|
Janaka (other)
Janaka (, IAST: ''Janaka'') is the King of Videha who ruled from Mithila, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Janaka was married to Sunayana. He is the father of Sita and Urmila in the epic. The term Janaka was also the title adopted by all the kings of Videha, who were the descendants of the King Nimi and his son King Mithi. The King Mithi is considered as the first King of Videha who was titled with the term ''Janaka''. Janaka is revered as being an ideal example of non-attachment to material possessions. He was intensely interested in spiritual discourse and considered himself free from worldly illusions. His interactions with sages and seekers such as Ashtavakra and Sulabha are recorded in the ancient texts. Legend Birth and ancestry Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east, the Mahananda River to the west, the Himalayas t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics of Hinduism known as the ''Itihasas'', the other being the ''Mahabharata''. The epic narrates the life of Rama, the seventh ''avatar'' of the Hindu deity Vishnu, who is a prince of Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows Exile of Lord Rama, his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across the forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana; the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana, the king of Lanka, that resulted in bloodbath; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya along with Sita to be crowned as a king amidst jubilation and celebration. Scholarly estimates for the earliest stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
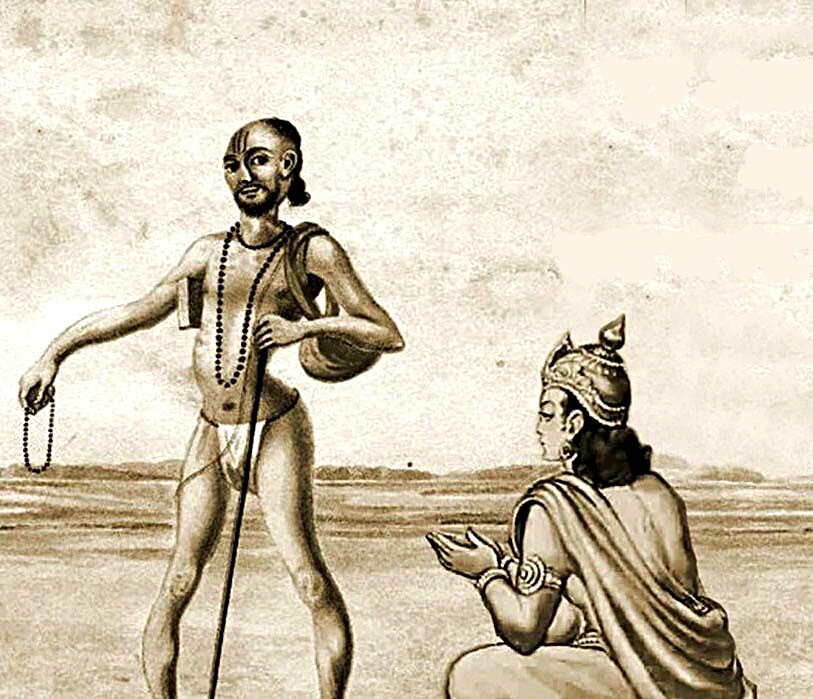
Sulabha
Sulabha ( Sanskrit: सुलभ ) was a female scholar who lived during the Mithila Kingdom. She was a Vedic scholar knownas Brahmavadini. In ''Rigaveda'', a ''Samhita'' attributed to her was called ''Saulabha Samhita'', later lost. ''Sulabha'' was a learned woman who belonged to the mendicant order. She renounced worldly possessions and followed a spiritual path. The text describes her as well-versed in Yoga, an ancient Indian discipline for physical, mental, and spiritual development. Early life Sulabha was a wandering Indian ascetic Y''ogini''. She had philosophical debates with the philosopher king Janaka. She engaged in philosophical debate with King Janaka. She challenged traditional gender roles and argued for women's equality in achieving spiritual liberation. Her story of debating King Janaka is mentioned in ''Mokshadharma Parva'' Chapter 321 of Shanti Parva in ''Mahabharata''. In the story Yudhishthira asked Bhishma about the liberation of self without giving up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagalakshmi
Nagalakshmi () is a serpent goddess and the wife of Shesha, a ''nagaraja'' (king of the Nāga, serpents) and one of the two Vahana, mounts of Vishnu featured in Hindu mythology. She is considered to be the personification of the divine ocean called the Kshira Sagara. Legend Nagalakshmi's legend is mainly found in the ''Garga Samhita (Vaishnavite text), Garga Samhita''. In this, the Kshira Sagara is personified as her. In Chapter 3 of the ''Balabhadra Khanda'' of the ''Garga Samhita'', it is mentioned that she incarnated on earth along with her husband. The Kshira Sagara is the fifth from the centre of the seven oceans. It surrounds the continent known as Krauncha. According to Hindu scriptures, the Deva (Hinduism), devas and asuras worked together for a millennium to churn this ocean in order to acquire amrita, the elixir of immortal life. It is described as the place where the deity Vishnu reclines over his serpent-mount Shesha, accompanied by his consort, Lakshmi. Incar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, , ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of wealth, fortune, prosperity, beauty, fertility, sovereignty, and abundance. She along with Parvati and Sarasvati, form the trinity of goddesses called the Tridevi. Lakshmi has been a central figure in Hindu tradition since pre-Buddhist times (1500 to 500 BCE) and remains one of the most widely worshipped goddesses in the Hindu pantheon. Although she does not appear in the earliest Vedic literature, the personification of the term '' shri''—auspiciousness, glory, and high rank, often associated with kingship—eventually led to the development of Sri-Lakshmi as a goddess in later Vedic texts, particularly the ''Shri Suktam''. Her importance grew significantly during the late epic period (around 400 CE), when she became particularly associated with the preserver god Vishnu as his consort. In this role, Lakshmi is seen as the ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janaka Welcomes Rama
Janaka (, IAST: ''Janaka'') is the King of Videha who ruled from Mithila (region), Mithila, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Janaka was married to Sunayana (Ramayana), Sunayana. He is the father of Sita and Urmila in the epic. The term Janaka was also the title adopted by all the kings of Videha, who were the descendants of the Nimi (king), King Nimi and his son King Mithi. The King Mithi is considered as the first King of Videha who was titled with the term ''Janaka''. Janaka is revered as being an ideal example of non-attachment to material possessions. He was intensely interested in spiritual discourse and considered himself free from worldly illusions. His interactions with sages and seekers such as Ashtavakra and Sulabha are recorded in the ancient texts. Legend Birth and ancestry Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Birth Of Sita - Raja Janaka Of Mithila Carrying Her In His Lap
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devarata Janaka
Devarata Janaka () was the sixth descendant of King Nimi in Janaka Dynasty of the ancient Videha Kingdom. He belonged to Ikshwaku descendants. He became the king of Videha Kingdom after his father ''Suketu''. According to Valmiki Ramayana, Devarata Janaka received the famous divine bow of Lord Shiva named as "'' Pinaka''" for its safe-keeping. Description According to the texts, from the lifeless body of King Nimi after his death, Mithi was born who became the first King Janaka. Thereafter, King Mithi's son was ''Udavasu'' from whom ''Nandivardhana'' was born; his son was ''Suketu'' (also known as ''Sukesha'') from whom ''Devarata'' was born. In Ramayana, Shreedwaja Janaka father of Sita, narrated the story of the divine bow Pinaka at the Swayamvar Sabha of Lord Rama and Goddess Sita in Mithila. He told that at the time of the destruction of Daksha Yagya, Lord Shiva told the Devatas, "In your eagerness to participate in the Yagya, you could not take my share. So I will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation (sattva). Vishnu is known as ''The Preserver'' within the Trimurti, the triple deity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva.Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' () (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme Lord who creates, protects, and transforms the Hindu cosmology, universe. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power (Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the supreme being is with qualities (Saguna Brahman, Saguna), and has definite form, but is limitless, transcendent and unchanging absolute Brahman, and the primal Atma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimi (Vedic King)
Nimi () is a king of the Suryavamsha (Solar dynasty) featured in Hindu mythology. He is considered to be the first king of the Videha kingdom and is regarded to be the ancestor to the Janaka lineage of Mithila. Nimi is the grandson of Manu, and a son of Ikshvaku. According to Vayu Purana, King Nimi established a city known as ''Jayantapura'' near the Gautam Ashram. Hinduism Nimi's yajña Once, Nimi performed a yajña and invited Sage Vasishtha to be the main priest to conduct the ceremony. However, the sage had already committed to conduct a yajña for Indra, and he told Nimi that he would officiate as the head priest after having conducted Indra's yajña. Nimi went away without replying. Sage Vashistha was under the impression that King Nimi has assented to wait for him. The sage conducted Indra's yajña and rushed to preside at Nimi's yajña only to find that the yajña was already being conducted by Gautama. Sage Vasishtha got angry and cursed King Nimi that "he would c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganga
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ... and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of highest mountains on Earth, 100 peaks exceeding elevations of above sea level lie in the Himalayas. The Himalayas abut on or cross territories of Himalayan states, six countries: Nepal, China, Pakistan, Bhutan, India and Afghanistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus River, Indus, the Ganges river, Ganges, and the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Tsangpo–Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahananda River
The Mahananda ( ) is a trans-boundary river that flows through the Indian states of Bihar and West Bengal before crossing into Bangladesh. It is an important tributary of the Ganges. Course The Mahananda river system consists of two streams- one is locally known as Fulahar river and the other Mahananda. The Fulahar originates in the Himalayas in Nepal and traverses through the Indian state of Bihar and merges with the Ganges in left opposite to Rajmahal. The Mahananda originates in the Himalayas: Paglajhora Falls on Mahaldiram Hill near Chimli, east of Kurseong in Darjeeling district at an elevation of . It flows through Mahananda Wildlife Sanctuary and descends to the plains near Siliguri. It touches Jalpaiguri district. It enters Bangladesh near Tentulia in Panchagarh District, flows for after Tentulia and returns to India. After flowing through Uttar Dinajpur district in West Bengal and Kishanganj, Purnia and Katihar districts in Bihar, it enters Malda distric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |