|
Jagannatha Samrat
Paṇḍita Jagannātha Samrāṭ (1652–1744) was an Indian astronomer and mathematician who served in the court of Jai Singh II of Amber, and was also his guru. Jagannātha, whose father's name was Gaṇeśa, and grandfather's Viṭṭhala was from a Vedic family originally from Maharashtra. At the suggestion of Jai Singh, he learned Arabic and Persian, in order to study Islamic astronomy. Having become proficient in these languages, he translated texts in these languages into Sanskrit. These translations include: * ''Rekhā-gaṇita'', a translation of Euclid's ''Elements'' made from Nasir al-Din al-Tusi's Arabic recension of the same. For this work, he had to coin more than a hundred Sanskrit mathematical terms * ''Siddhānta-sāra-kaustubha'', a translation of Ptolemy's ''Almagest'' from Nasir al-Din al-Tusi's Arabic version His original works include: * ''Siddhānta-samrāṭ'', which describes astronomical instruments, their design and construction, and observations. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, solar astronomy, the origin or evolution of stars, or the formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers usually fall under either of two main types: observational and theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate models of things that cannot be observed. Because it takes millions to billions of years for a system of stars or a galaxy to complete a life cycle, astronomers must observe snapsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrolabe
An astrolabe ( grc, ἀστρολάβος ; ar, ٱلأَسْطُرلاب ; persian, ستارهیاب ) is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. Historically used by astronomers, it is able to measure the altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time (and vice versa), to survey, or to triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes. The astrolabe's importance comes not only from the early developments into the study of ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Indian Mathematicians
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Indian Mathematicians
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (Roman numerals, MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (Roman numerals, MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Indian Astronomers
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Indian Astronomers
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French '' Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1744 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6 – The Royal Navy ship ''Bacchus'' engages the Spanish Navy privateer ''Begona'', and sinks it; 90 of the 120 Spanish sailors die, but 30 of the crew are rescued. * January 24 – The Dagohoy rebellion in the Philippines begins, with the killing of Father Giuseppe Lamberti. * February – Violent storms frustrate a planned French invasion of Britain. * February 22– 23 – Battle of Toulon: The British fleet is defeated by a joint Franco-Spanish fleet. * March 1 (approximately) – The Great Comet of 1744, one of the brightest ever seen, reaches perihelion. * March 13 – The British ship ''Betty'' capsizes and sinks off of the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana) near Anomabu. More than 200 people on board die, although there are a few survivors. * March 15 – France declares war on Great Britain. April–June * April – '' The Female Spectator'' (a monthly) is founded by Eliza Haywoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1652 Births
Year 165 ( CLXV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Orfitus and Pudens (or, less frequently, year 918 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 165 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * A Roman military expedition under Avidius Cassius is successful against Parthia, capturing Artaxata, Seleucia on the Tigris, and Ctesiphon. The Parthians sue for peace. * Antonine Plague: A pandemic breaks out in Rome, after the Roman army returns from Parthia. The plague significantly depopulates the Roman Empire and China. * Legio II ''Italica'' is levied by Emperor Marcus Aurelius. * Dura-Europos is taken by the Romans. * The Romans establish a garrison at Doura Europos on the Euphrates, a control point for the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helaine Selin
Helaine Selin (born 1946) is an American librarian, historian of science, author and the editor of several bestselling books. Career Selin attended Binghamton University, where she earned her bachelor's degree. She received her MLS from SUNY Albany. She was a Peace Corps volunteer from the fall of 1967 through the summer of 1969 as an English teacher in Malawi. She retired in 2012 from being the science librarian at Hampshire College. Selin is well known for being the editor of '' Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures'' (1997) which is one of the first books which allows readers to "compare a variety of traditional systems of mathematics and cosmologies." ''Mathematics Across Cultures: The History of Non-Western Mathematics'' (2000), is considered by '' Mathematical Intelligencer'' as a companion to the ''Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures''. The journal, '' Mathematics an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
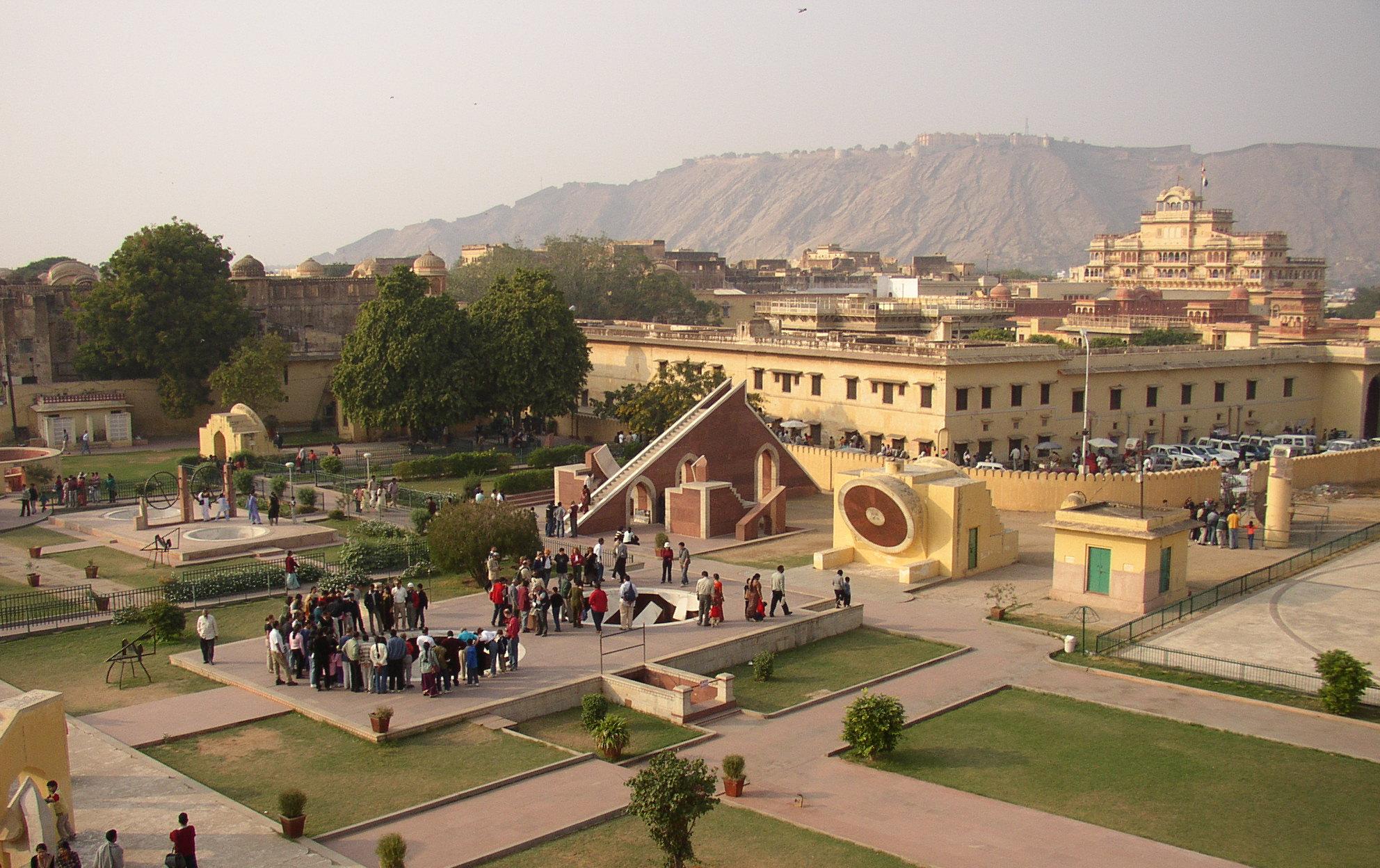
Jantar Mantar
A Jantar Mantar (Hindustani pronunciation: ͡ʒən̪t̪ər mən̪t̪ər is an assembly of stone-built astronomical instruments, designed to be used with the naked eye. There were five Jantar Mantars in India, all of them built at the command of the Rajah Jai Singh II, who had a keen interest in mathematics, architecture and astronomy; The largest example is the equinoctial sundial belonging to Jaipur's assembly of instruments, consisting of a gigantic triangular gnomon with the hypotenuse parallel to the Earth's axis. On either side of the gnomon is a quadrant of a circle, parallel to the plane of the equator. The instrument can be used with an accuracy of about 2 seconds by a "skilled observer" to measure the time of day, and the declination of the Sun and the other heavenly bodies. It is the world's largest stone sundial, known as the Vrihat Samrat Yantra. The Jaipur Jantar Mantar is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canonized a geocentric model of the Universe that was accepted for more than 1,200 years from its origin in Hellenistic Alexandria, in the medieval Byzantine and Islamic worlds, and in Western Europe through the Middle Ages and early Renaissance until Copernicus. It is also a key source of information about ancient Greek astronomy. Ptolemy set up a public inscription at Canopus, Egypt, in 147 or 148. N. T. Hamilton found that the version of Ptolemy's models set out in the ''Canopic Inscription'' was earlier than the version in the ''Almagest''. Hence the ''Almagest'' could not have been completed before about 150, a quarter-century after Ptolemy began observing. Names The name comes from Arabic ', with ' meaning "the", and ''magesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematical model, models, and mathematics#Calculus and analysis, change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagoreans, Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |