|
James Henry Carleton
James Henry Carleton (December 27, 1814 – January 7, 1873) was an American military officer who served in the United States Army during the American Civil War and American Indian Wars. He became notorious for his involvement in the Long Walk of the Navajo, in which he led an ethnic cleansing campaign against the indigenous Navajo people. Early life and career Carleton was born in Lubec, Maine. He was commissioned as a lieutenant in the U.S. Army in 1839, during the Aroostook War, and took part in the Mexican–American War. He served in the 1st U.S. Dragoons in the American West, participating as a lieutenant in an 1844 expedition to the Pawnee and the Oto. One of Carleton's children, Henry Guy Carleton (1852–1910) was a journalist, playwright, and inventor. Mountain Meadows Massacre In May 1859, Maj. Carleton and K Company of the 1st Dragoons out of Fort Tejon, California, were detailed to escort Maj. Henry Prince, a paymaster with government funds, to the Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubec, Maine
Lubec ( ) is a town in Washington County, Maine, United States. It is the easternmost municipality in the contiguous U.S. (see extreme points of the United States) and is the country's closest continental location to Africa. The town, with a population of 1,237 at the 2020 census, is home to Quoddy Head State Park. History Located on a peninsula overlooking an ice-free harbor, the town was first settled about 1775. Originally part of Eastport, it was set off and incorporated on June 21, 1811, and named for Lübeck, Germany. Following the War of 1812, Lubec was the site of considerable smuggling trade in gypsum, although principal industries remained agriculture and fisheries. By 1859, there was a tannery, three gristmills and nine sawmills; by 1886, there were also two shipyards, three boatbuilders and three sailmakers. From 1897 to 1898, the town was the site of a swindle in the sale of stock in the Electrolytic Marine Salts Company, the brainchild of Reverend Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, (April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848) was an invasion of Second Federal Republic of Mexico, Mexico by the United States Army. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory because it refused to recognize the Treaties of Velasco, signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna after he was captured by the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens who had moved from the United States to Texas after 1822 wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States had previously prevented annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, was a conflict initially fought by European colonization of the Americas, European colonial empires, the United States, and briefly the Confederate States of America and Republic of Texas against various Tribe (Native American), American Indian tribes in North America. These conflicts occurred from the time of the earliest colonial settlements in the 17th century until the end of the 19th century. The various wars resulted from a wide variety of factors, the most common being the desire of settlers and governments for Indian tribes' lands. The European powers and their colonies enlisted allied Indian tribes to help them conduct warfare against each other's colonial settlements. After the American Revolution, many conflicts were local to specific states or regions and frequently involved disputes over land use; some entailed cycles of violent reprisal. As American pioneer, American settlers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Adobe Walls
The First Battle of Adobe Walls took place between the United States Army and Native Americans. The Kiowa, Comanche and Plains Apache (Kiowa Apache) tribes drove from the battlefield a United States column that was responding to attacks on white settlers moving into the Southwest. The battle on November 25, 1864, resulted in light casualties on both sides.Trosser, John (2004). Adobe Walls Texas September 7, 2007. Background The Battle of Adobe Walls occurred on November 25, 1864, in the vicinity of Adobe Walls, the ruins of William Bent's abandoned adobe trading post and saloon, located on the northern side of the Canadian River 17 miles (27 km) northeast of present-day Stinnett in Hutchinson County. The battle came about when General James Henry Carleton, commander of the military District of New Mexico, decided to punish severely the plains tribes of the Kiowa and Comanche, whom he deemed responsible for attacks on wagon trains on the Santa Fe Trail. The Indians saw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
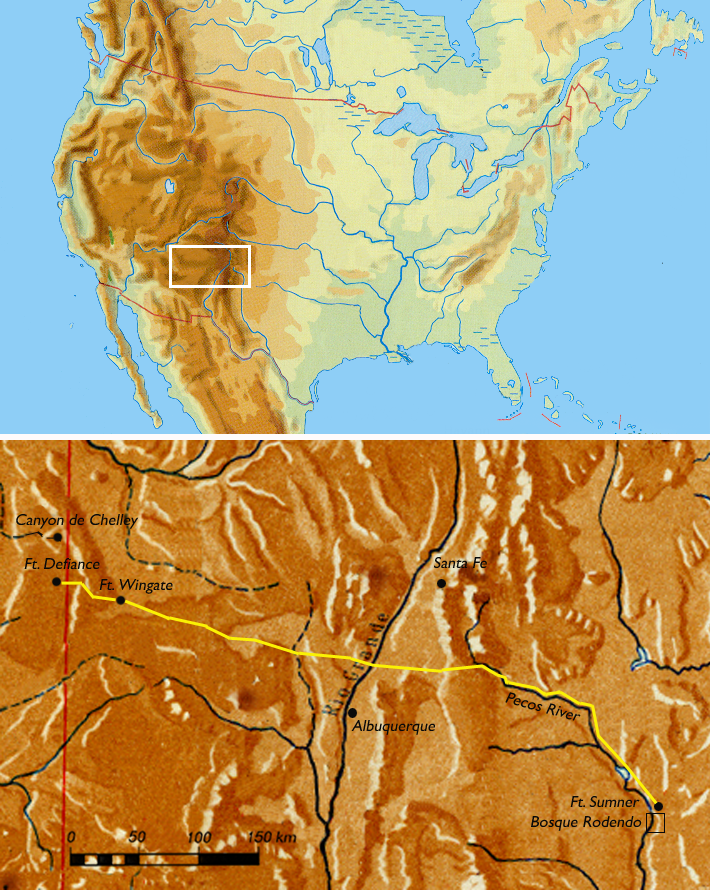
Long Walk Of The Navajo
The Long Walk of the Navajo, also called the Long Walk to Bosque Redondo (), was the deportation and ethnic cleansing of the Navajo people by the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government and the United States Army, United States army. Navajos were Death march, forced to walk from their land in western New Mexico Territory (modern-day Arizona and New Mexico) to Bosque Redondo in eastern New Mexico. Some 53 different forced marches occurred between August 1864 and the end of 1866. In total, 10,000 Navajos and 500 Mescalero Apache were forced to the internment camp in Bosque Redondo. During the forced march and internment, up to 3,500 people died from starvation and disease over a four-year period. In 1868, the Navajo were allowed to return to their ancestral homeland following the Treaty of Bosque Redondo.M. Annette Jaimes (1992). ''The State of Native America: Genocide, Colonization, and Resistance''. p. 34. South End Press Some anthropologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navajo Wars
The term Navajo Wars covers at least three distinct periods of conflict in the American West: the Navajo against the Spanish (late 16th century through 1821); the Navajo against the Mexican government (1821 through 1848); and the Navajo (Diné) against the United States (after the 1847–48 Mexican–American War). These conflicts ranged from small-scale raiding to large expeditions mounted by governments into territory controlled by the Navajo. The Navajo Wars also encompass the widespread raiding that took place throughout the period; the Navajo raided other tribes and nearby settlements, who in return raided into Navajo territory, creating a cycle of raiding that perpetuated the conflict. Spanish period Facundo Melgares, the last Spanish governor of New Mexico before independence in 1821, conducted two unsuccessful expeditions against the Navajo, who were attacking the New Mexican settlers. In October 1821 he sued for peace. Timeline * 1582: Espejo-Beltrain "found here peac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Apache Pass
The Battle of Apache Pass was fought in 1862 at Apache Pass, Arizona, in the United States, between Apache warriors and the Union volunteers of the California Column. It was one of the largest battles between the Americans and the Chiricahua during the Apache Wars. Background In early 1862 Col. James H. Carleton sent units from Fort Yuma to Tucson, Arizona, which had recently been occupied by a Confederate force, Company A, Arizona Rangers. After a small engagement known as the Battle of Picacho Pass just north of Tucson between a detachment of Carleton's cavalry and Confederate pickets, the Union forces advanced on Tucson in three columns. They arrived in Tucson on May 20, forcing the heavily outnumbered Confederate garrison to withdraw to Texas without a fight. After capturing Confederate Arizona's western outpost, Carleton prepared to march east with his main body in July, intending to enter New Mexico through Apache Pass in southeast Arizona. To prepare for the advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache Wars
The Apache Wars were a series of armed conflicts between the United States Army and various Apache tribal confederations fought in the Southwestern United States, southwest between 1849 and 1886, though minor hostilities continued until as late as 1924. After the Mexican–American War in 1846, the United States annexed conflicted territory from Mexico which was the home of both settlers and Apache tribes. Conflicts continued as American settlers came into traditional Apache lands to raise livestock and crops and to mine minerals. The U.S. Army established forts to fight Apache tribal war parties and force Apaches to move to designated Indian reservations created by the U.S. in accordance with the Indian Removal Act. Some reservations were not on the traditional areas occupied by the Apache. In 1886, the U.S. Army put over 5,000 soldiers in the field to fight, which Geronimo Campaign, resulted in the surrender of Geronimo and 30 of his followers. This is generally considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Tucson (1862)
Union forces entered Tucson on May 20, 1862, with a force of 2,000 men without firing a shot. Background Just prior to the American Civil War in the late 1850s, the cities of Tucson and Mesilla in southern New Mexico Territory petitioned the United States government to create a separate Territory of Arizona. The proposal was defeated after representatives from the Northern "free" states and the Southern "slave" states could not agree on how to divide New Mexico Territory. Southerners wanted an east–west division, whereas Northerners favored a north–south division of the territory. After the war began, the Confederacy established the Arizona Territory in February 1862 using the east–west boundary. Subsequently, the United States created Arizona Territory in 1863 using the current state boundary. Anglo-Arizonans had hoped the creation of a new territory would strengthen their communications with the east and allow for more military aid. Apaches had been fighting a bloody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Picacho Pass
The Battle of Picacho Pass, also known as the Battle of Picacho Peak, was an engagement of the American Civil War on April 15, 1862. The action occurred around Picacho Peak, northwest of Tucson, Arizona. It was fought between a Union cavalry patrol from California and a party of Confederate pickets from Tucson, and marks the westernmost battle of the American Civil War involving fatalities (though a skirmish known as the Battle of Stanwix Station was 40 miles further west and 80 miles from the California border in the direction of Fort Yuma). Background After a Confederate force of about 120 cavalrymen arrived at Tucson from Texas on February 28, 1862, they proclaimed Tucson the capital of the western district of the Confederate Arizona Territory, which comprised what is now southern Arizona and southern New Mexico. Mesilla, near Las Cruces, was declared the territorial capital and seat of the eastern district of the territory. The property of Tucson Unionists was con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |