Fire—The Descent") of Hermann Broch's novel ''The Death of Virgil'', and straightaway began composing ''Le Temps restitué''. He finished a first draft in Paris on 20 October 1957, and then added a new beginning and cover page dated 11 December of the same year. In this respect, it forms the basis for all the subsequent works in the cycle. He then devised a revised plan for the second book, which included details of the intended orchestration of ''Le Temps restitué'', but set aside the draft in fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Death Of Virgil
''The Death of Virgil'' () is a 1945 novel by the Austrian author Hermann Broch. The narrative imagines the last hours of life of the Roman poet Virgil, in the port of Brundisium (Brindisi), whence he had accompanied the emperor Augustus, his decision – frustrated by the emperor – to burn his ''Aeneid'', and his final reconciliation with his destiny. Virgil's heightened perceptions as he dies recall his life and the age in which he lives. The novel examines the relationship between poetry and life, especially poetry and politics, taking a critical view of the value of literature in times of upheaval. Heavily influenced by the structure and interior monologue James Joyce's '' Ulysses'', the novel also can be read as criticizing the narcissism of artists' self-reflection. Broch began the novel during the rise of Nazi Party, writing part of it while imprisoned after the Anschluss. After his emigration to the US, it was published in German and English simultaneously in 1945. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novel
A novel is an extended work of narrative fiction usually written in prose and published as a book. The word derives from the for 'new', 'news', or 'short story (of something new)', itself from the , a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ''novellus'', diminutive of ''novus'', meaning 'new'. According to Margaret Doody, the novel has "a continuous and comprehensive history of about two thousand years", with its origins in the Ancient Greek and Roman novel, Medieval Chivalric romance, and the tradition of the Italian Renaissance novella.Margaret Anne Doody''The True Story of the Novel'' New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1996, rept. 1997, p. 1. Retrieved 25 April 2014. The ancient romance form was revived by Romanticism, in the historical romances of Walter Scott and the Gothic novel. Some novelists, including Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Ann Radcliffe, and John Cowper Powys, preferred the term ''romance''. Such romances should not be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |