|
Jagdgeschwader 300
''Jagdgeschwader'' 300 (JG 300) was a Luftwaffe fighter aircraft, fighter-Wing (air force unit), wing of World War II. JG 300 was formed on 26 June 1943 in Deelen as Stab/Versuchskommando Herrmann, from July 18, 1943 as Stab/JG Herrmann and finally renamed on August 20, 1943 to Stab/JG 300. Its first ''Geschwaderkommodore'' was Oberstleutnant Hajo Herrmann. Genesis and ''Wilde Sau'' JG 300 had its origins in April 1943, when Major Hajo Herrmann, a decorated bomber pilot, advocated the use of single-seat day fighters as night fighters against the Royal Air Force (RAF) bomber offensive. He suggested that single seat fighters could operate in the bombers' general target area using the light of target indicators, massed searchlights and the fires on the ground to spot their targets. These operations were tested over Berlin during May and June 1943 and codenamed ''Wilde Sau (Luftwaffe night fighter tactics), Wilde Sau''. Recruiting a group of experienced bomber pilots and former ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial German Navy, Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk (air base), Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the Luftwaffe's existence was publicly acknowledged and officially established on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a Luftwaffe detachment sent to aid Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagdgeschwader 11
''Jagdgeschwader'' 11 (JG 11) was a fighter wing () of the German Luftwaffe during World War II. Its primary role was the defense of Northern Germany against Allied day bomber raids. Formed in April 1943 as a split from ''Jagdgeschwader 1'', the unit primarily used the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and Focke-Wulf Fw 190. The unit was initially based along the North German coast, protecting the northern flank of occupied Europe. During the summer of 1943, as the unescorted bombers penetrated deeper into Germany, JG 11 saw intensive action, with about 40 percent of some 1,200 claims submitted by the Western Front fighter wings in this period being credited to JG 1 and JG 11 . JG 11 trialled new tactics such as dropping 250 kg bombs on top of the bomber formations or using the heavy-calibre ''Werfer-Granate 21'' unguided, underwing-launched rockets. In spring of 1944 the introduction of P-51 Mustang made the job of units such as JG 11 very difficult as they fought through the escor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Bretschneider
Klaus Bretschneider (4 May 1920 – 24 December 1944) was a German Luftwaffe ace and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross () during World War II. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battlefield bravery or successful military leadership. Career Bretschneider was born on 4 May 1920 in Berlin-Steglitz, at the capital of the Weimar Republic. He was posted into the newly raised ''Jagdgeschwader'' 300 (JG 300—300th Fighter Wing) in July 1943. There he was posted to 6. ''Staffel'', flying " Wilde Sau" single-seat night fighter missions. Bretschneider claimed his first aerial victory on the night of 27/28 August 1943. That night, the Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command attacked Nürnberg. At 01:55, Bretschneider shot down a Short Stirling bomber east of Nürnberg. The destruction of the bomber was also claimed by anti-aircraft artillery unit but the destruction was later credited to Bretschneider. On the night of 5/6 September, Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Of The Reich
The Defence of the Reich () is the name given to the strategic defensive aerial campaign fought by the Luftwaffe of Nazi Germany over German-occupied Europe and Germany during World War II against the Allied strategic bombing campaign. Its aim was to prevent the destruction of German civilians, military and civil industries by the Western Allies. The day and night air battles over Germany during the war involved thousands of aircraft, units and aerial engagements to counter the Allies bombing campaigns. The campaign was one of the longest in the history of aerial warfare and with the Battle of the Atlantic and the Allied naval blockade of Germany was the longest of the war. The Luftwaffe fighter force defended the airspace of German-occupied Europe against attack, first by RAF Bomber Command and then against the RAF and United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) in the Combined Bomber Offensive. In the early years, the Luftwaffe was able to inflict a string of defeats on Allied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
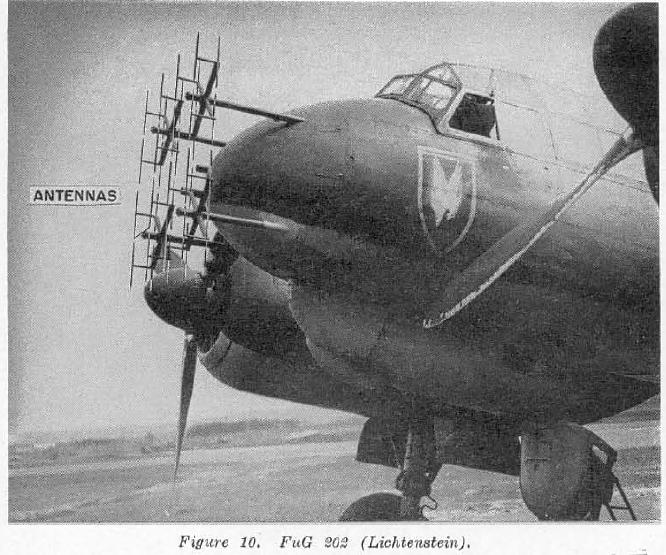
Lichtenstein Radar
The Lichtenstein radar was among the earliest airborne radars available to the Luftwaffe in World War II and the first one used exclusively for air interception. Developed by Telefunken, it was available in at least four major revisions, called FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C, FuG 212 Lichtenstein C-1, FuG 220 Lichtenstein SN-2 and the very rarely used FuG 228 Lichtenstein SN-3. (FuG is short for ''Funk-Gerät'', radio set). The Lichtenstein series remained the only widely deployed airborne interception radar used by the Germans on their night fighters during the war — the competing FuG 216 through 218 ''Neptun'' mid- VHF band radar systems were meant as a potentially more versatile stop-gap system through 1944, until the microwave-based FuG 240 "Berlin" could be mass-produced; the ''Berlin'' system was still being tested when the war ended. FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C Early FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C units were not deployed until 1942. They operated at a maximum RF output power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nachtjagdgruppe 10
''Nachtjagdgruppe'' 10 (NJGr 10) was a German Luftwaffe night fighter ''gruppe'' (group) during World War II. It was formed on 1 January 1944 at Werneuchen with 3 ''Staffel'' (squadrons). It was subordinated to the 1. ''Jagd-Division'' (1st fighter division), stationed at Döberitz. On 6 March 1945, NJGr 10 transferred to Liebenwalde and disbanded in April 1945. The remnants of NJGr 10 were absorbed by Nachtjagdgeschwader 5 (5th Night Fighter Wing). Its main task was to explore new and revised tactical deployment of night fighters, test the latest search and detection equipment in conjunction with the test site for radar equipment under combat conditions (''Erprobung von Radarsysteme für die Nachtjagd''), and place the anti-Mosquito effort under a more centralised command. 1./NJGr 10 1st ''Staffel'' was formed from parts of I/Jagdgeschwader 300 (1st Group of 300th Fighter Wing) and commanded by Hauptmann Friedrich-Karl Müller. 1/NJGr 10 was stationed in Werneuchen, flying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kammhuber Line
The Kammhuber Line was the name given by the Allies to the German night-fighter air-defence system established in western Europe in July 1940 by Colonel Josef Kammhuber. It consisted of a series of control sectors equipped with radars and searchlights and an associated night fighter. Each sector would direct the night fighter into visual range to target intruding bombers. The Line proved very effective against initial RAF Bomber Command tactics. However, the RAF analyzed the German system and developed a counter-measure. On the night of 30/31 May 1942 in its 1,000 plane raid against Cologne, Bomber Command introduced the use of the bomber stream. The concentration of bombers through a few of the boxes ovewhelmed the defenses. In response, the Germans converted their ground radar into a radar network which would follow the path of the British bombers, while a controller directed the night fighters into the stream. Measure and counter-measure continued until October 1944, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the Strategic bombing during World War II#Europe, strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bombing campaign against Germany became Area bombing directive, less restrictive and increasingly targeted industrial sites and the civilian manpower base essential for German war production. In total 501,536 operational sorties were flown, of bombs were dropped and 8,325 aircraft lost in action. Bomber Command crews also suffered a high casualty rate: 55,573 were killed out of a total of 125,000 aircrew, a 44.4% death rate. A further 8,403 men were wounded in action, and 9,838 became prisoners of war. Bomber Command stood at the peak of its post-war Armed forces, military power in the 1960s, the V bombers holding the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent and a supplemental force of English Electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naxos Radar Detector
The Naxos radar warning receiver was a World War II German countermeasure to S band microwave radar produced by a cavity magnetron. Introduced in September 1943, it replaced Metox, which was incapable of detecting centimetric radar. Two versions were widely used, the FuG 350 Naxos Z that allowed night fighters to home in on H2S radars carried by RAF Bomber Command aircraft, and the FuMB 7 Naxos U for U-boats, offering early warning of the approach of RAF Coastal Command patrol aircraft equipped with ASV Mark III radar. A later model, Naxos ZR, provided warning of the approach of RAF night fighters equipped with AI Mk. VIII radar. Background Prior to the introduction of the cavity magnetron, radar systems used traditional vacuum tube electronics and were limited to about 1.5 m wavelength in UK use, and as low as 50 cm in German systems. Both could receive the transmissions of their opposing radar systems and radar warning receivers were widely used by both sides in a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30th Fighter Division (Germany)
__NOTOC__ 30th Fighter Division (''30. Jagd Division'') was one of the primary divisions of the German Luftwaffe in World War II. It was formed in September 1943 in Berlin and disbanded on 16 March 1944. The Division was subordinated to the Luftwaffenbefehlshaber Mitte (September 1943 – February 1944) and the I. Jagdkorps (February 1944 – March 1944). Commanding officers * Oberst Hajo Herrmann, September 1943 – 16 March 1944 Subordinated units *Jagdgeschwader 300 *Jagdgeschwader 301 * Jagdgeschwader 302 See also *Luftwaffe Organisation The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ... References {{Divisions of the Luftwaffe Air divisions of the Wehrmacht Luftwaffe Military units and formations established in 1943 Military units and formations disestablished in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JG 302
''Jagdgeschwader 302 (JG 302)'' was a ''Luftwaffe'' fighter-wing of World War II. ''JG 302'' was formed on 1 November 1943 in Stade, Germany with a theoretical establishment of ''Stab'' and three ''Gruppen'' (groups) known as a "'' Wilde Sau''" (wild boar) single-seat night fighter unit. After re-equipping with the Focke-Wulf 190 A-8, ''I./JG 302'' was redesignated ''III.''/''JG 301'' on 30 September. ''JG 302'' made a known total of at least 348 air victory claims Operations 1944 The unit's primary mission, when formed in late 1943, was to intercept Royal Air Force (RAF) heavy bombers at night, flying modified single-engined day fighters. Eventually ''JG 302'' also engaged United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) bombers by day. Initially, the pilots recruited were a mix of former bomber pilots and instructors, experienced in night and instrument flying. During the night of 22 November, ''Hauptmann'' Heinrich Wurzer (26 victories, 24 by day, all with ''JG 302'') shot down a RA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JG 301
''Jagdgeschwader'' 301 (JG 301) was a Luftwaffe fighter-wing of World War II. The order to form JG 301 was issued on 26 September 1943 and formed on 1 October 1943 in Neubiberg with '' Stab'' and three ''Gruppen'' (groups) as a " Wilde Sau" (wild boar) single-seat night fighter unit. The ''Geschwader'' was equipped with the Bf 109G and was reorganised with four ''Staffeln'' per ''Gruppe''. Jagdgeschwader 50, a specialist anti-Mosquito unit, was disbanded in October 1943 and absorbed into I./JG 301. II./JG 301 was redesignated as II./ JG 302 on 30 September 1944 and replaced by I./JG 302. II./JG 7 was attached to IV./JG 301 on 24 November 1944 and disbanded on 19 January 1945. 1943 During October 1943, while I./JG 301 was formed in Neubiberg from Jagdgeschwader 50, II./JG 301 was formed at Altenburg from elements of II./ JG 300. Without its own contingent of fighters, II./JG 301 had to share aircraft that belonged to I./ JG 11. In November 1943, the unit was designated as I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |