|
James Harry Lacey
James Harry Lacey, (1 February 1917 – 30 May 1989), known as Ginger Lacey, was one of the top scoring Royal Air Force fighter pilots of the Second World War and was the second-highest scoring RAF fighter pilot of the Battle of Britain, behind Pilot Officer Eric Lock of No. 41 Squadron RAF. Lacey was credited with 28 enemy aircraft destroyed, five probables and nine damaged. Early life Lacey was born on 1 February 1917 in Wetherby, West Yorkshire. He left King James Grammar School, Knaresborough"Fighter Aces of the RAF" by ECR Baker, published William Kimber 1962, 450017109 in 1933, and continued his education at Leeds Technical College. He spent four years as an apprentice pharmacist in Leeds. RAF career Lacey joined the RAFVR (Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve) in January 1937 as a trainee pilot at Perth, Scotland. In 1938, he then took an instructor's course, becoming an instructor at the Yorkshire Flying School, accumulating 1,000 hours of flight time before the war. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetherby
Wetherby ( ) is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the City of Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is close to West Yorkshire county's border with North Yorkshire and lies approximately from Leeds city centre, from York and from Harrogate. The town stands on the River Wharfe and, for centuries, it has been a crossing place and staging post on the A1 road (Great Britain), Great North Road midway between London and Edinburgh. Wetherby Bridge, which spans the River Wharfe, is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and a Grade II listed building, listed structure. The course of the A1 road (Great Britain), Old Great North Road passes through the town and, as result of its situation on the road, as well as being a major Drovers' road, cattle droving route from Scotland to London, many coaching inns were established in Wetherby which are still used by travellers today. The town lies in the Wetherby (ward), Wetherby ward of Leeds City Council and the Wetherby and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds College Of Technology
Leeds College of Technology (formerly Kitson College) was a further education college in Leeds, in West Yorkshire, England. With a strong technical bias, the college supported the computing, engineering, social care and transport industries. In addition, the college was a national centre for print training and offered English language learning and teaching (ESOL). The Woodhouse Lane building was built in 1957 and opened in 1959, it was part of Leeds City College until June 2019 when the college closed after 60 years of activity and these facilities were moved to a brand new campus at Quarry Hill, Leeds, Quarry Hill opposite the Leeds City bus station, bus station. It was founded in 1824 as part of the Leeds Mechanics' Institute, and in 1868 the college became the Leeds Institute of Science, Art and Literature, then the Branch College of Engineering and Science. It was renamed Kitson College in 1967 in honour of James Kitson, 1st Baron Airedale, and then Leeds College of Technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dornier Do 17
The Dornier Do 17 is a twin-engined light bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Dornier Flugzeugwerke. Large numbers were operated by the ''Luftwaffe'' throughout the Second World War. The Do 17 was designed during the early 1930s as a '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that was intended to use its speed to outrun opposing fighter aircraft. It was a lightly built aircraft, possessing a twin tail, " shoulder wing" and typically powered by a pair of Bramo 323P radial engines. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 23 November 1934; it entered regular service with the ''Luftwaffe'' three years later. Sometimes referred to as the ''Fliegender Bleistift'' ("flying pencil") or the ''Eversharp'', the Do 17 was a relatively popular aircraft among its crews due to its handling, especially at low altitude, which made the type harder to hit than other German bombers of the era. During 1937, the Do 17 made its combat debut during the Spanish Civil War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdgeschwader 27
''Jagdgeschwader'' 27 (JG 27) "''Afrika''" was a fighter wing of the Luftwaffe during World War II. The wing was given the name "Africa" for serving in the North African Campaign predominantly alone in the period from April 1941 to September 1942. Elements of JG 27 fought in every major theatre of operations in which the Wehrmacht operated. Stab JG 27 was created in October 1939 and assigned two ''gruppen'' (groups) in the Phoney War. The wing's first campaign was Fall Gelb, the battles of the Low Countries and France. In the second half of 1940 JG 27 received a third ''gruppe'' and fought in the Battle of Britain. In 1941 it returned to Germany then fought in the German invasion of Yugoslavia and Battle of Greece in April 1941. The wing was then separated with two ''gruppen'' sent to support Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941. I. ''Gruppe'' was sent to Italian Libya beginning JG 27s North African Campaign from mid-April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
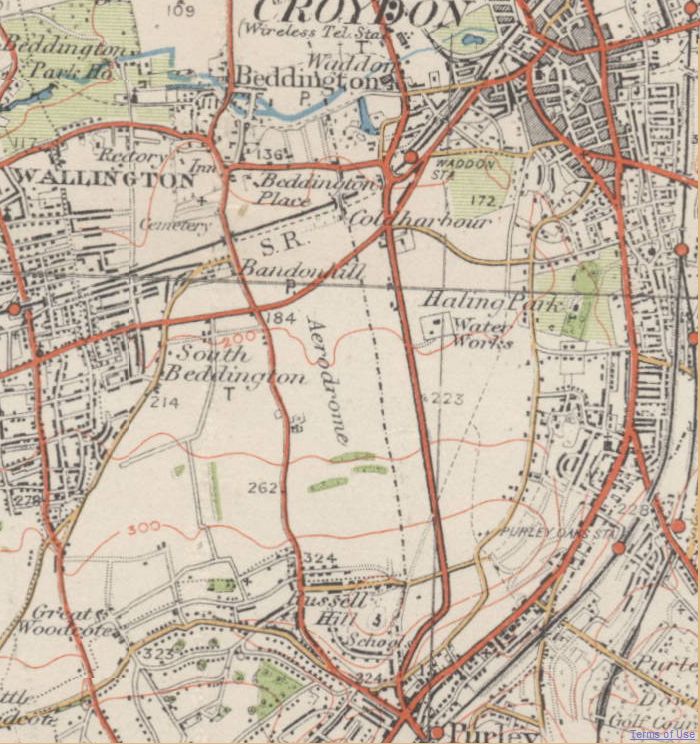
RAF Croydon
Croydon Airport was the UK's only international airport during the interwar period. It opened in 1920, located near Croydon, then part of Surrey. Built in a Neoclassical style, it was developed as Britain's main airport, handling more cargo, mail, and passengers than any other UK airport at the time. Innovations at the site included the world's first air traffic control, the first airport terminal and the world's first airport hotel (the Gate Lodge, now the Aerodrome Hotel ). It was home to Britain's first national airline, Imperial Airways, founded through a government sponsored four-airline merger in 1924. During World War II the airport was named RAF Croydon as its role changed to that of a fighter airfield during the Battle of Britain; and in 1943 RAF Transport Command was founded at the site, which used the airport to transport thousands of troops into and out of Europe. After the Second World War, its role returned to civil aviation, but the lack of available land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Gravesend
Gravesend Airport, located southeast of Gravesend town centre, Kent and west of Rochester. It was operated from 1932 until 1956. It was initially a civil airfield, and became a Royal Air Force station known as RAF Gravesend during the Second World War, when it was under the control of RAF Fighter Command during the Battle of Britain. It was the first RAF station to operate the North American Mustang III. The airport returned to civilian use at the conclusion of the Second World War, although it remained under the ownership of the Air Ministry until its closure in 1956. Civil operation The airport was operated by Gravesend Aviation Ltd served Gravesend and has a significant place in the history of British aviation. From 1933 to 1936 it was home to Percival Aircraft, building the famous Mew Gull racing aircraft among others, before the company moved to Luton. After 1936 Essex Aero was based on the site, and maintained the airfield's link with racing aeroplanes by preparing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croix De Guerre
The (, ''Cross of War'') is a military decoration of France. It was first created in 1915 and consists of a square-cross medal on two crossed swords, hanging from a ribbon with various degree pins. The decoration was first awarded during World War I, again in World War II, and in other conflicts; the '' croix de guerre des théâtres d'opérations extérieures'' ("cross of war for external theatres of operations") was established in 1921 for these. The was also commonly bestowed on foreign military forces allied to France. The may be awarded either as an individual award or as a unit award to those soldiers who distinguish themselves by acts of heroism involving combat with the enemy. The medal is awarded to those who have been " mentioned in dispatches", meaning a heroic deed or deeds were performed meriting a citation from an individual's headquarters unit. The unit award of the with palm was issued to military units whose members performed heroic deeds in combat and were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Bf 110
The Messerschmitt Bf 110, often known unofficially as the Me 110,Because it was built before ''Bayerische Flugzeugwerke'' became Messerschmitt AG in July 1938, the Bf 110 was never officially given the designation Me 110. is a twin-engined (destroyer, heavy fighter), fighter-bomber (''Jagdbomber'' or ''Jabo''), and night fighter (''Nachtjäger'') designed by the German aircraft company Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW) and produced by successor company Messerschmitt. It was primarily operated by the ''Luftwaffe'' and was active throughout the Second World War. Development of the Bf 110 commenced during the first half of the 1930s; one early proponent of the type was Hermann Göring, who believed its heavy armament, speed, and range would make it the premier offensive fighter of the ''Luftwaffe''. Early variants were armed with a pair of MG FF 20 mm cannon, four 7.92 mm (.323 in) MG 17 machine guns, and one 7.92 mm (.323 in) MG 15 machine gun for defence (late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a monoplane fighter aircraft that was designed and initially produced by the Nazi Germany, German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt#History, Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW). Together with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the Bf 109 formed the backbone of the ''Luftwaffe's'' fighter force during the World War II. It was commonly called the Me 109 by Allied aircrew and some German aces/pilots, even though this was not the official model designation. The Bf 109 was designed by Willy Messerschmitt and Robert Lusser, who worked at BFW during the early to mid-1930s. It was conceived as an interceptor aircraft, interceptor. However, later models were developed to fulfill multiple tasks, serving as Escort fighter, bomber escort, fighter-bomber, day fighter, day-, night fighter, night-, all-weather fighter, ground-attack aircraft, and aerial reconnaissance aircraft. It was one of the most advanced fighters when the fighter first appeared, being furnished with an all-me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KG 53
''Kampfgeschwader'' 53 "Legion Condor" (KG 53; English: ''Condor Legion'') was a Luftwaffe bomber wing during World War II. Its units participated on all of the fronts in the European Theatre until it was disbanded in May 1945. At all times it operated the German bomber type Heinkel He 111. Only the 15th (kroat) Squadron of KG 53 (15.(kroat)/KG 53), established in Agram (Zagreb) July 1942, operated the Dornier Do 17 Z. Operational history ''Kampfgeschwader 53'' was formed on 1 May 1939 with '' Stab''/KG 53 and I. ''Gruppe'' at Ansbach, II. ''Gruppe'' at Schwäbisch Hall and III. ''Gruppe'' at Giebelstadt near Würzburg. Invasion of Poland The Geschwader was initially put on "standby" in western Germany, in case of an Allied offensive. As a result, most of its ''Gruppen'' did not see action in the campaign. I./KG 53 was put under the command of ''Luftflotte 1''. It had a strength of 31 He 111s, all serviceable. It was committed from the first day, but on 6 September it was mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and medium bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a wolf in sheep's clothing. Due to restrictions placed on Germany after the First World War prohibiting bombers, it was presented solely as a civil airliner, although from conception the design was intended to provide the nascent Luftwaffe with a heavy bomber. Perhaps the best-recognised German bomber of World War II due to the distinctive, extensively glazed "greenhouse" nose of the later versions, the Heinkel He 111 was the most numerous Luftwaffe bomber during the early stages of the war. It fared well until it met serious fighter opposition during the Battle of Britain, when its defensive armament was found to be inadequate. As the war progressed, the He 111 was used in a wide variety of roles on every front in the European theatre. It was used as a strategic bomber during the Battle of Britain, a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedan, France
Sedan () is a commune in the Ardennes department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. It is also the chef-lieu (administrative centre) of the arrondissement of the same name. Sedan is notable as the site of two major battles between the armed forces of France and Germany, both of which were won by Germany. The First Battle of Sedan in 1870 sealed the fate of the Second French Empire and paved the way to the foundation of the German Empire, leading to the subsequent annual celebration of " Sedan Day" in Germany. The Second Battle of Sedan in 1940 achieved a decisive breakthrough by ''Wehrmacht'' forces in the Battle of France and ultimately led to the collapse of the French Third Republic. Location The town is situated about 200 km from Paris, 85 km north-east of Reims, and 10 km south of the border with Belgium. The historic centre occupies a peninsula formed by a bend in the river Meuse. Sedan station has rail connections to Charleville-Mézières, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |