|
Jared Bernstein
Jared Bernstein (born 1955) is an American economist. He is a senior fellow at the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. From 2009 to 2011, Bernstein was the chief economist and economic adviser to Vice President Joe Biden in the Obama Administration. In 2008, Michael D. Shear described Bernstein as a progressive and "a strong advocate for workers". Bernstein is currently a Member of the Council of Economic Advisers in the Biden administration. Early life and education Bernstein graduated with a bachelor's degree in music from the Manhattan School of Music where he studied double bass with Orin O'Brien. He also earned a Master of Social Work from Hunter College as well as a master's degree in philosophy and a PhD in social welfare from Columbia University. He is of Jewish descent. Career Bernstein has taught at Howard University, Columbia University, and New York University. His areas of interest include "federal, state and international economic policies, specifically t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Economic Advisers
The Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) is a United States agency within the Executive Office of the President established in 1946, which advises the President of the United States on economic policy. The CEA provides much of the empirical research for the White House and prepares the publicly-available annual Economic Report of the President. Activities Economic Report of the President The report is published by the CEA annually in February, no later than 10 days after the Budget of the US Government is submitted. The president typically writes a letter introducing the report, serving as an executive summary and used for press coverage. The report proceeds with several hundred pages of qualitative and quantitative research by reviewing the impact of economic activity in the previous year, outlining the economic goals for the coming year (based on the President's economic agenda), and making numerical projections of economic performance and outcomes. Public criticism usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bass
The double bass (), also known simply as the bass () (or #Terminology, by other names), is the largest and lowest-pitched Bow (music), bowed (or plucked) string instrument in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding unorthodox additions such as the octobass). Similar in structure to the cello, it has four, although occasionally five, strings. The bass is a standard member of the orchestra's string section, along with violins, viola, and cello, ''The Orchestra: A User's Manual'' , Andrew Hugill with the Philharmonia Orchestra as well as the concert band, and is featured in Double bass concerto, concertos, solo, and chamber music in European classical music, Western classical music.Alfred Planyavsky [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a federal agency within the legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress. Inspired by California's Legislative Analyst's Office that manages the state budget in a strictly nonpartisan fashion, the CBO was created as a nonpartisan agency by the Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974. Whereas politicians on both sides of the aisle have criticized the CBO when its estimates have been politically inconvenient, economists and other academics overwhelmingly reject that the CBO is partisan or that it fails to produce credible forecasts. There is a consensus among economists that "adjusting for legal restrictions on what the CBO can assume about future legislation and events, the CBO has historically issued credible forecasts of the effects of both Democratic and Republican legislative proposals." History The Congressional Budget Office was created by Title II of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of federal laws governing occupational safety and health, wage and hour standards, unemployment benefits, reemployment services, and occasionally, economic statistics. It is headed by the Secretary of Labor, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The purpose of the Department of Labor is to foster, promote, and develop the well being of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States; improve working conditions; advance opportunities for profitable employment; and assure work-related benefits and rights. In carrying out this mission, the Department of Labor administers and enforces more than 180 federal laws and thousands of federal regulations. These mandates and the regulations that implement them cover many workplace activities for about 10&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Policy Institute
The Economic Policy Institute (EPI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit American, left-leaning think tank based in Washington, D.C., that carries out economic research and analyzes the economic impact of policies and proposals. Affiliated with the labor movement the EPI is usually described as presenting a left-leaning and pro- union viewpoint on public policy issues. Since 2021, the EPI has been led by economist Heidi Shierholz, a former Chief Economist of the Department of Labor The EPI has a sister organization, the EPI Policy Center, which is a 501(c)(4) group. History EPI was founded in 1986 by economists Jeff Faux, Lester Thurow, Ray Marshall, Barry Bluestone, Robert Reich, and Robert Kuttner. Since 2021, Heidi Shierholz has served as the EPI's president. Shierholz succeeded Thea Lea, who was appointed by President Joe Biden to a position in the Department of Labor. Policy proposals EPI supported Bernie Sanders's Medicare for All proposal. In a March 2020 policy pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994, and superseded the 1988 Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement between the United States and Canada. The NAFTA trade bloc formed one of the largest trade blocs in the world by gross domestic product. The impetus for a North American free trade zone began with U.S. president Ronald Reagan, who made the idea part of his 1980 presidential campaign. After the signing of the Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement in 1988, the administrations of U.S. president George H. W. Bush, Mexican President Carlos Salinas de Gortari, and Canadian prime minister Brian Mulroney agreed to negotiate what became NAFTA. Each submitted the agreement for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socioeconomic Mobility In The United States
Socioeconomic mobility in the United States refers to the upward or downward movement of Americans from one social class or economic level to another, through job changes, inheritance, marriage, connections, tax changes, innovation, illegal activities, hard work, lobbying, luck, health changes or other factors. This vertical mobility can be the change in socioeconomic status between parents and children ("inter-generational"); or over the course of a lifetime ("intra-generational"). Socioeconomic mobility typically refers to "relative mobility", the chance that an individual American's income or social status will rise or fall in comparison to other Americans, but can also refer to "absolute" mobility, based on changes in living standards in America. In recent years, several studies have found that vertical intergenerational mobility is lower in the US than in some European countries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Inequality In The United States
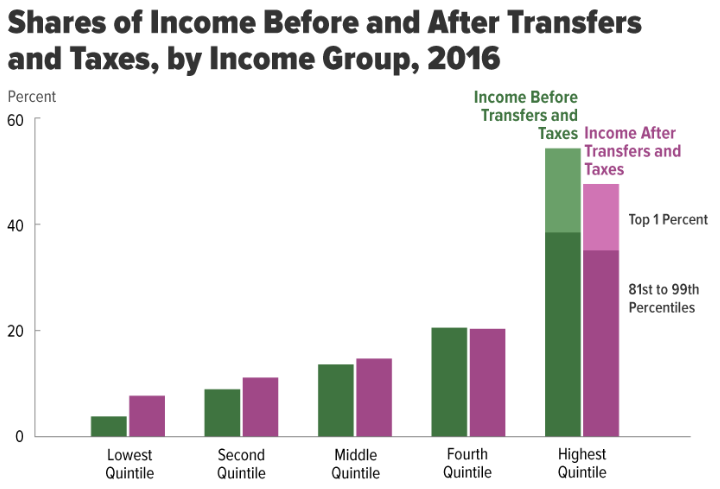
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in the 1920s and 2000s, with a 30-year period of relatively lower inequality between 1950 and 1980. The U.S. has the highest level of income inequality among its (post-)industrialized peers.United Press International (UPI), June 22, 2018"U.N. Report: With 40M in Poverty, U.S. Most Unequal Developed Nation"/ref> When measured for all households, U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed countries before taxes and transfers, but is among the highest after taxes and transfers, meaning the U.S. shifts relatively less income from higher income households to lower income households. In 2016, average market income was $15,600 for the lowest quintile and $280,300 for the highest quintile. The degree of inequality accelerated within the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Class Squeeze
The middle-class squeeze refers to negative trends in the standard of living and other conditions of the middle class of the population. Increases in wages fail to keep up with inflation for middle-income earners, leading to a relative decline in real wages, while at the same time, the phenomenon fails to have a similar effect on the top wage earners. People belonging to the middle class find that inflation in consumer goods and the housing market prevent them from maintaining a middle-class lifestyle, undermining aspirations of upward mobility. Overview Origin of the term Current U.S. Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi used the term in November 2006 to provide context to the domestic agenda of the U.S. Democratic Party. The Center for American Progress (CAP) issued a report of the same title in September 2014. As well as this, the term was further propelled into the public consciousness when it was used by former UK Labour Party leader Ed Miliband, who promised to come to the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then- Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin. In 1832, the non-denominational all-male institution began its first classes near City Hall based on a curriculum focused on a secular education. The university moved in 1833 and has maintained its main campus in Greenwich Village surrounding Washington Square Park. Since then, the university has added an engineering school in Brooklyn's MetroTech Center and graduate schools throughout Manhattan. NYU has become the largest private university in the United States by enrollment, with a total of 51,848 enrolled students, including 26,733 undergraduate students and 25,115 graduate students, in 2019. NYU also receives the most applications of any private institution in the United States and admission is considered highly selective. NYU is organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard University
Howard University (Howard) is a Private university, private, University charter#Federal, federally chartered historically black research university in Washington, D.C. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity" and accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education. Tracing its history to 1867, from its outset Howard has been nonsectarian and open to people of all sexes and races. It offers undergraduate, graduate and professional degrees in more than 120 programs, more than any other historically black colleges and universities, historically black college or university (HBCU) in the nation. History 19th century Shortly after the end of the American Civil War, members of the First Congregational Society of Washington considered establishing a theological seminary for the education of black clergymen. Within a few weeks, the project expanded to include a provision for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P20220401HF-0044 (52063714727)
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''. History The Semitic Pê (mouth), as well as the Greek Π or π ( Pi), and the Etruscan and Latin letters that developed from the former alphabet, all symbolized , a voiceless bilabial plosive. Use in writing systems In English orthography and most other European languages, represents the sound . A common Digraph (orthography), digraph in English is , which represents the sound , and can be used to transliterate ''phi'' in loanwords from Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor .... In German, the digraph is common, representing a lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)




.jpg)
