|
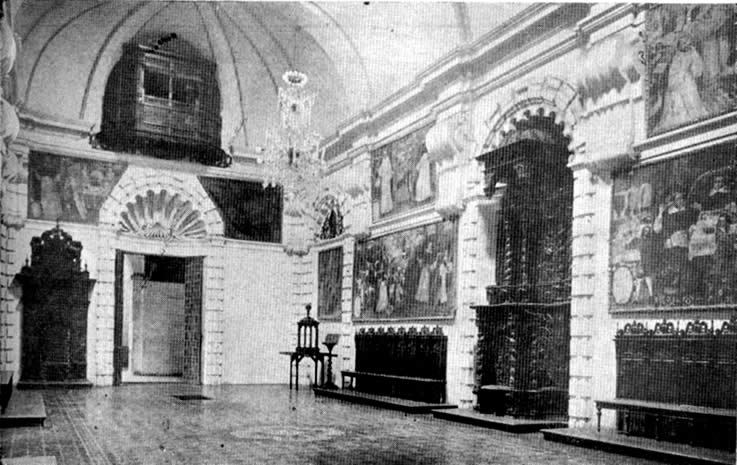
Javier Alzamora Valdez Building
The Javier Alzamora Valdez Building () is located in the historic center of Lima, Peru. It stands at the intersection of Abancay and Colmena avenues, next to the University Park. Formerly the headquarters of the Ministry of Education, it's the main location of the Superior Court of Justice of Lima, part of the Judiciary of Peru. History Construction began on the building on October 27, 1952 and was inaugurated on July 17, 1954 as part of the public works carried out during the '' Ochenio'' of General Manuel A. Odría. President Odría and his Ministry of Education, , were present both at the laying of the first stone and at the inauguration of the now completely constructed building. There was a project to build a twin tower in front of the building, on Abancay avenue, which would complete a circular space, but only the foundations and basement were built. It is what later became known as the "El Hueco" Shopping Center. Originally it served as the headquarters of the Ministry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
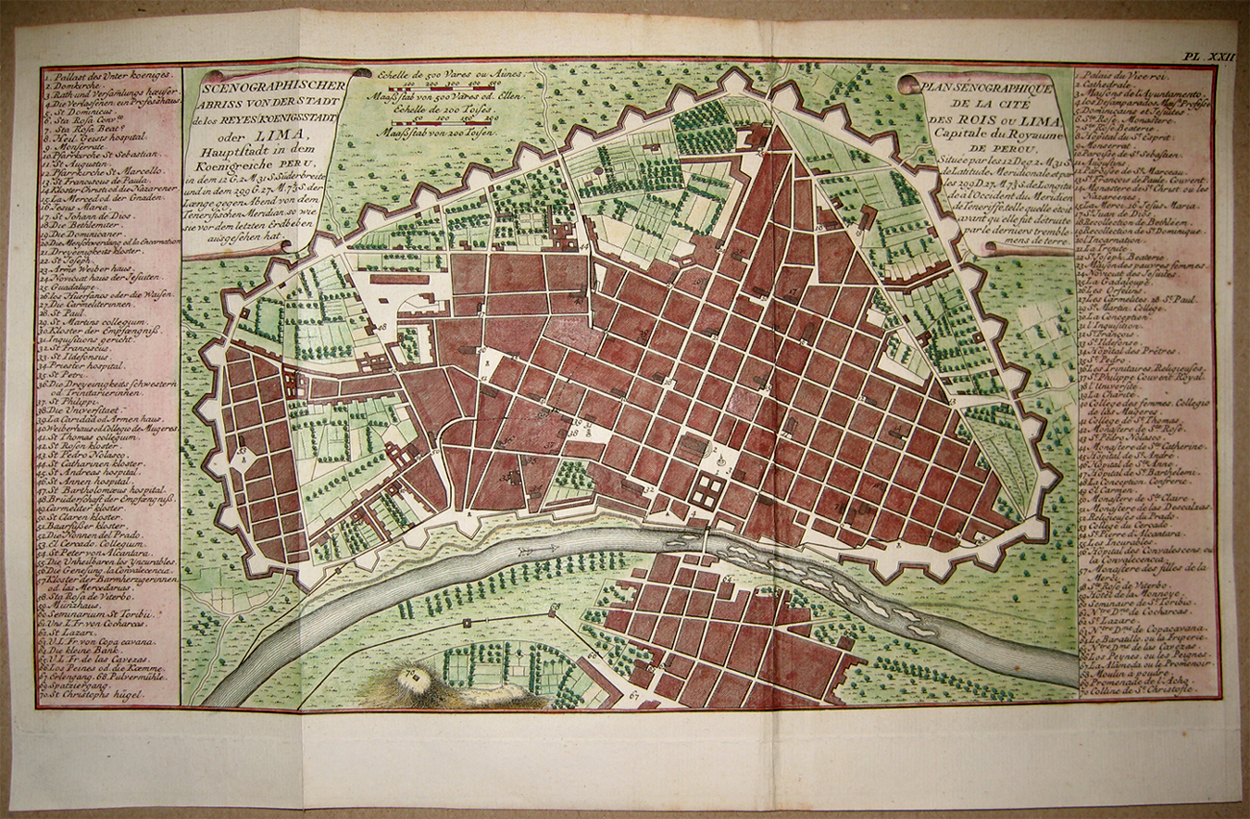
Historic Centre Of Lima
The Historic Centre of Lima () is the historic city centre of the city of Lima, the capital of Peru. Located in the city's districts of Lima and Rímac, both in the Rímac Valley, it consists of two areas: the first is the Monumental Zone established by the Peruvian government in 1972, and the second one—contained within the first one—is the World Heritage Site established by UNESCO in 1988, whose buildings are marked with the organisation's black-and-white shield. Founded on January 18, 1535, by Conquistador Francisco Pizarro, the city served as the political, administrative, religious and economic capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru, as well as the most important city of Spanish South America. The evangelisation process at the end of the 16th century allowed the arrival of several religious orders and the construction of churches and convents. The University of San Marcos, the so-called "Dean University of the Americas", was founded on May 12, 1551, and began its func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Borja District
San Borja is a district of the Lima Province in Peru, and one of the upscale districts that comprise the city of Lima. Originally part of the district of Surquillo and San Isidro, it became officially established as a separate district on June 1, 1983. Geography San Borja is bordered by the districts of San Luis and La Victoria on the north, Santiago de Surco on the east and south, Surquillo on the southwest and San Isidro on the west. The Rio Surco (Surco river) traverses the district in a north–south direction. This is not an actual river, it is a canal fed from the Rimac river and used to irrigate public parks. San Borja is approximately above sea level. The terrain is mostly flat, with a gentle downward east–west slope. Climate San Borja has a climate typical of the Peruvian coastal area. The weather is mild, with warm summers and cool winters, and humid all year round. It never rains but during the months from June to October its streets dampen due to a fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Buildings In Peru
This list of tallest buildings in Peru ranks Peruvian skyscrapers that stand at least 95 metres (311 ft), based on standard height measurement. This includes architectural details but does not include antenna masts. Tallest buildings See also *List of tallest buildings in South America Notes References {{TBSW Lists of buildings and structures in Peru, Tallest Lists of tallest buildings in South America, Peru Skyscrapers in Peru, * Lists of tallest structures by country, Peru Peru-related lists of superlatives, Buildings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ica, Peru
Ica () ( Quechua: ''Ika'') is a city and the capital of the Department of Ica in southern Peru. While the area was long inhabited by varying cultures of indigenous peoples, the Spanish ''conquistador'' Jerónimo Luis de Cabrera claimed its founding in 1563. As of the 2017 census, it had a population of over 282,407. The city suffered extensive damage and loss of life during the 2007 Peru earthquake. History In 2007, researchers found the fossil remains of a prehistoric penguin, '' Icadyptes salasi'', which inhabited the Atacama Desert about 30 million years ago. Scientists estimate it was about tall, with a beak. Evidence of prehistoric indigenous civilizations has been found in the nearby deserts, such as that of Paracas. Other cultures include the Chincha and the Inca, the latter of whom ruled this area beginning in the 14th century. Numerous pre-Columbian archeological artifacts are now displayed in the '' Museo Regional de Ica''. The Inca were still in power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Peru Earthquake
The 2007 Peru earthquake, which measured 8.0 on the moment magnitude scale, hit the central coast of Peru on August 15 at 23:40:57 UTC (18:40:57 local time) and lasted two minutes. The epicenter was located south-southeast of Lima at a depth of . At least 595 people died and over 2,290 people were injured. Earthquake This earthquake occurred at the boundary between the Nazca and South American tectonic plates, which are converging at a rate of per year. The earthquake occurred as thrust faulting on the interface between the two plates, with the South American plate moving up and seaward over the Nazca plate. Experts say this kind of earthquake is produced about once every 100 years. The earthquake had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity (MMI) of XI (''Extreme'') assigned at two areas of the Pan-American Highway which was severely damaged at and from the epicenter, respectively. MMI IX (''Violent'') assigned to the Pisco-Chincha Alta area. Coastal Peru has a history of very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Quarters March
The Four Quarters March or Four Suyos March () was a popular mobilization and later riots held in Peru on July 26, 27 and 28, 2000. The march was organized in opposition of Alberto Fujimori's third consecutive election as president of Peru and its last day coincided with Fujimori's inauguration. The protests were led by Alejandro Toledo, Carlos Ferrero and David Waisman, leaders of the Peruvian political party Perú Posible, and seconded by various social movements, anti-Fujimorist sectors, parties mostly of the left but also of social democracy, center and democratic right such as APRA, the Christian People's Party (PPC) and Acción Popular. In the case of the PPC and APRA, who from days before, with their bases in Metropolitan Lima, were preparing the environment, they took to the streets on July 27 together with the protestors and congregated in the Paseo de los Héroes Navales until late at night of that day. The reason for this massive march was the accusation of fraud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Manuel Ugarte Eléspuru
Juan Manuel Ugarte Eléspuru (1911–2004) was a Peruvian painter, sculptor, writer, academic administrator, and historian. Biography Juan Manuel Ugarte Eléspuru was born in 1911, in Lima, Peru. He went to school in Germany and Spain, and studied art in Buenos Aires. Ugarte Eléspuru was director of the National Superior Autonomous School of Fine Arts, Lima (Spanish: ''Escuela Nacional Superior Autónoma de Bellas Artes del Perú'') from 1950 to 1973. He exhibited his work at the 2nd II Bienal Hispanoamericana de Arte in 1954, in Havana, Cuba Havana (; ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. References Writers from Lima[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teodoro Núñez Ureta
Teodoro Núñez Ureta (1912–1988) was a Peruvian painter and a writer, noted for an original and distinctive style in Latin American art. His work often celebrated the life of the simple people of the Andes and the countryside, as distinct from a Spanish colonial legacy which had tended to ignore such topics. Biography Teodoro Núñez Ureta was born in 1912, in the provincial city of Arequipa, Peru. He was a child of a poor family. He began to learn to draw and paint on his own. His talent was discovered and nurtured at the Centro Artístico de Arequipa under Jose G. Alvarez. He became a professor and ultimately held the Chair of Art History and Aesthetics (1936–1950), at the Faculty of Arts of the Universidad Nacional de San Agustin Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa. His costumbrista article "La Abuela" (The Grandmother) won him a National Journalism Award in 1943. His unique talents drew attention throughout Peru, especially in the national capital. Lima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education In Peru
Education in Peru is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education, which oversees formulating, implementing and supervising the national educational policy. According to the Constitution of Peru, education is compulsory and free in public schools for the initial, primary and secondary levels.''Constitución Política del Perú'', Article Nº 17. It is also free in public universities for students who are unable to pay tuition and have an adequate academic performance. Throughout Peru's history, the nation's educational structure and quality has remained poor. Elites who organized the educational system promoted conservatism and authoritarianism while also defending a social hierarchy that prevented a social mobility that would improve the lives of citizens. The ineffectiveness of regulation, corruption and the government's lack of interest in improvements has contributed to the low quality of Peru's educational structure. Peru's lack of higher education accreditatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mural Painting
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage. Word mural in art The word ''mural'' is a Spanish adjective that is used to refer to what is attached to a wall. The term ''mural'' later became a noun. In art, the word began to be used at the beginning of the 20th century. In 1906, Dr. Atl issued a manifesto calling for the development of a monumental public art movement in Mexico; he named it in Spanish ''pintura mural'' (English: ''wall painting''). In ancient Roman times, a mural crown was given to the fighter who was first to scale the wall of a besieged town. "Mural" comes from the Latin ''muralis'', meaning "wall painting". This word is related to ''murus'', meaning "wall". History Antique art Murals of sorts date to Upper Paleolithic times such as the cave paintings in the Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave in Borneo (40,000� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimor
Chimor (also Kingdom of Chimor or Chimú Empire) was the political grouping of the Chimú culture (). The culture arose about 900 CE, succeeding the Moche culture, and was later conquered by the Inca Empire, Inca emperor Topa Inca Yupanqui around 1470, fifty years before the arrival of the Spanish in the region. Chimor was the largest kingdom in the Late Intermediate Period, encompassing 1,000 kilometres (620mi) of coastline. According to Chimú oral tradition, oral history, the history of Chimor began with the arrival of :es:Taycanamo, Taycanamo in the Moche Valley from the sea on a Pre-Columbian rafts, balsa raft. From there, his descendants would conquer surrounding areas starting with his son :es:Guacricur, Guacriur. Guacricur integrated Chimú's reign over the lower valley and :es:Ñancempinco, Ñancempinco, Taycanamo's grandson would expand the kingdom by conquering the upper valley. Ñançenpinco began to further expansion both north and south of the Moche Valleys. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Sol (1863–1985)
The sol, later ( English: gold sol), was the currency of Peru between 1863 and 1985. It had the ISO 4217 currency code PES. It was subdivided into 10 ''dineros'' or 100 ''centavos''. It also had two different superunits over its circulation life, the inca (1881–1882) and later the gold pound (1898–1931, abbreviated ''Lp.''), both worth 10 soles. History The sol was introduced in 1863 when Peru completed its decimalization, replacing the '' real'' at a rate of 1 sol = 10 reales. The sol also replaced the Bolivian peso at par, which had circulated in southern Peru.The sol and the boliviano were both pegged at 5 French francs). Between 1858 and 1863, coins had been issued denominated in reales, centavos and escudos. The sol was initially pegged to the French franc at a rate of 1 sol = 5 francs (S/. 5.25 to and S/. 1.08 to US$1). In 1880 and 1881, silver coins denominated in '' pesetas'', were issued, worth 20 centavos to the peseta. In 1881, the ''inca'', worth t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |