|
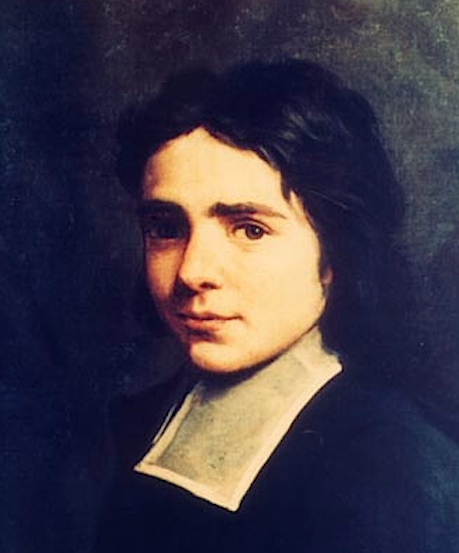
Jacques-Désiré Laval
Jacques-Désiré Laval (18 September 1803 – 9 September 1864) was a French people, French Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic priest who served in the Catholic missions, missions in Mauritius; he was a professed member from the Holy Ghost Fathers, Spiritans. He is known as the "Apostle of Mauritius" due to his tireless work in aiding the poor and ill. Laval also educated the flock he was assigned to for those people were uneducated and were former slaves for the most part. His skills in medicine made him a distinguished figure in the region since his expertise allowed him to tend to those who suffered illness that manifested more so during times of an epidemic. On 29 April 1979 he became the first beatified member of his religious order. Life Jacques-Désiré Laval was born on 18 September 1803 in Croth, the son of Jacques Laval, successful farmer. His parents had three daughters before him and hoped for a boy. He grew up in a pious household. His mother died when he was seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatification
Beatification (from Latin , "blessed" and , "to make") is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their name. ''Beati'' is the plural form, referring to those who have undergone the process of beatification; they possess the title of "Blessed" () (abbreviation "Bl.") before their names and are often referred to in English as "a Blessed" or, plurally, "Blesseds". It is the third stage of the ordinary process of Canonization#Since 1983, official recognitions for Catholic saints: Servant of God, Venerable#Catholic, Venerable, Blessed, and Saint. History Local Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops had the power of beatifying until 1634, when Pope Urban VIII, in the apostolic constitution ''CĹ“lestis Jerusalem'' of 6 July, reserved the power of beatifying to the Holy See. Since the reforms of 1983, as a rule, (for non-martyred Venerables) one Miracle, miracle must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombeau De J-D Laval
A tombeau (plural tombeaux) is a musical composition (earlier, in the early 16th century, a poem) commemorating the death of a notable individual. The term derives from the French word for "tomb" or "tombstone". The vast majority of tombeaux date from the 17th century and were composed for lute or other plucked string instruments. The genre gradually fell out of use during the 18th century, but reappeared in the early 20th. History "In instrumental music, ''tombeau'' signifies a musical 'tombstone' (French ''le tombeau'' = tomb). The musical genre of the tombeau is generally connected with music for the lute of the 17th and 18th centuries. Of some 60+ surviving pieces, most are intended for the lute or theorbo, 5 for the baroque guitar, 7 for the viola da gamba and 3 for harpsichord. The earliest example of this genre seems to be the ''Tombeau de Mezangeau'' (1638) by French lutenist Ennemond Gaultier." "Musical predecessors are memorial pavans like those by Anthony Holborne ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of United States cities by population, 67th-most populous city in the U.S., with a population of 302,971 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is located in Western Pennsylvania, southwestern Pennsylvania at the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River, which combine to form the Ohio River. It anchors the Greater Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh metropolitan area, which had a population of 2.457 million residents and is the largest metro area in both the Ohio Valley and Appalachia, the Pennsylvania metropolitan areas, second-largest in Pennsylvania, and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 26th-largest in the U.S. Pittsburgh is the principal city of the greater Pittsburgh–New Castle–Weirton combined statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duquesne University
Duquesne University of the Holy Spirit ( ; also known as Duquesne University or Duquesne) is a Private university, private Catholic higher education, Catholic research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Founded by members of the Holy Ghost Fathers, Congregation of the Holy Spirit, Duquesne first opened as the Pittsburgh Catholic College of the Holy Ghost in October 1878 with an enrollment of 40 students and a faculty of six. In 1911, the college became the first Catholic university-level institution in Pennsylvania. It is named for an 18th-century governor of New France, Michel-Ange Duquesne de Menneville. Duquesne has since expanded to over 9,300 graduate and undergraduate students within a self-contained hilltop campus in Pittsburgh's Bluff (Pittsburgh), Bluff neighborhood. The school maintains an associate campus in Rome and encompasses ten schools of study. The university hosts international students from more than 80 countries although most students—ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoplectic
Apoplexy () refers to the rupture of an internal organ and the associated symptoms. Informally or metaphorically, the term ''apoplexy'' is associated with being furious, especially as "apoplectic". Historically, it described what is now known as a hemorrhagic stroke, typically involving a ruptured blood vessel in the brain; modern medicine typically specifies the anatomical location of the bleeding, such as cerebral apoplexy, ovarian apoplexy, or pituitary apoplexy. Historical meaning From the late 14th to the late 19th century, the diagnosis ''apoplexy'' referred to any sudden death that began with abrupt loss of consciousness, especially when the victim died within seconds after losing consciousness. The word ''apoplexy'' was sometimes used to refer to the symptom of sudden loss of consciousness immediately preceding death. Strokes, ruptured aortic aneurysms, and even heart attacks were referred to as apoplexy in the past, because before the advent of biomedical science, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiritans
The Congregation of the Holy Spirit (officially the Congregation of the Holy Spirit under the protection of the Immaculate Heart of the Virgin Mary; ) is a religious congregation for men in the Catholic Church. Members are often known as Holy Ghost Fathers or, in continental Europe and the Anglosphere, as Spiritans, and members use the postnominals CSSp. History Claude Poullart des Places Claude Poullart des Places was born on 26 February 1679, in Rennes, the capital city of Brittany, France. He was the eldest child and only son of Francis des Places and Jeanne le Meneust. Claude was tutored at home before being enrolled at the age of nine or ten as a day student in the nearby Jesuit College of St. Thomas, thus beginning his lifelong association with the Society of Jesus. Graduating at 16, Claude studied at the University of Caen, Normandy, before graduating at 22 with a Licentiate in Law from the Law School of Nantes. In 1701 Claude Poullart began his studies for the prie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Libermann
Francis Mary Paul Libermann (; born Jacob Libermann; 12 April 1802 – 2 February 1852) was a French Jewish convert to Catholicism and a Spiritan priest. He is best known for founding the Society of the Holy Heart of Mary, which later merged with the Spiritans. He is often referred to as "The Second Founder of the Spiritans". He was declared venerable in the Catholic Church on 1 June 1876, by Pope Pius IX. Early life Jacob Libermann was born into an Orthodox Jewish family in Saverne, Alsace, France in 1802. As a young man, Libermann prepared to follow in the footsteps of his father, the Chief Rabbi of Saverne. He would later relate how he lost his faith in Judaism after entering a yeshiva. Treated with disdain by two of the professors there, he began to read French literature, especially Rousseau, with the result that he became an agnostic. Later during this period of agnosticism, another rabbinical student gave him a Hebrew translation of the Gospels. Being always a very mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyacinthe-Louis De Quélen
Hyacinthe-Louis De QuĂ©len (8 October 1778 – 31 December 1839) was an Archbishop of Paris. He was the fourth archbishop to serve the Paris diocese after the restoration of the French hierarchy in 1802. Biography De QuĂ©len was born in Paris, in the QuĂ©len noble Breton family. His motto "Em Pob Emser Quelen" and the older Breton expression for "Better death than dishonour" figure in stained glass in the Lazarist church in the rue de Sèvres. He was educated at the College of Navarre and the seminary in St. Sulpice. Ordained in 1807, he served a year as Vicar-General of Saint-Brieuc and then became secretary to Joseph Fesch, uncle to Napoleon Bonaparte. When the latter was exiled from his diocese of Lyon under the Bourbon Restoration, de QuĂ©len exercised his ministry at Saint-Sulpice and in the military hospitals. Under the Bourbons, he became successively spiritual director of the schools in the archdiocese, Vicar-General of Paris, and coadjutor archbishop to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Paris
The Archdiocese of Paris (; ) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. It is one of twenty-three archdioceses in France. The original diocese is traditionally thought to have been created in the 3rd century by St. Denis and corresponded with the Civitas Parisiorum; it was elevated to an archdiocese on October 20, 1622. Before that date the bishops were suffragan to the archbishops of Sens. History Paris was a Christian centre at an early date, its first apostles being St. Denis and his companions, Sts. Rusticus and Eleutherius. Until the Revolution the ancient tradition of the Parisian Church commemorated the seven stations of St. Denis, the stages of his apostolate and martyrdom: * (1) the ancient monastery of Notre-Dame-des-Champs of which the crypt, it was said, had been dedicated to the Blessed Virgin by St. Denis on his arrival in Paris; * (2) the Church of St-Etienne-des-Grès (now disappeared), which stood on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordination
Ordination is the process by which individuals are Consecration in Christianity, consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the religious denomination, denominational hierarchy composed of other clergy) to perform various religious rites and ceremonies. The process and ceremonies of ordination vary by religion and denomination. One who is in preparation for, or who is undergoing the process of ordination is sometimes called an ordinand. The liturgy used at an ordination is commonly found in a book known as an Order of Mass, Ordinal which provides the ordo (ritual and rubrics) for celebrations. Christianity Catholic, Orthodox, Lutheran and Anglican churches In Catholicism and Orthodoxy, ordination is one of the seven sacraments, variously called holy orders or ''Christian laying on of hands, cheirotonia'' ("Laying on of Hands"). Apostolic succession is considered an essential and necessary concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Église Saint-Sulpice, Paris
The Church of Saint-Sulpice () is a Catholic church in Paris, France, on the east side of Place Saint-Sulpice, in the 6th arrondissement. Only slightly smaller than Notre-Dame and Saint-Eustache, it is the third largest church in the city. It is dedicated to Sulpitius the Pious. Construction of the present building, the second on the site, began in 1646. During the 18th century, an elaborate gnomon, the Gnomon of Saint-Sulpice, was constructed in the church. Saint-Sulpice is also known for its Great Organ, one of the most significant organs in the world. History The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the Society of Saint-Sulpice, a clerical congregation, and a seminary attached to the church. Anne of Austria laid the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |