|
Janusiscus
''Janusiscus schultzei'' is an extinct gnathostome vertebrate dating from the Early Devonian period in Siberia, approximately 415 million years ago. It may be the sister group of the last common ancestor of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) or Osteichthyes (bony fish). This makes ''J. schultzei'' a sister species to all living jawed vertebrates. The species name is in honor of Hans-Peter Schultze; the genus named after Janus In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ..., the Roman god of duality. Taxonomy The following cladogram is simplified from Giles ''et al.'', 2015: References External links Ancient fossil may rewrite fish family treeViviane Callier. Jan. 12, 2015, 1:45 PM Monotypic prehistoric fish genera Fossil taxa described in 2015 Fossils of Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2015 In Fish Paleontology
This list of fossil fishes described in 2015 is a list of new taxa of Agnatha, jawless vertebrates, placoderms, Acanthodii, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes and other fishes of every kind that have been binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2015, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of fishes that occurred in the year 2015. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species. Research * A study of the body sizes of Devonian and Carboniferous vertebrates (jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, cartilaginous fishes, Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes and Sarcopterygii, sarcopterygians, including tetrapods) is published by Lauren Sallan, Sallan & Galimberti (2015), who conclude that following the Hangenberg event the majority of vertebrate lineages experienced persistent reductions in body size for at least 36 million years, and that the few large-bodied survivors of the Hangenberg event failed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
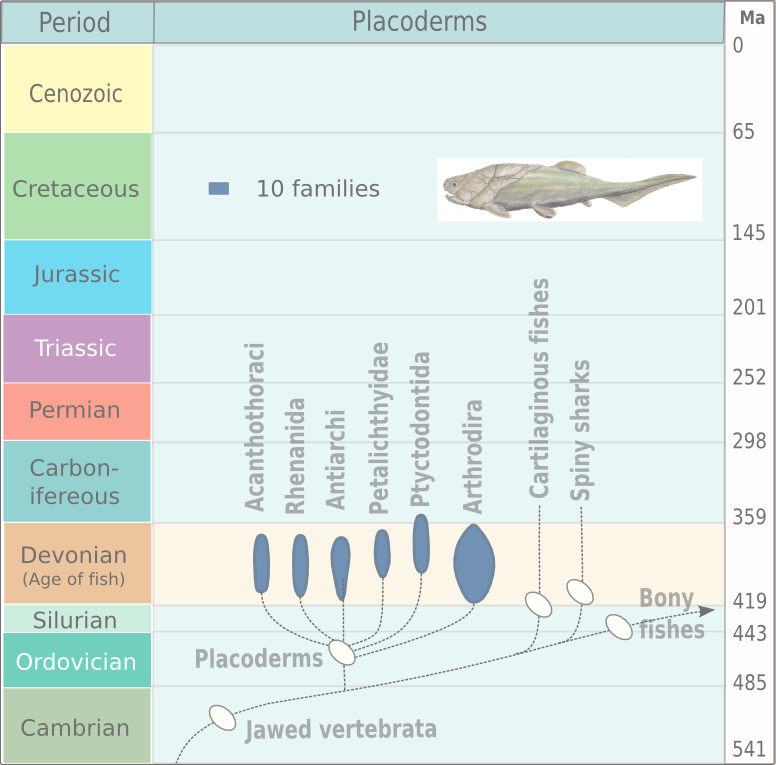
Antiarchi
Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coined by Edward Drinker Cope, who, when examining some fossils that he thought were armored tunicates related to '' Chelyosoma'', mistakenly thought that the orbital fenestra (i.e., the hole in the headshield for the eyes, nose and pineal foramen) was the opening for the mouth, or oral siphon, and that the opening for the anal siphon was on the other side of the body, as opposed to having both oral and anal siphons together at one end. The front portions of their bodies were heavily armored, to the point of literally resembling a box with eyes, with the sometimes scaled, sometimes naked rear portions often becoming sinuous, particularly with later forms. The pair of pectoral fins were modified into a pair of caliper-like, or arthropod-like l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Russia
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2015
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Prehistoric Fish Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthodii
Acanthodii or acanthodians is an extinct class of gnathostomes (jawed fishes). They are currently considered to represent a paraphyletic grade of various fish lineages basal to extant Chondrichthyes, which includes living sharks, rays, and chimaeras. Acanthodians possess a mosaic of features shared with both osteichthyans (bony fish) and chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fish). In general body shape, they were similar to modern sharks, but their epidermis was covered with tiny rhomboid platelets like the scales of holosteians ( gars, bowfins). The popular name "spiny sharks" is because they were superficially shark-shaped, with a streamlined body, paired fins, a strongly upturned tail, and stout, largely immovable bony spines supporting all the fins except the tail—hence, "spiny sharks". However, acanthodians are not true sharks; their close relation to modern cartilaginous fish can lead them to be considered " stem-sharks". Acanthodians had a cartilaginous skeleton, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are covered by a bony ring, which supports the eye, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenanida
Rhenanida ("Rhine (fish)") is an order of scaly placoderms. Unlike most other placoderms, the rhenanids' armor was made up of a mosaic of unfused scales and tubercles. The patterns and components of this "mosaic" correspond to the plates of armor in other, more advanced placoderms, suggesting that the ancestral placoderm had armor made of unfused components, as well. All rhenanids were flattened, ray-like, bottom-dwelling predators that lived in marine environments. Evolution The rhenanids were once presumed to be the most primitive, or at least the closest to the ancestral placoderm, as their armor was made up of a mosaic of tubercles, as opposed to the solidified plates of "advanced" placoderms, such as antiarchs and arthrodires. However, comparing the skull anatomies of ''Jagorina pandora'' with those of antiarchs, the rhenanids are considered to be the sister group of the antiarchs (together with their respective Acanthothoracid relatives). Presence in the fossil record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptyctodontida
The ptyctodontids ("folded-teeth") are placoderms of the order Ptyctodontida, containing the family Ptyctodontidae. With their big heads, big eyes, reduced armor and long bodies, the ptyctodontids bore a superficial resemblance to modern day chimaeras (Holocephali). Their armor was reduced to a pattern of small plates around the head and neck. Like the extinct and related acanthothoracids, and the living and unrelated holocephalians, most of the ptyctodontids are thought to have lived near the sea bottom and preyed on shellfish. On account of their radically reduced armor, some paleontologists have suggested that the Ptyctodontida were not actually placoderms, but actual holocephalians, some primitive group of elasmobranch fish, or even were the ancestors of the holocephalians, including the chimaeras. Thorough anatomical examinations of whole fossil specimens reveal that the profound similarities between these two groups are actually very superficial. The major differences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petalichthyida
Petalichthyida is an Extinction (biology), extinct Order (biology), order of small, flattened placoderm fish. They are typified by their splayed pectoral fins, exaggerated lateral spines, flattened bodies, and numerous tubercles that decorated all of the plates and scales of their armor. They reached a peak in diversity during the Early Devonian and were found throughout the world, particularly in Europe (especially in Germany), North America, Asia, South America, and Australia. The petalichthids ''Lunaspis'' and ''Wijdeaspis'' are among the best known. The earliest and most primitive known petalichthyid is ''Diandongpetalichthys'', which is from earliest Devonian-aged strata of Yunnan. The presence of ''Diandongpetalichthys'', along with other primitive petalichthyids including ''Neopetalichthys'' and ''Quasipetalichthys'', and more advanced petalichthyids, suggest that the order may have arisen in China, possibly during the late Silurian. Because they had compressed body fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteostraci
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed " ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |