|
Jalaleddin (novella)
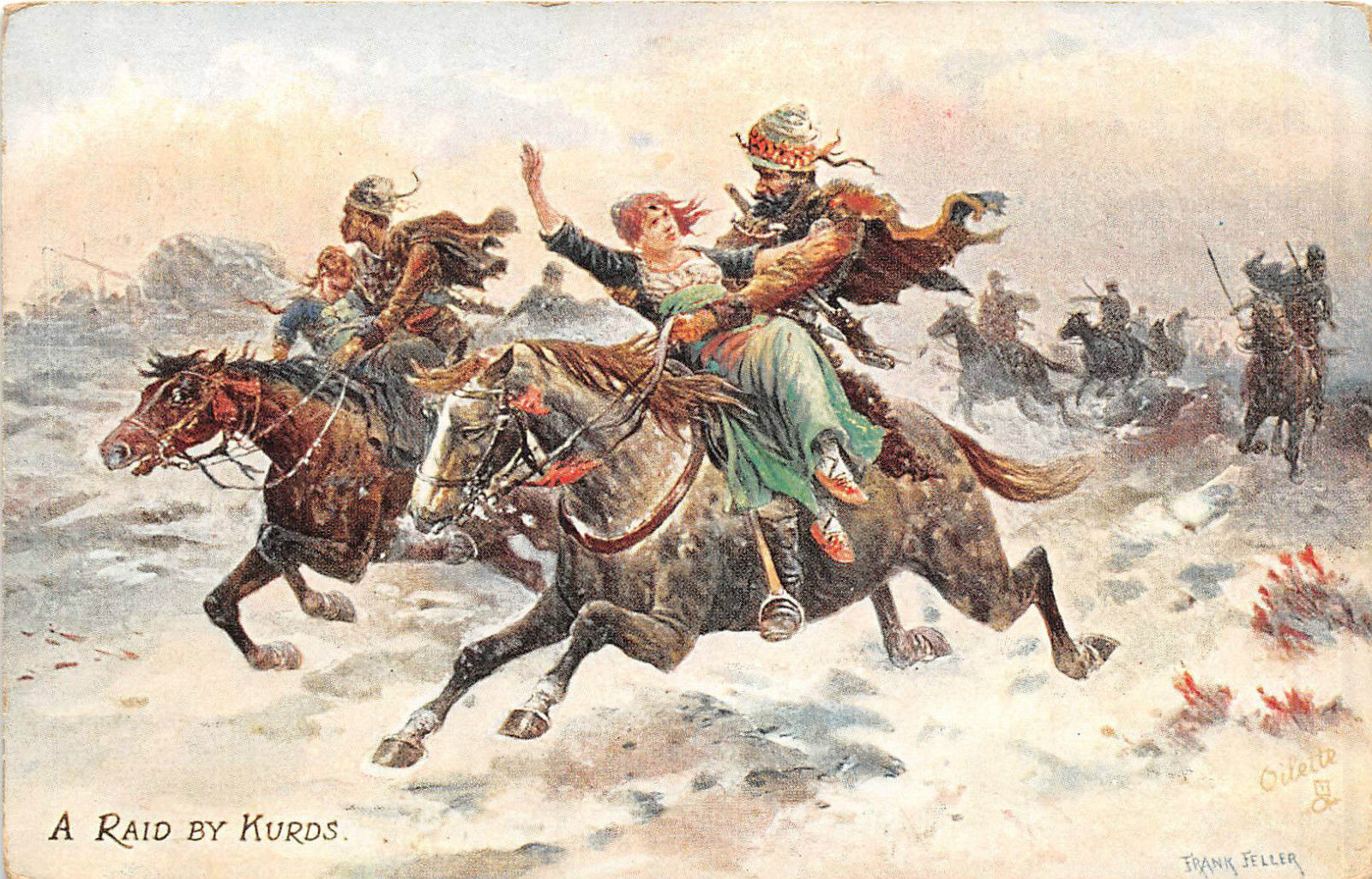
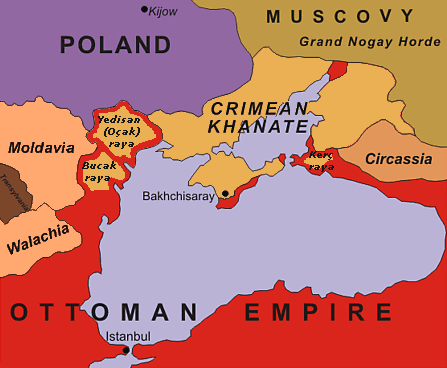
Jalaleddin () was the first of the Armenian writer Raffi's famous works of historical fiction and a milestone in modern Armenian literature. The novella was first published in serialized form across eight issues of ''Mshak'', a Tiflis-based Armenian newspaper, in 1878 (exactly one year after the events depicted). Its title is based on the name of Sheikh Jalaleddin, a Kurdish chief who led his forces on a violent campaign against Armenian and Assyrian villages in the eastern part of Van province at the beginning of the last Russo-Turkish War (1877–78) The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo .... While the story is fictional, Raffi based the historical details on eyewitness accounts. Much of the key historical information provided by Raffi corresponds with British correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffi (novelist)
Hakob Melik Hakobian ( hy, Յակոբ Մելիք-Յակոբեան ( classical); 1835–1888), better known by his pen name Raffi ( hy, Րաֆֆի; fa, رافی), was an Armenian author and leading figure in 19th-century Armenian literature. Biography Raffi was the eldest son in a family of hereditary Armenian gentry and was born in 1835 in Payajuk, a village of northwestern Iran. His father was a wealthy farmer, merchant and the highest civil authority of the village. Thus, Raffi’s economic background and special status within the family eventually made it possible for him to acquire a privileged education, one in which he was exposed to the full spectrum of classical, Russian and Western European masterpieces of literature. His education began in the home of the village priest, Father Mser. There, in a small room adjacent to the barn, boys of all ages and levels of learning were taught under pressure of corporal punishment for failing in their lessons. In his novel called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Fiction
Historical fiction is a literary genre in which the plot takes place in a setting related to the past events, but is fictional. Although the term is commonly used as a synonym for historical fiction literature, it can also be applied to other types of narrative, including theatre, opera, cinema, and television, as well as video games and graphic novels. An essential element of historical fiction is that it is set in the past and pays attention to the manners, social conditions and other details of the depicted period. Authors also frequently choose to explore notable historical figures in these settings, allowing readers to better understand how these individuals might have responded to their environments. The historical romance usually seeks to romanticize eras of the past. Some subgenres such as alternate history and historical fantasy insert intentionally ahistorical or speculative elements into a novel. Works of historical fiction are sometimes criticized for lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mshak
''Mshak'' ( hy, Մշակ meaning ''The Toiler'') was an Armenian language literary and political daily newspaper ( weekly when established) published from 1872–1920 in Tiflis, Russian Empire (now Tbilisi, Georgia). It was founded by Grigor Artsruni. ''Mshak'' was famous particularly for its serialization of notable Armenian literary works, such as '' Jalaleddin''. ''Mshak'' was also known for its publication of liberal ideas, promoting the creation of a united Armenian state inside the Russia. In 1921, after the Soviet invasion of Georgia, ''Mshak'', along with other anti-Bolshevik media, was closed. Editors The following is the list of the editors of ''Mshak'': See also * Armenians in Tbilisi *Armenian literature Armenian literature begins around AD 400 with the invention of the Armenian alphabet by Mesrop Mashtots. History Early literature Only a handful of fragments have survived from the most ancient Armenian literary tradition preceding the Christia ... Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novella
A novella is a narrative prose fiction whose length is shorter than most novels, but longer than most short stories. The English word ''novella'' derives from the Italian ''novella'' meaning a short story related to true (or apparently so) facts. Definition The Italian term is a feminine of ''novello'', which means ''new'', similarly to the English word ''news''. Merriam-Webster defines a novella as "a work of fiction intermediate in length and complexity between a short story and a novel". No official definition exists regarding the number of pages or words necessary for a story to be considered a novella, a short story or a novel. The Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers Association defines a novella's word count to be between 17,500 and 40,000 words. History The novella as a literary genre began developing in the Italian literature of the early Renaissance, principally Giovanni Boccaccio, author of '' The Decameron'' (1353). ''The Decameron'' featured 100 tales (named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million people. Tbilisi was founded in the 5th century AD by Vakhtang I of Iberia, and since then has served as the capital of various Georgian kingdoms and republics. Between 1801 and 1917, then part of the Russian Empire, Tiflis was the seat of the Caucasus Viceroyalty, governing both the northern and the southern parts of the Caucasus. Because of its location on the crossroads between Europe and Asia, and its proximity to the lucrative Silk Road, throughout history Tbilisi was a point of contention among various global powers. The city's location to this day ensures its position as an important transit route for energy and trade projects. Tbilisi's history is reflected in its architecture, which is a mix of medieval, neoclassical, Beaux Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11 and the Crimean War, which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century. History Conflict begins (1568–1739) Before Peter the Great The first Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570) occurred after the conquest of Kazan and Astrakhan by the Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible. The Ottoman sultan Selim II tried to squeeze the Russians out of the lower Volga by sending a military expedition to Astrakhan in 1569. The Turkish expedition ended in disaster for the Ottoman army, which could not take Astrakhan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arshag Chobanian
Arshag Chobanian (; 15 July 1872 – 9 June 1954) was an Armenian short story writer, journalist, editor, poet, translator, literary critic, playwright, philologist, and novelist. Biography His father was a respected goldsmith. In 1898 he founded his famous periodical ''Anahit''. His connections and acquaintances with prominent literary and intellectual figures in France allowed him to write about the Armenian genocide and injustices freely in popular French newspapers such as Mercure de France. He became a strong advocate of western support in order to save the Armenians from the oppression of the Ottoman government. After joining the Ramgavar party, he met with Boghos Nubar and participated in the Armenian National Delegation during the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. In 1933 he visited Soviet Armenia and met with prominent intellectuals. After returning to Paris, he died on 9 June 1954. Literary career Arshag Chobanian is considered one of the fundamental Armenian reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian-language Novels
Armenian ( classical: , reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian Highlands, today Armenian is widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by the priest Mesrop Mashtots. The total number of Armenian speakers worldwide is estimated between 5 and 7 million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek (and Phrygian) and Indo-Iranian were dialectally close to each other;''Handbook of Formal Languages'' (1997p. 6 withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Novels
Armenian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia * Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent ** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the world * Armenian language, the Indo-European language spoken by the Armenian people ** Armenian alphabet, the alphabetic script used to write Armenian ** Armenian (Unicode block) * Armenian Apostolic Church * Armenian Catholic Church People * Armenyan, or in Western Armenian, an Armenian surname **Haroutune Armenian (born 1942), Lebanon-born Armenian-American academic, physician, doctor of public health (1974), Professor, President of the American University of Armenia **Gohar Armenyan (born 1995), Armenian footballer **Raffi Armenian (born 1942), Armenian-Canadian conductor, pianist, composer, and teacher Others * SS ''Armenian'', a ship torpedoed in 1915 See also * * Armenia (other) * Lists of Armenians This is a list o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novels Set In Armenia
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself from the la, novella, a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ''novellus'', diminutive of ''novus'', meaning "new". Some novelists, including Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Ann Radcliffe, John Cowper Powys, preferred the term "romance" to describe their novels. According to Margaret Doody, the novel has "a continuous and comprehensive history of about two thousand years", with its origins in the Ancient Greek and Roman novel, in Chivalric romance, and in the tradition of the Italian renaissance novella.Margaret Anne Doody''The True Story of the Novel'' New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1996, rept. 1997, p. 1. Retrieved 25 April 2014. The ancient romance form was revived by Romanticism, especially the historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |