|
James Elam (physician)
James Otis Elam (May 31, 1918 – July 10, 1995) was an American physician and respiratory researcher. Elam was born in Austin, Texas. He completed his undergraduate education at the University of Texas at Austin in 1942. He then studied at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. After doing an internship at Bethesdal Naval Hospital in 1945-1946 Elam went to the University of Minnesota for advanced studies. Based on his research at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York for understanding carbon dioxide absorption, he developed a prototype ventilator device that efficiently could absorb carbon dioxide during surgery, dubbed the Roswell Park ventilator. This was further developed into the ''Air-Shields Ventimeter'' ventilator that were used for a period of almost 50 years. Elam contributed significantly to the development and understanding of modern rescue breathing, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), and brought it to the attention of the medical co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laerdal
Laerdal is a multinational company that develops products and programs for healthcare providers, voluntary organizations, educational institutions, hospitals, and the military worldwide. Laerdal has over 2,000 employees in 26 countries. The headquarters is located in Stavanger, Norway. History Laerdal was founded in 1940 by Åsmund S. Lærdal as a children’s publishing and toy company. During the years as a toy developer, Lærdal learned about a synthetic plastic material, now known as PVC, that was suited for the casting of toys and dolls. The use of soft plastics revolutionized the toy industry and by 1960, more than 100 million toy cars, under the brand Tomte, had been sold in 100 countries. The Laerdal Anne doll was named "Toy of the Year" and became a bestseller throughout Europe. Due to this experience with soft plastics, The Norwegian Civil Defense called on Laerdal to design natural-looking imitation wounds for military training. In 1958, Laerdal was approached by No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins University Alumni
Johns may refer to: Places * Johns, Mississippi, an unincorporated community * Johns, Oklahoma, United States, a community * Johns Creek (Chattahoochee River), Georgia, United States * Johns Island (other), islands in Canada and the United States * Johns Mountain, a summit in Georgia * Johns River (other) * Johns Township, Appanoose County, Iowa, United States Other uses * Johns (surname) * Johns Hopkins (1795–1873), American entrepreneur, investor and philanthropist * ''johns'' (film), a 1996 film starring David Arquette and Lukas Haas See also * John (other) John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Secon ... * Justice Johns (other) * {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas At Austin Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1995 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 Births
The ceasefire that effectively ended the First World War took place on the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month of this year. Also in this year, the Spanish flu pandemic killed 50–100 million people worldwide. In Russia, this year runs with only 352 days. As the result of Julian to Gregorian calendar switch, 13 days needed to be skipped. Wednesday, January 31 ''(Julian Calendar)'' was immediately followed by Thursday, February 14 ''(Gregorian Calendar)''. Events World War I will be abbreviated as "WWI" January * January – 1918 flu pandemic: The "Spanish flu" ( influenza) is first observed in Haskell County, Kansas. * January 4 – The Finnish Declaration of Independence is recognized by Soviet Russia, Sweden, Germany and France. * January 8 – American president Woodrow Wilson presents the Fourteen Points as a basis for peace negotiations to end the war. * January 9 – Battle of Bear Valley: U.S. troops engage Yaqui Native Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
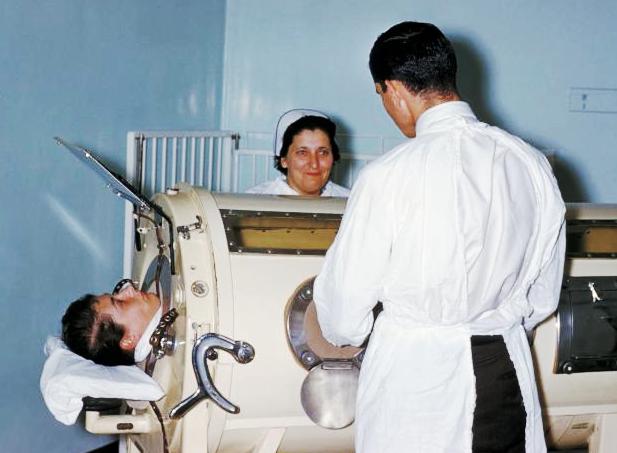
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
The history of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can be traced as far back as the ancient Egyptian literature, literary works of Old Kingdom of Egypt, ancient Egypt (c. 2686 – c. 2181 BC). However, it was not until the 18th century that credible reports of cardiopulmonary resuscitation began to appear in the medical literature. Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, Mouth-to-mouth ventilation has been used for centuries as an element of CPR, but it fell out of favor in the late 19th century with the widespread adoption of manual resuscitative techniques such as the Marshall Hall (physiologist), Marshall Hall method, Silvester's method, the Edward Albert Sharpey-Schafer, Shafer method and the Holger Nielsen technique. The technique of mouth-to-mouth ventilation would not come back into favor until the late 1950s, after its "accidental rediscovery" by James Elam (physician), James Elam. The modern elements of resuscitation for sudden cardiac arrest include CPR (consisting of ventilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albion O
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than "Britain" today. The name for Scotland in most of the Celtic languages is related to Albion: ''Alba'' in Scottish Gaelic, ''Albain'' (genitive ''Alban'') in Irish, ''Nalbin'' in Manx and ''Alban'' in Welsh and Cornish. These names were later Latinised as ''Albania'' and Anglicised as ''Albany'', which were once alternative names for Scotland. ''New Albion'' and ''Albionoria'' ("Albion of the North") were briefly suggested as names of Canada during the period of the Canadian Confederation. Francis Drake gave the name New Albion to what is now California when he landed there in 1579. Etymology The toponym in English is thought to derive from the Greek word , Latinised as (genitive ). The root ' is also found in Gaulish and Galatian 'world' and Welsh (Old W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789).See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 It operates under the authority, direction, and control of the United States Secretary of Defense, United States secretary of defense. It is one of the six armed forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Army is the most senior branch in order of precedence amongst the armed services. It has its roots in the Continental Army, formed on 14 June 1775 to fight against the British for independence during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins School Of Medicine
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (JHUSOM) is the medical school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Established in 1893 following the construction of the Johns Hopkins Hospital, the school is known for being a center of biomedical research and innovation, and is routinely ranked as one of the top medical schools in the United States. The School of Medicine is located in Baltimore, Maryland, where it shares a campus in East Baltimore with the School of Nursing, Bloomberg School of Public Health, and Johns Hopkins Hospital, the school's primary teaching hospital. As part of the larger Johns Hopkins Medicine health system, the school is also affiliated with numerous regional hospitals and medical centers including the Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Johns Hopkins Howard County Medical Center, Suburban Hospital in Montgomery County, Sibley Memorial Hospital in Washington, D.C. History Before his death in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a Dependencies of Norway, dependency, and not a part of the Kingdom; Norway also Territorial claims in Antarctica, claims the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. Norway has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Oslo. The country has a total area of . The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden, and is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast. Norway has an extensive coastline facing the Skagerrak strait, the North Atlantic Ocean, and the Barents Sea. The unified kingdom of Norway was established in 872 as a merger of Petty kingdoms of Norway, petty kingdoms and has existed continuously for years. From 1537 to 1814, Norway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |