|
James Haughton (Ireland)
James Haughton (5 May 1795 – 20 February 1873), nicknamed Vegetable Haughton, was an Irish social reformer, temperance and vegetarianism activist. He served as President of the Vegetarian Society from 1870 to 1873. Biography Early life and education James Haughton, son of Samuel Pearson Haughton (1748–1828), by Mary, daughter of James Pim of Rushin, Queen's County (now County Laois), Ireland, was born in Carlow and educated at Ballitore, County Kildare, from 1807 to 1810, under James White, a Quaker. Although educated as a Friend, he joined the Unitarians in 1834, and remained throughout his life a strong believer in their tenets. Career After filling several situations to learn his business, in 1817 Haughton settled in Dublin, where he became a corn and flour agent, in partnership with his brother William. He retired in 1850. Activism Haughton supported the anti-slavery movement at an early period and took an active part in it until 1838, going in that year to Lond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlow, County Carlow
Carlow ( ; ) is the county town of County Carlow, in the south-east of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, from Dublin. At the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, it had a population of 27,351, the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, twelfth-largest urban center in Ireland. The River Barrow flows through the town and forms the historic boundary between counties County Laois, Laois and Carlow. However, the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 included the town entirely in County Carlow. The settlement of Carlow is thousands of years old and pre-dates written Irish history. The town has played a major role in Irish history, serving as the capital of the country in the 14th century. The town is in a townland and Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name. Etymology The name is an anglicisation of the Irish language, Irish ''Ceatharlach''. Historically, it was anglicised as ''Caherlagh'', ''Caterlagh'' and ''Catherlagh'', which are closer to the Irish spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavement is the placement of a person into slavery, and the person is called a slave or an enslaved person (see ). Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, suffering a military defeat, or exploitation for cheaper labor; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race or sex. Slaves would be kept in bondage for life, or for a fixed period of time after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and existed in most socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1795 Births
Events January–June * January – Central England records its coldest ever month, in the CET records dating back to 1659. * January 14 – The University of North Carolina opens to students at Chapel Hill, becoming the first state university in the United States. * January 16 – War of the First Coalition: Flanders campaign: The French occupy Utrecht, Netherlands. * January 18 – Batavian Revolution in Amsterdam: William V, Prince of Orange, Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic (Republic of the Seven United Netherlands), flees the country. * January 19 – The Batavian Republic is proclaimed in Amsterdam, ending the Dutch Republic (Republic of the Seven United Netherlands). * January 20 – French troops enter Amsterdam. * January 23 – Flanders campaign: Capture of the Dutch fleet at Den Helder: The Dutch fleet, frozen in Zuiderzee, is captured by the French 8th Hussars. * February 7 – The Eleventh Amendment to the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccles Street
Eccles Street () is a street in Dublin, Ireland. History Eccles Street began on 6 March 1769 when Ambrose Eccles, Isaac-Ambrose Eccles leased three parcels of land in the area. The street is named after his family, including his grandfather John Eccles (mayor), Sir John Eccles, Lord Mayor of Dublin 1710–11 who owned property on the street. In James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses (novel), Ulysses'' (published 1922, set in 1904), the protagonist Leopold Bloom lives at 7 Eccles Street, and the building was treated as a landmark by Joyce fans. No. 7 was demolished in 1967 by the neighbouring Dominican convent as part of an extension development to their school. The door was saved. Other notable people associated with the street include the architect Francis Johnston (architect), Francis Johnston (1760–1829), who lived at number 64, and publisher Fergus O'Connor (publisher), Fergus O'Connor (c.1876–1952), who had a premises at number 44. Architecture The Mater Misericordiae Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
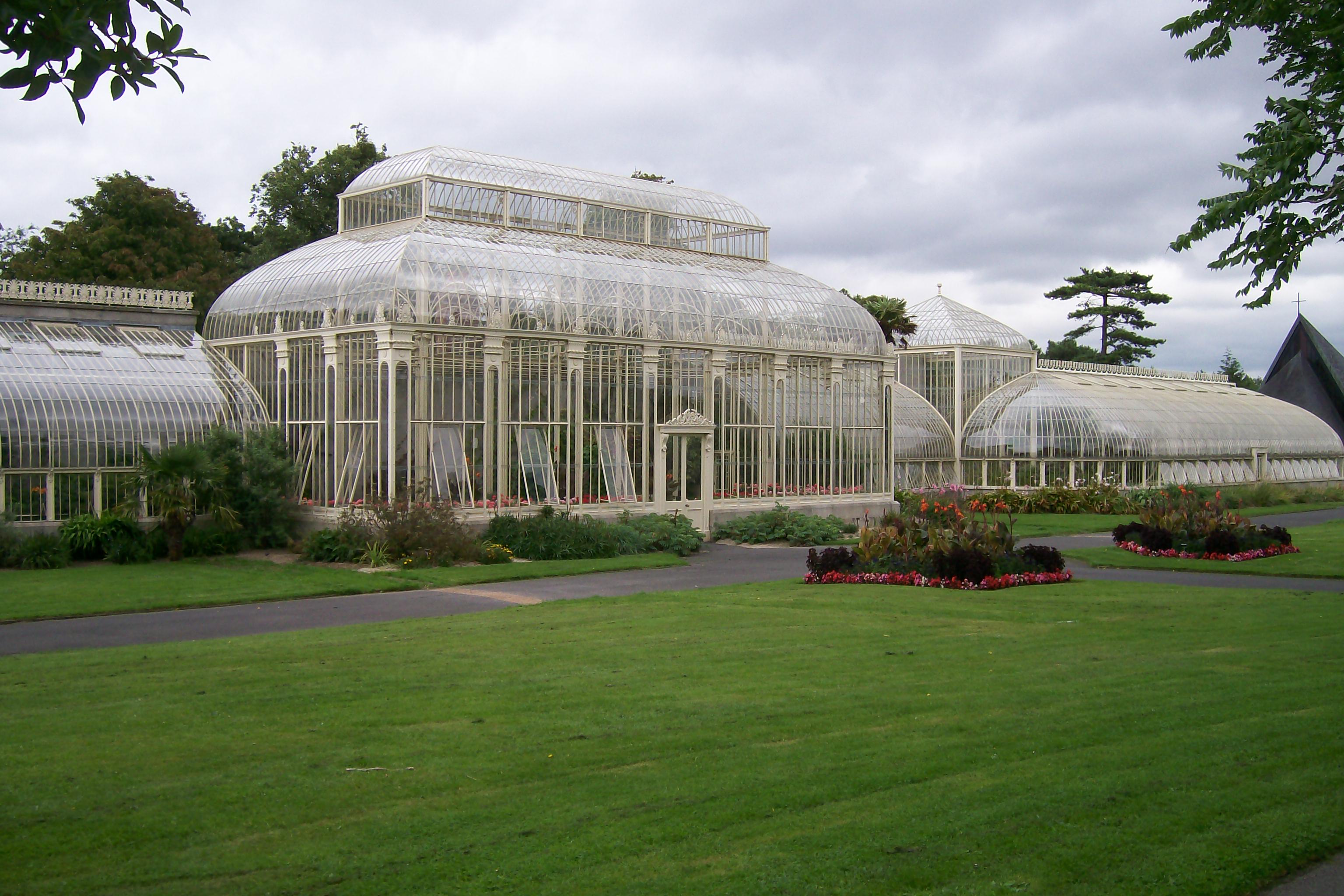
Irish National Botanic Gardens
The National Botanic Gardens (Irish: ''Garraithe Náisiúnta na Lus'') is a botanical garden in Glasnevin, 5 km north-west of Dublin city centre, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The 19.5 hectares are situated between Glasnevin Cemetery and the River Tolka where it forms part of the river's floodplain. The gardens were founded in 1795 by the Royal Dublin Society, Dublin Society (later the Royal Dublin Society) and are today in State ownership through the Office of Public Works. They house approximately 20,000 living plants and many millions of dried plant specimens. There are several architecturally notable greenhouses. The Glasnevin site is the headquarters of the National Botanic Gardens of Ireland which has a satellite garden and arboretum at National Botanic Gardens Kilmacurragh, Kilmacurragh in County Wicklow. The gardens participate in national and international initiatives for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development. Director of the Gardens Dr. Matthew J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnybrook, Dublin
Donnybrook () is a district of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, on the southside (Dublin), southside of the city, in the Dublin 4 postal district. It is home to the Irish public service broadcaster Raidió Teilifís Éireann (RTÉ) and was once part of the Pembroke, Dublin, Pembroke Township. Its neighbouring suburbs are Ballsbridge, Sandymount, Ranelagh and Clonskeagh. Donnybrook is also a Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish mainly situated in the old Barony (Ireland), barony of Dublin (barony), Dublin. History Donnybrook Fair dates from a charter of King John of England in 1204 and was held annually until 1855. It began as a fair for livestock and agricultural produce but later declined, growing into more of a carnival and funfair. Drunkenness, fighting, and hasty marriages became commonplace and the people of Donnybrook were anxious that it should cease. Eventually, the fair's reputation for tumult was its undoing. From the 1790s on, there were campaigns against t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George M
''George M!'' is a Broadway theatre, Broadway musical based on the life of George M. Cohan, the biggest Broadway star of his day who was known as "The Man Who Owned Broadway." The book for the musical was written by Michael Stewart (playwright), Michael Stewart, John Pascal, and Francine Pascal. Music and lyrics were by George M. Cohan himself, with revisions for the musical by Cohan's daughter, Mary Cohan. The story covers the period from the late 1880s until 1937 and focuses on Cohan's life and show business career from his early days in vaudeville with his parents and sister to his later success as a Broadway singer, dancer, composer, lyricist, theatre director and theatre producer, producer. The show includes such Cohan hit songs as "Give My Regards To Broadway", "You're a Grand Old Flag", and "Yankee Doodle Dandy." Productions The musical opened on Broadway at the Palace Theatre (New York City), Palace Theatre on April 10, 1968, and closed on April 26, 1969, after 433 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Confederation
The Irish Confederation was an Irish nationalist independence movement, established on 13 January 1847 by members of the Young Ireland movement who had seceded from Daniel O'Connell's Repeal Association. Historian T. W. Moody described it as "the official organisation of Young Ireland".Moody, p 38. Historical background In June 1846, Sir Robert Peel's Tory Ministry fell, and the Whigs under Lord John Russell came to power. Daniel O'Connell, founder of the Repeal Association which campaigned for a repeal of the Act of Union of 1800 between Great Britain and Ireland, simultaneously attempted to move the Association into supporting the Russell administration and English Liberalism. The intention was that Repeal agitation would be damped down in return for a profuse distribution of patronage through Conciliation Hall, home of the Repeal Association. On 15 June 1846 Thomas Francis Meagher denounced English Liberalism in Ireland saying that there was a suspicion that the national ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Francis Meagher
Thomas Francis Meagher ( ; 3 August 18231 July 1867) was an Irish nationalism, Irish nationalist and leader of the Young Irelanders in the Young Irelander Rebellion of 1848, Rebellion of 1848. After being convicted of sedition, he was first sentenced to death but received transportation for life to Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) in Australia. In 1852, Meagher escaped and made his way to the United States, where he settled in New York City. He studied law, worked as a journalist, and traveled to present lectures on the Irish cause. The widower married for a second time in New York. At the beginning of the American Civil War, Meagher joined the United States Army, U.S. Army and rose to the rank of Brigadier general (United States), brigadier general. He was most notable for recruiting and leading the Irish Brigade (U.S.), Irish Brigade and encouraging support among Irish immigrants for the Union. By his first marriage in Ireland, he had one surviving son; the two never met. Fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Ireland
Young Ireland (, ) was a political movement, political and cultural movement, cultural movement in the 1840s committed to an all-Ireland struggle for independence and democratic reform. Grouped around the Dublin weekly ''The Nation (Irish newspaper), The Nation'', it took issue with the compromises and clericalism of the larger national movement, Daniel O'Connell's Repeal Association, from which it seceded in 1847. Despairing, in the face of the Great Irish Famine, Great Famine, of any other course, in 1848 Young Irelanders attempted an insurrection. Following the arrest and the exile of most of their leading figures, the movement split between those who carried the commitment to "physical force" forward into the Irish Republican Brotherhood, and those who sought to build a "League of North and South" linking an Independent Irish Party, independent Irish parliamentary party to tenant agitation for land reform. Origins The Historical Society Many of those later identified as You ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Connell (MP)
John O'Connell (24 December 1810 – 24 June 1858) was one of seven children (the third of four sons) of the Irish Nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell and his wife Mary. He followed his father as a Member of Parliament and leader of the Repeal Association. Life Educated at Clongowes Wood College, Trinity College Dublin, and the King's Inns, O'Connell was then called to the bar, but did not practice.John O’Connell at Ricorso He served in the United Kingdom Parliament as Member of Parliament for |
Repeal Association
The Repeal Association was an Irish mass membership political movement set up by Daniel O'Connell in 1830 to campaign for a repeal of the Acts of Union of 1800 between Great Britain and Ireland. The Association's aim was to revert Ireland to the fully devolved government briefly achieved by Henry Grattan and his patriots in the 1780s—that is, complete legislative independence for the Parliament of Ireland under the British Crown—but this time with Catholic voting rights that were now possible following the Act of Emancipation in 1829, supported by the electorate approved under the Irish Reform Act 1832. On its failure by the late 1840s the Young Ireland movement developed. Repealer candidates contested the 1832 United Kingdom general election The 1832 United Kingdom general election was held on 8 December 1832 to 8 January 1833. The first election to be held in the newly-reformed House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, the Whigs (British polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |